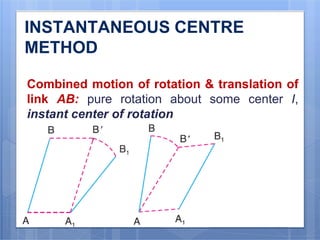
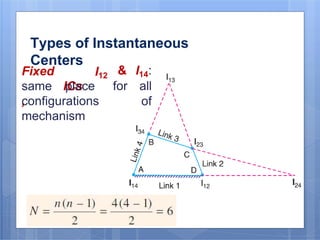
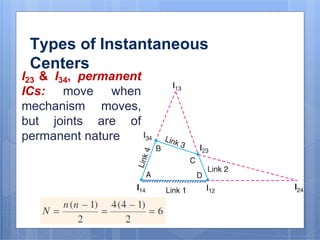
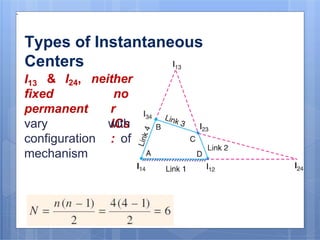
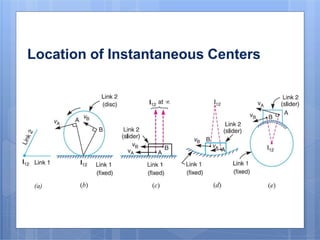
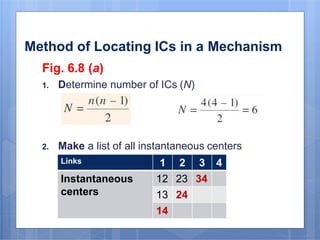
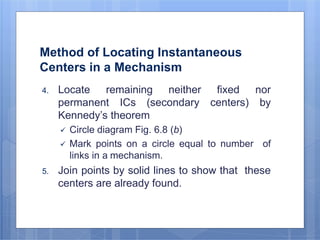
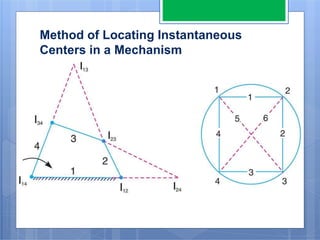
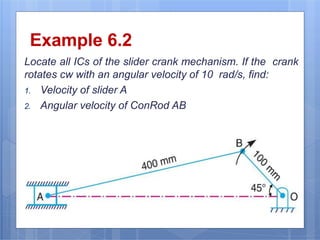
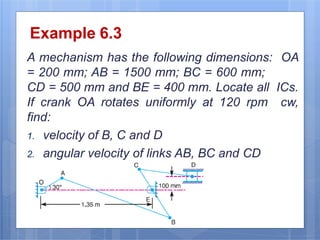
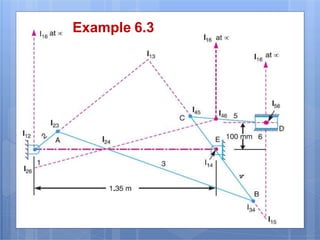
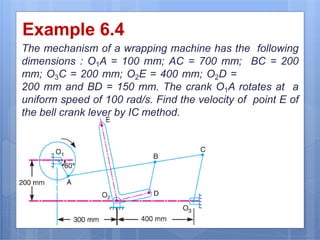
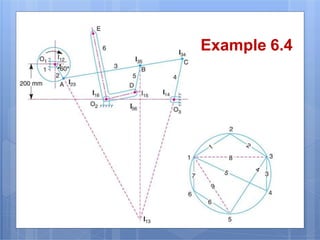
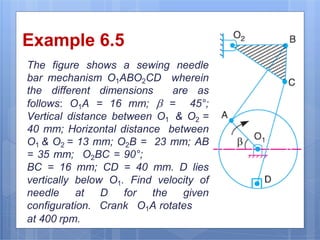
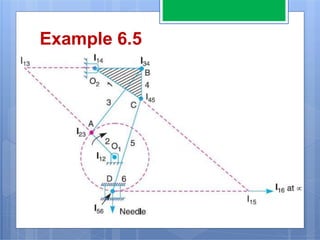
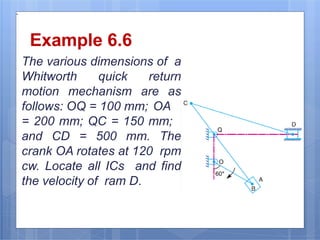
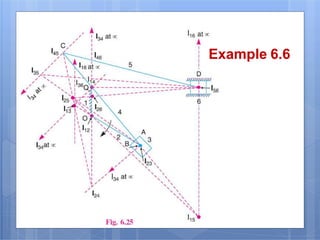
This document discusses the instantaneous center method for analyzing mechanisms. It defines key terms like instantaneous center, centrode, and axode. It explains how to determine the number and types of instant centers in a mechanism, including primary fixed/permanent centers and secondary centers. The document provides steps for locating all the instant centers using principles like Kennedy's theorem. It includes examples of applying the instant center method to determine velocities and angular velocities in different slider crank and linkage mechanisms.