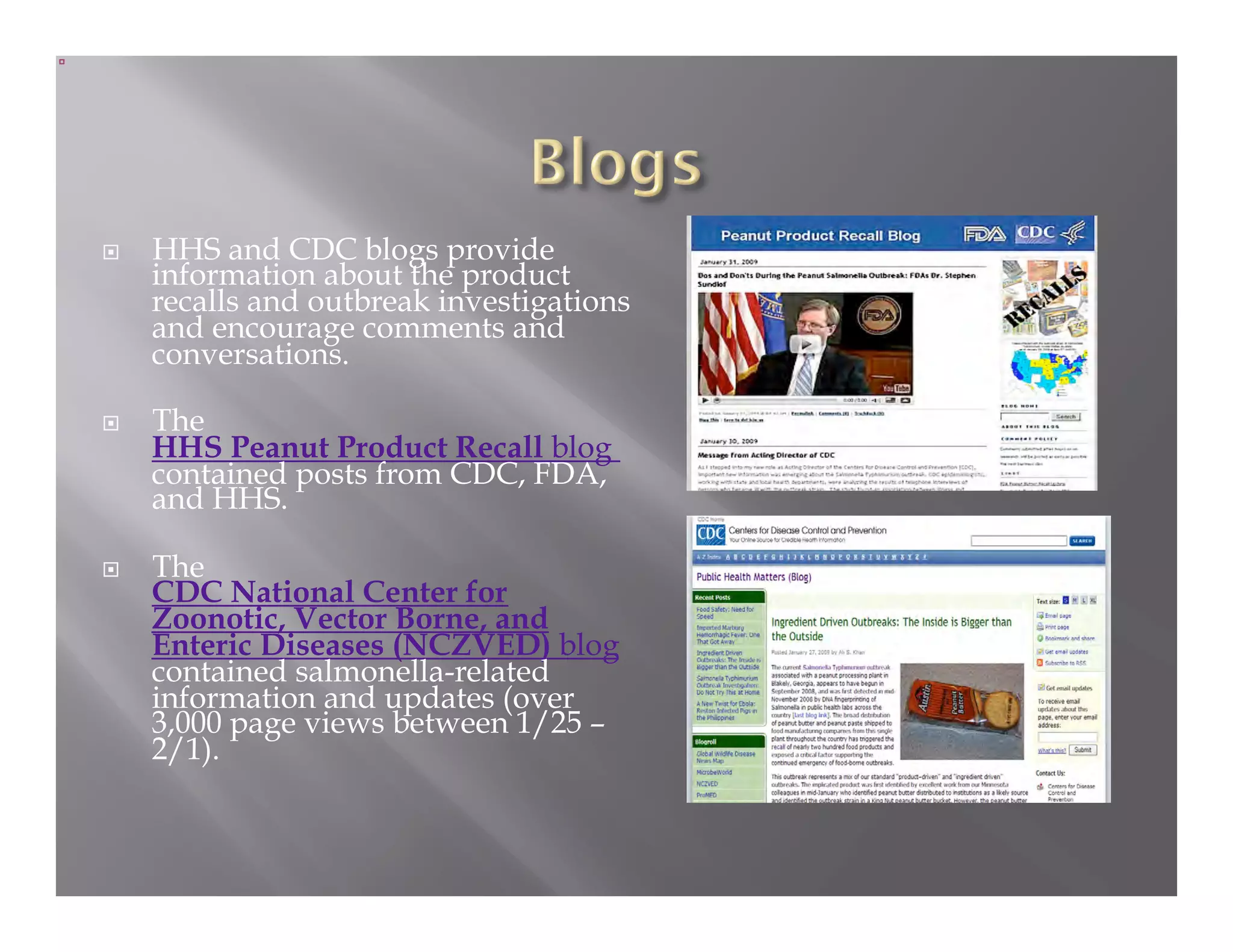
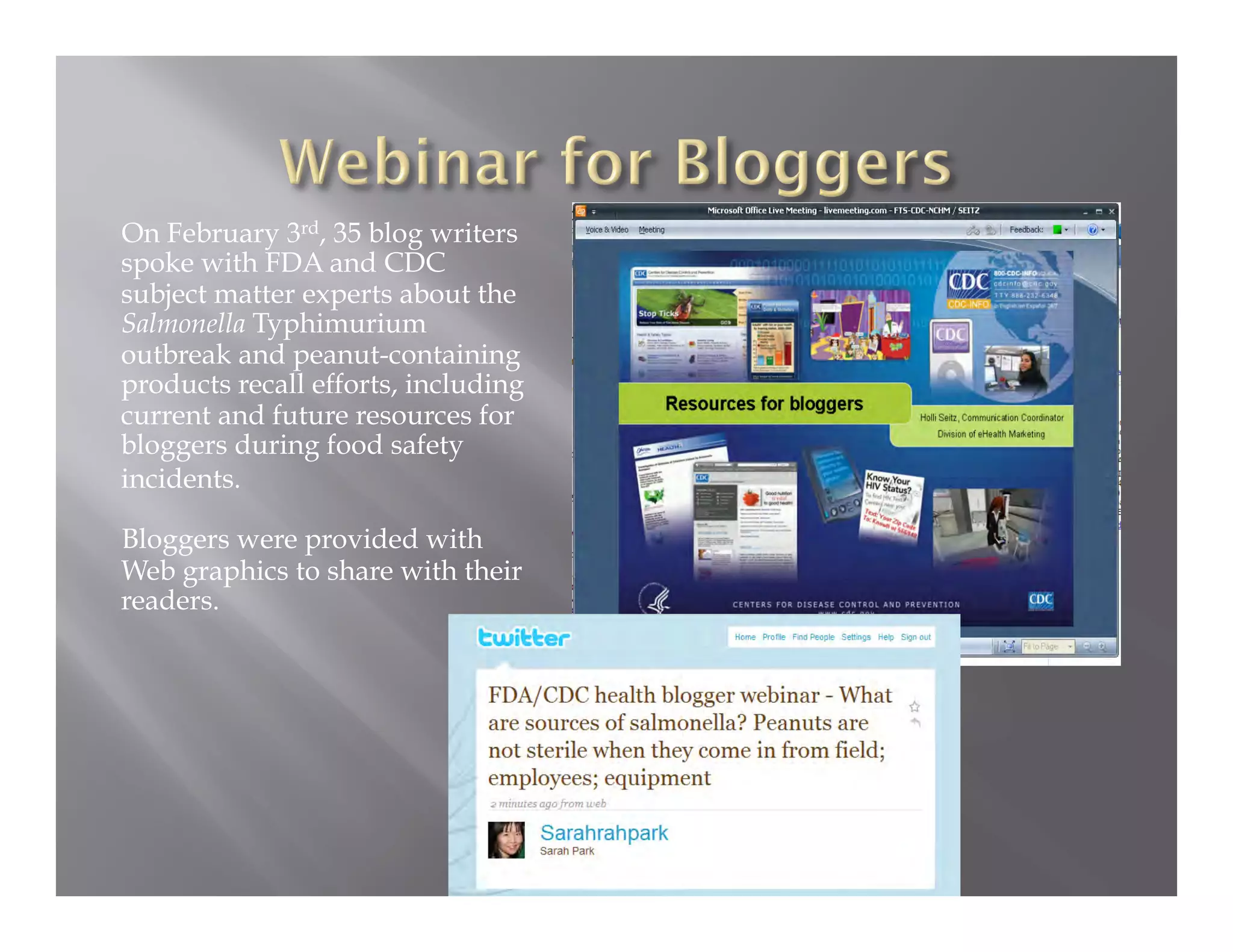
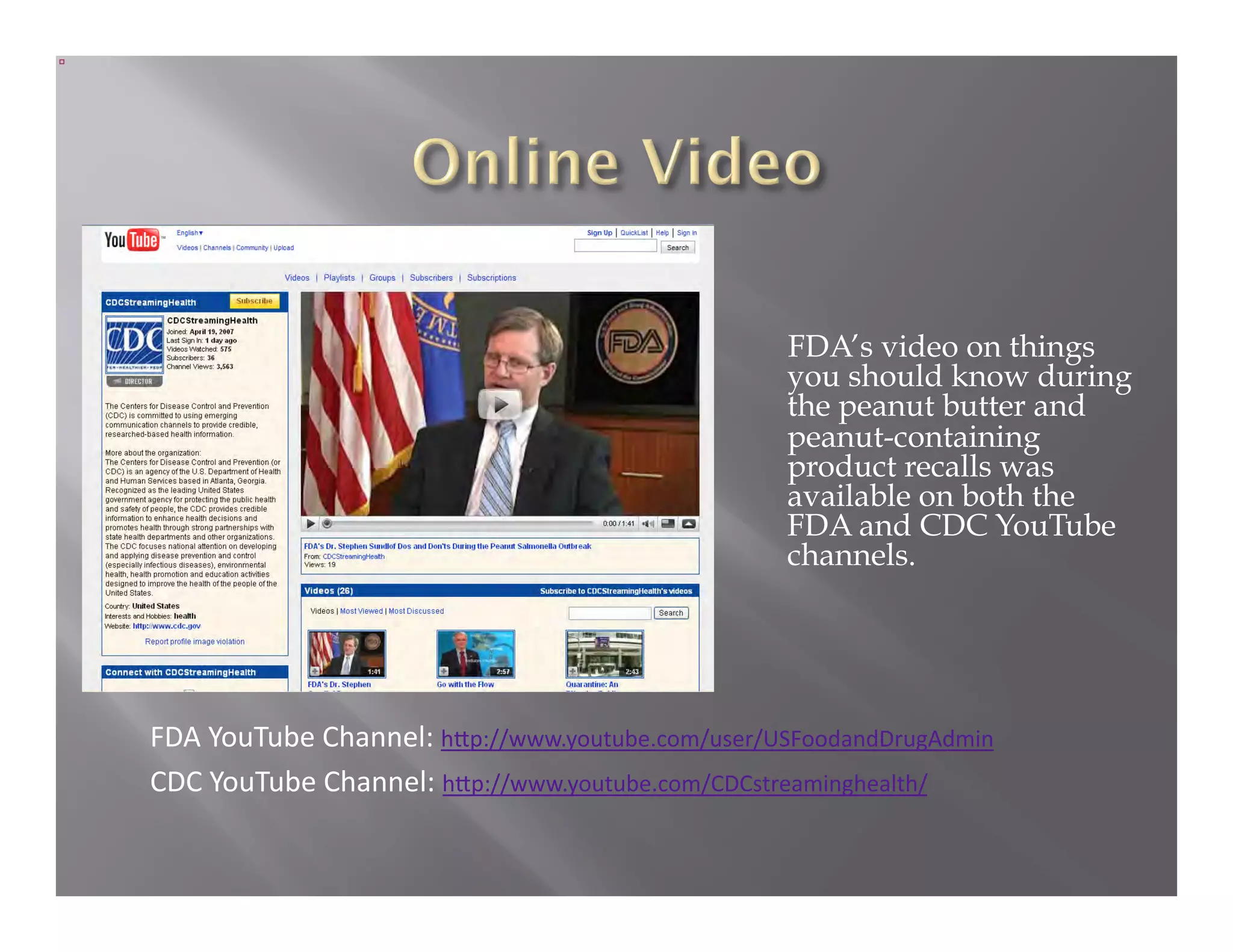
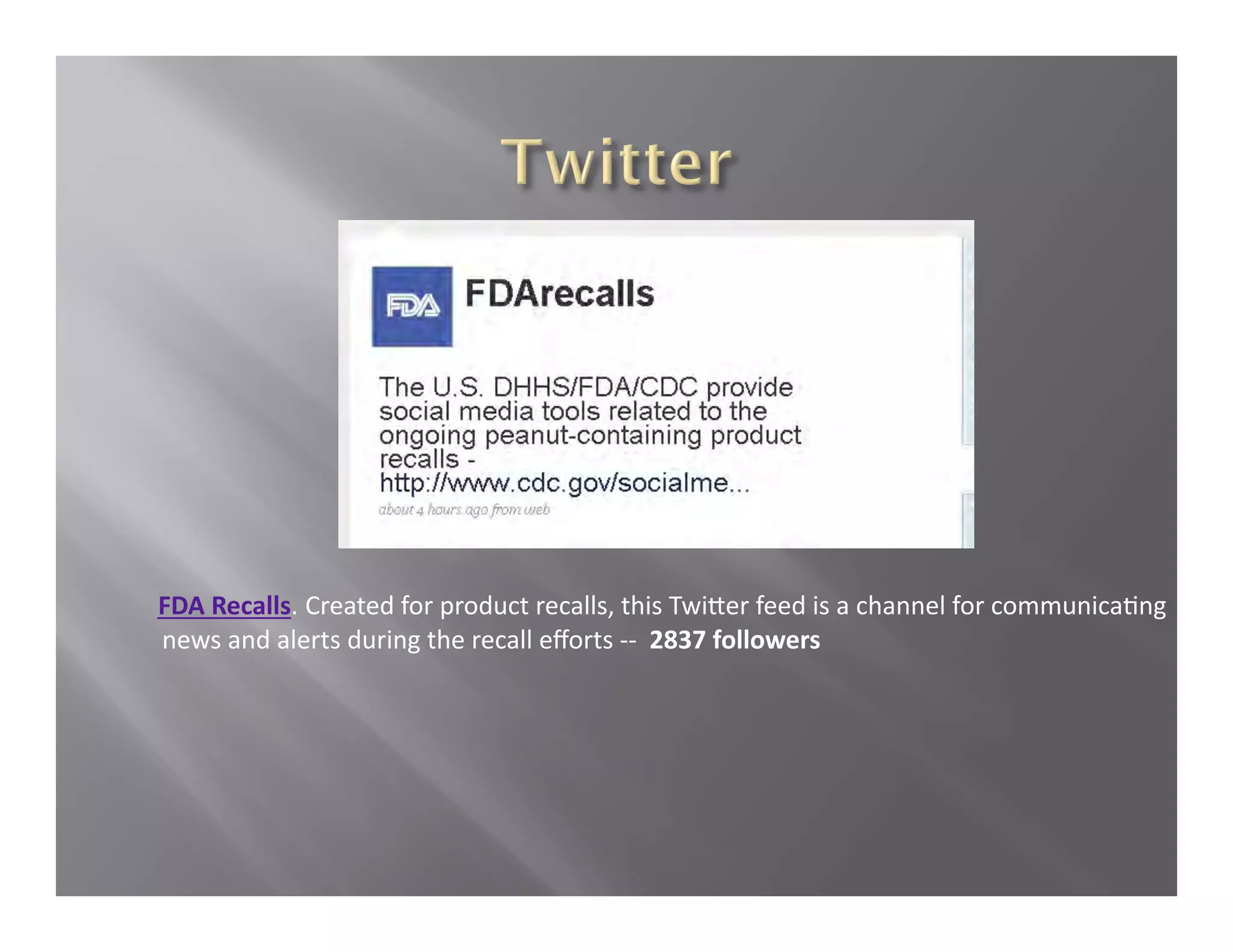
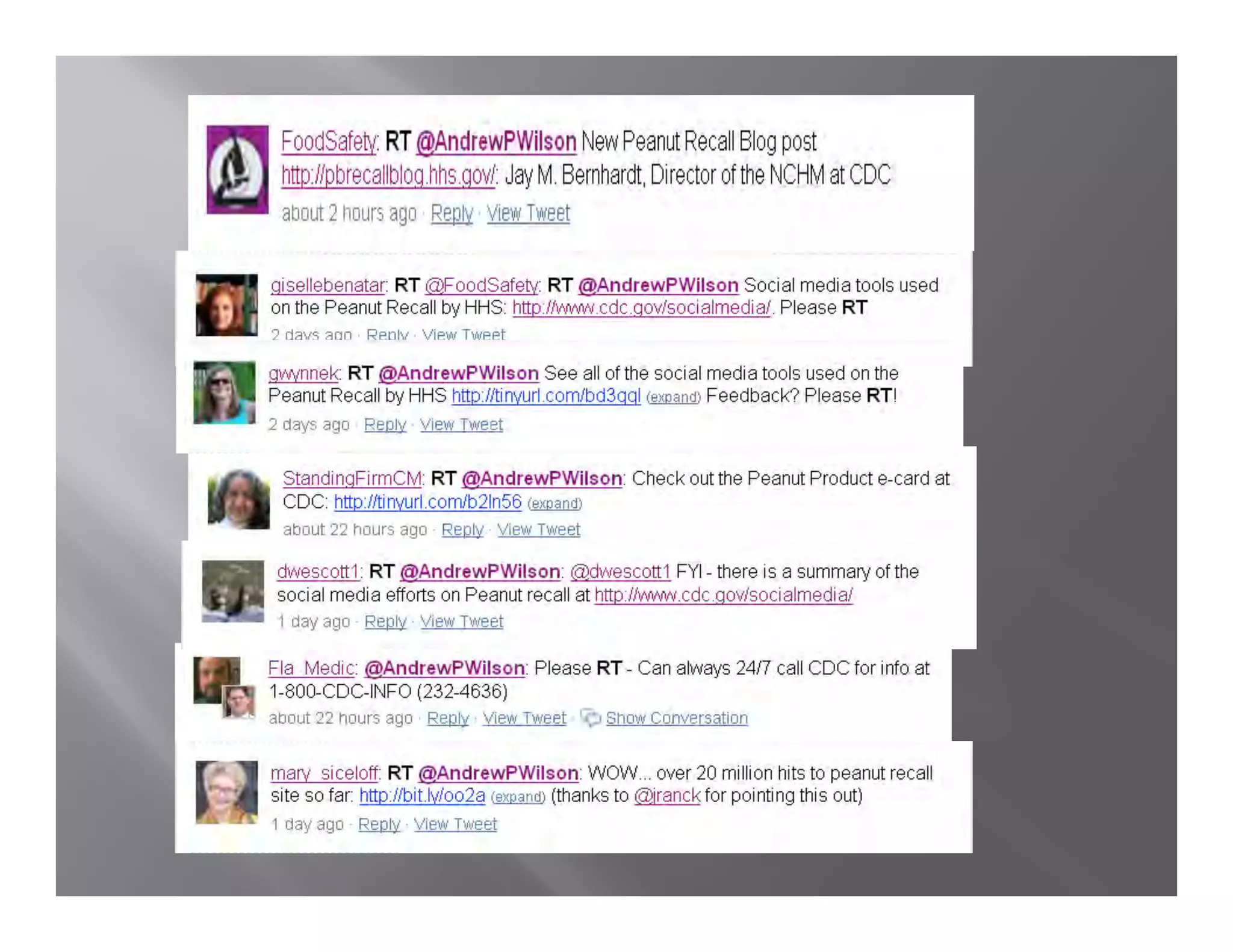
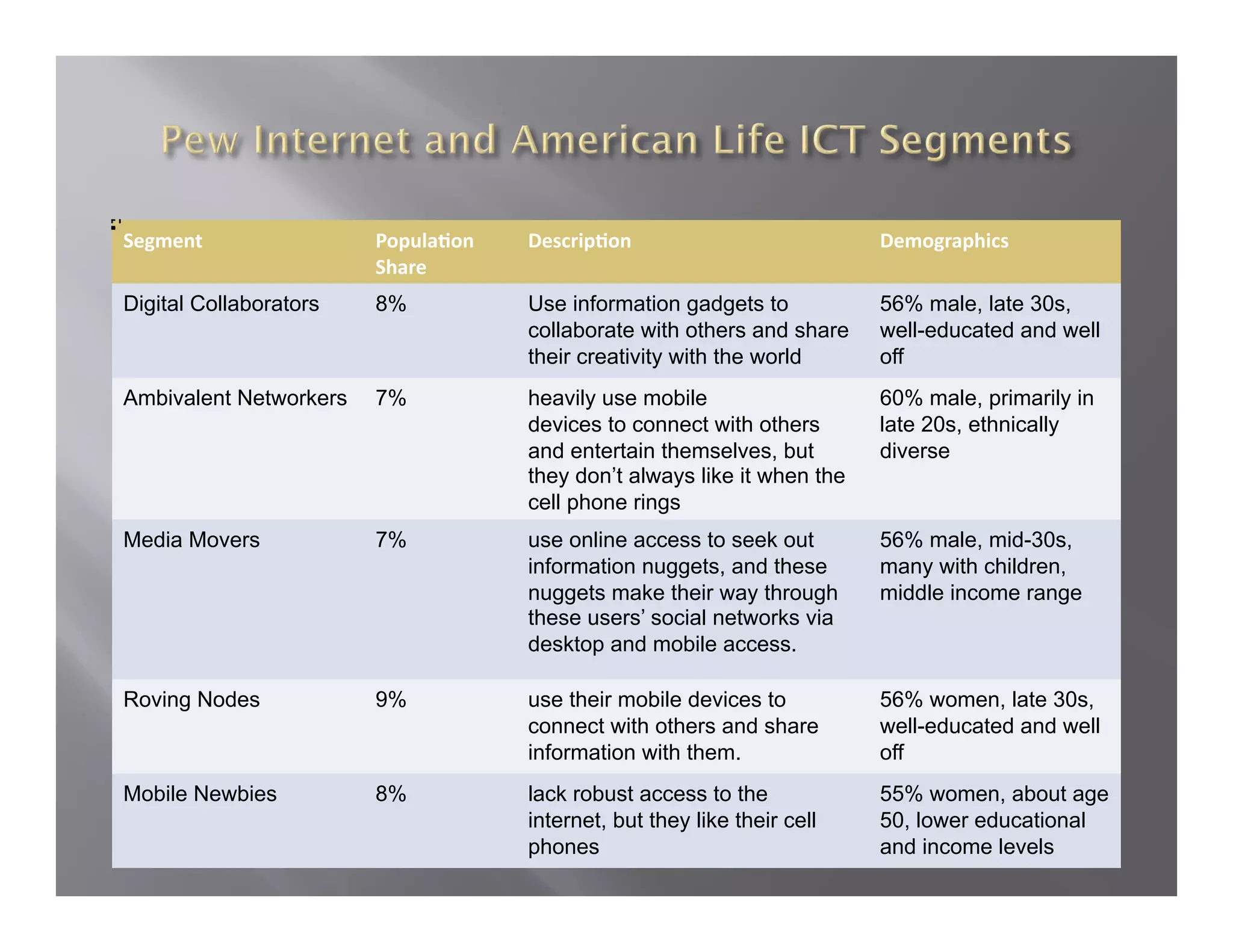
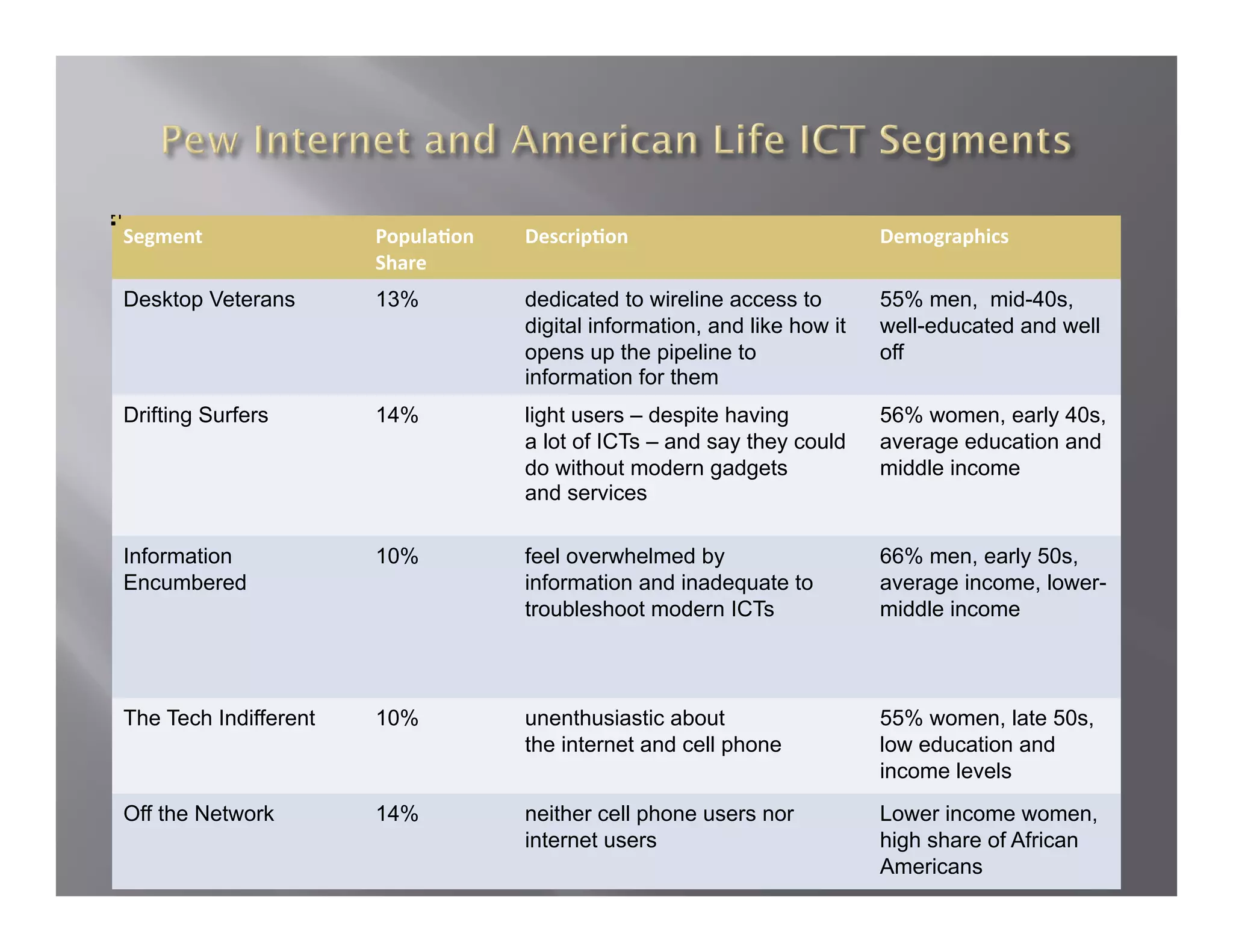
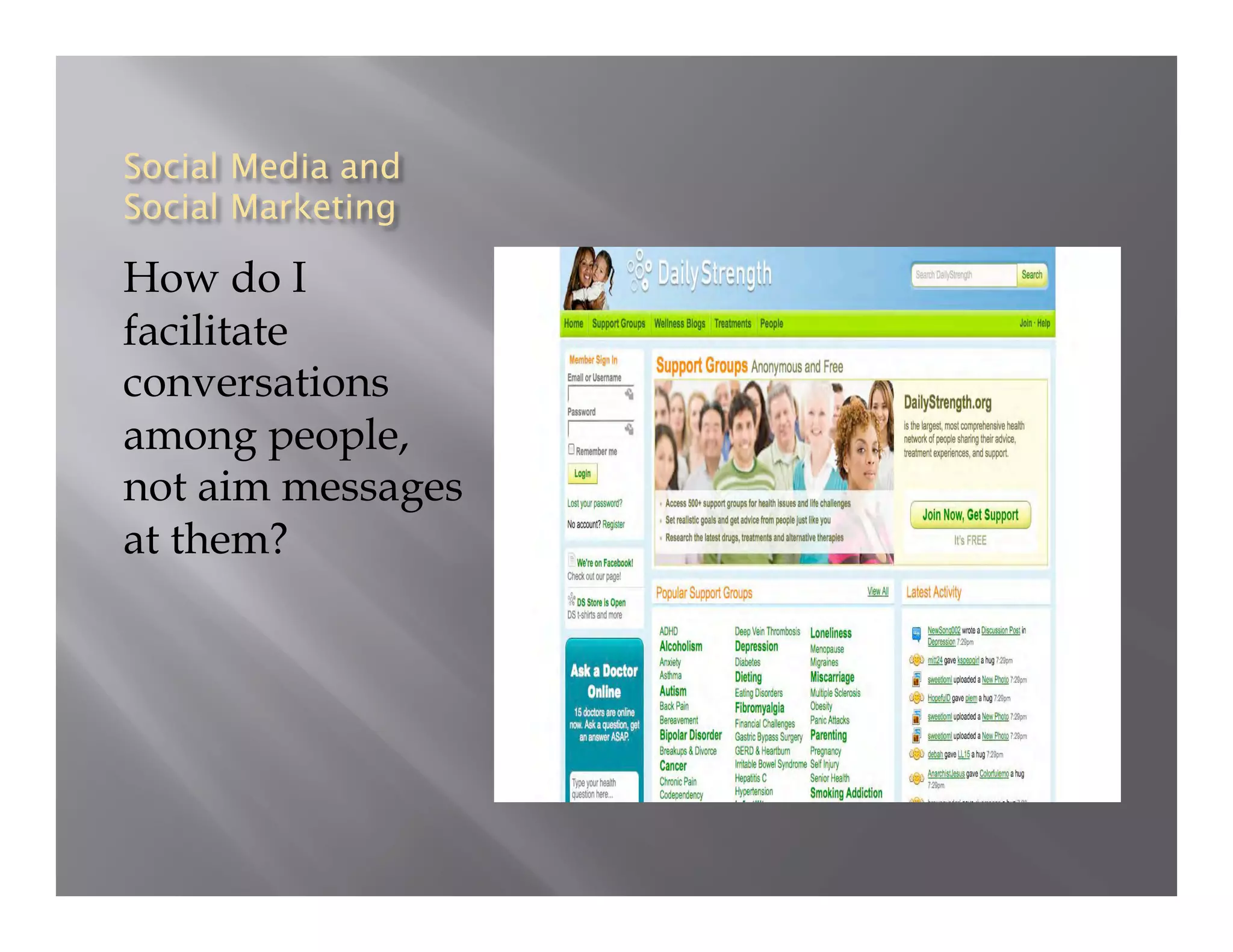
The document summarizes a seminar held by the Health Sponsorship Council on August 5, 2010. It discusses using social media to promote public health campaigns and provides examples of existing public health campaigns on social media platforms. It also outlines strategies for engaging influencers and communities online to spread health messages and behaviors.















![“The
most
frequently
cited
benefit
of
the
internet
was
in
helping
people
tap
into
[their]
social
networks”
–
Susannah
Fox.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insm-2010-lefebvre-100822211250-phpapp01/75/Insm-2010-lefebvre-19-2048.jpg)
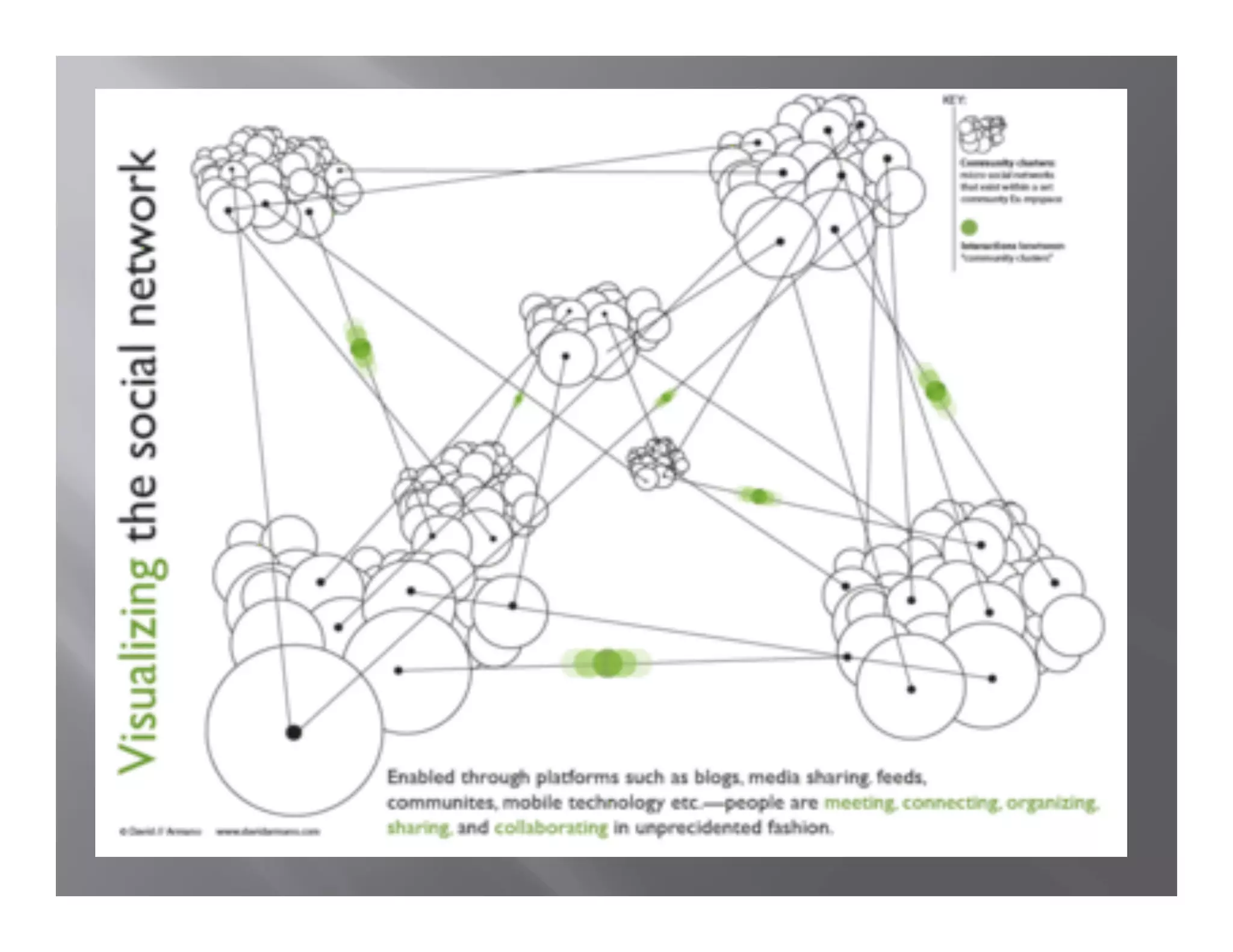





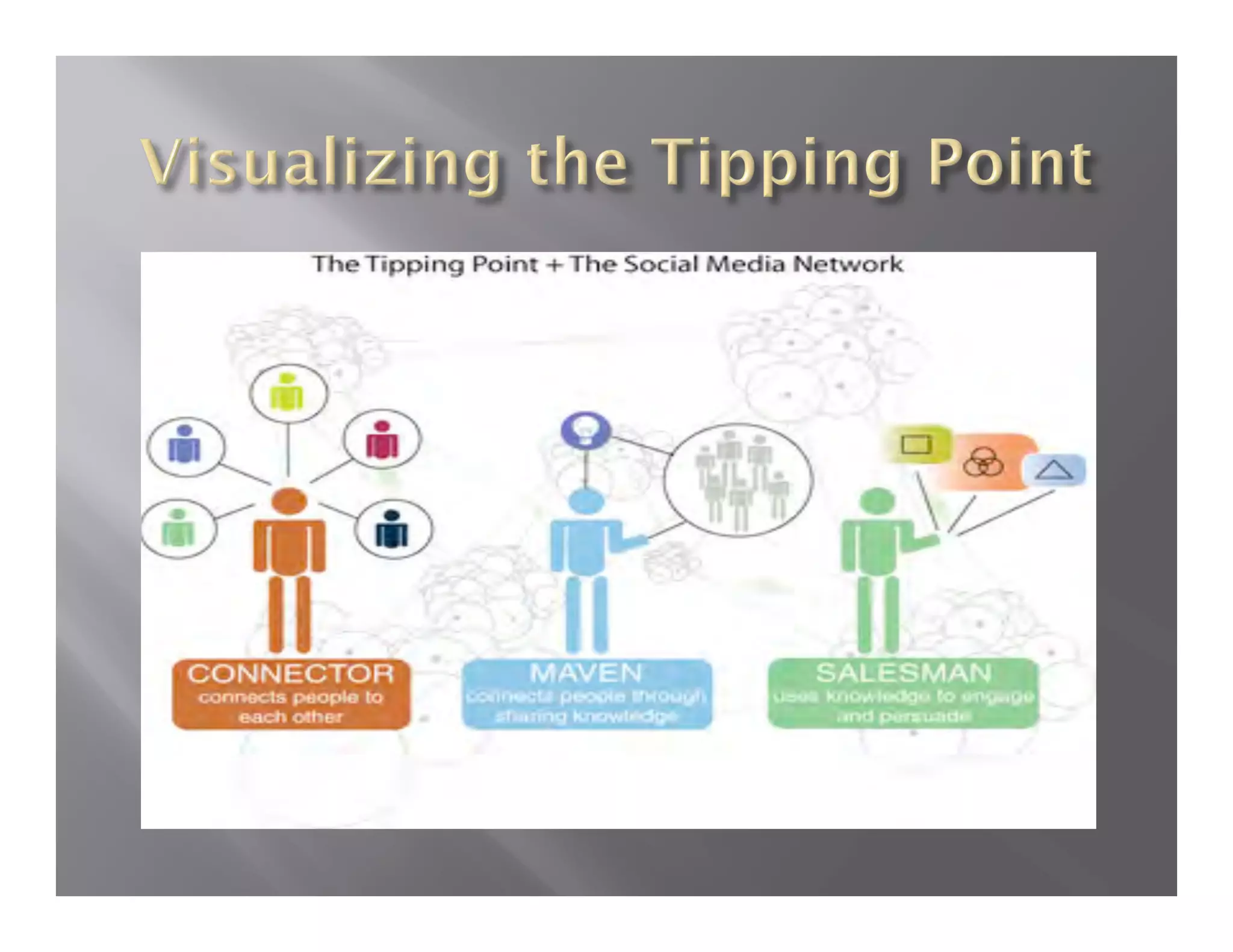



![ ‘Bridging’ and ‘bonding’ (building,
strengthening and using social connections)
Audience Benefits: access social network
resources and solves a problem
Focus on ‘boundary spanners’
Enhance salience and attractiveness of the ‘out
group’ [positive deviants] – put the
practitioners of ‘new’ behaviors in a light that
attracts imitation or modeling.
Build sustainable local capacities/assets](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insm-2010-lefebvre-100822211250-phpapp01/75/Insm-2010-lefebvre-30-2048.jpg)