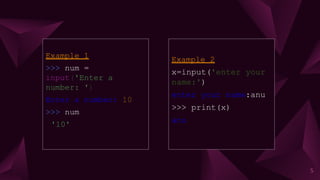
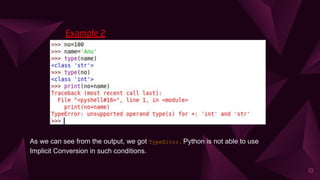
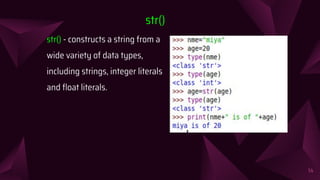
The document discusses input and output functions in Python like input() and print(). It explains that the input() function allows taking user input, displays an optional prompt, and returns the input as a string. Examples show how input() works and how eval() can evaluate expressions. The document also covers implicit and explicit type conversions, noting that implicit conversions are automatic while explicit conversions use functions like int(), float(), and str() and may lose data.

![Input statements
To allow flexibility, we might want to take the input from the
user. In Python, we have the input() function to allow this.
The syntax for input() is:
input([prompt])
where [prompt] is the string we wish to display on the
screen. It is optional.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inputandoutputstatements-221108124927-caf61429/85/Input-and-Output-Statements-pdf-3-320.jpg)