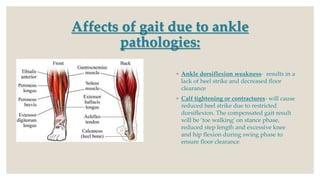
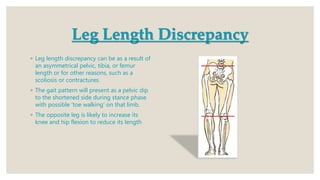
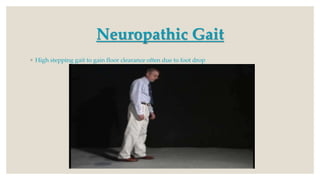
This document discusses gait assessment and analysis. There are two main ways to analyze gait: the Los Ranchos Amigos method and the standard/classic method. Gait can be affected by various musculoskeletal issues like hip, knee, foot/ankle pathology, leg length discrepancy, or pain. Specific conditions may cause deviations like "hip hiking" from arthritis, "scissor gait" from hip adductor contractures, or a Trendelenburg gait from hip abductor weakness. Common gait assessment tests are described like the Timed Up and Go, 6-Minute Walk Test, and Tinetti Test which evaluates gait and balance in older adults.