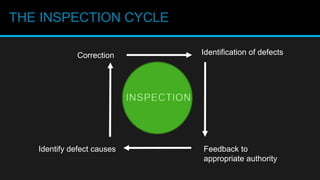
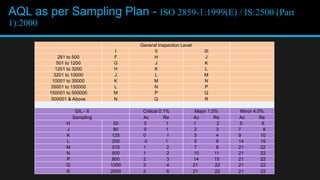
This document discusses in-process quality control. It defines quality and describes the in-process quality control process which includes understanding production parameters, creating control plans, monitoring parameters, reporting results, identifying defects, providing feedback, and correcting issues. It describes different types of in-process inspections and factors affecting inspections. The "4M's" of inspection - machine, method, material, and man - are also discussed as well as final inspections, sampling plans, quality control in distribution, acceptance quality limits, common defect types, and the importance of quality control.