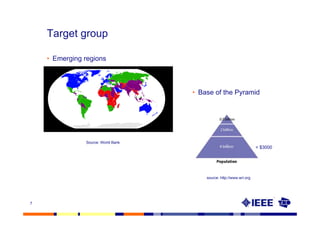
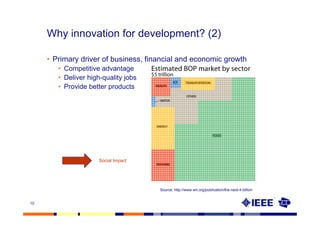
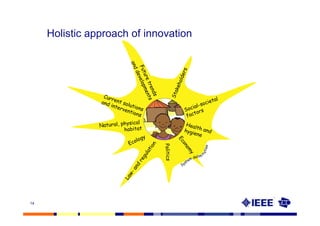
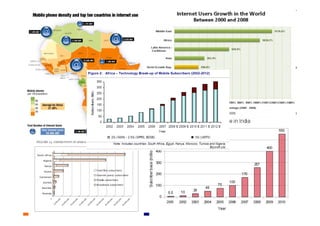
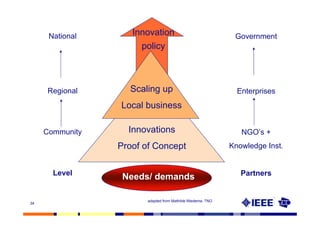
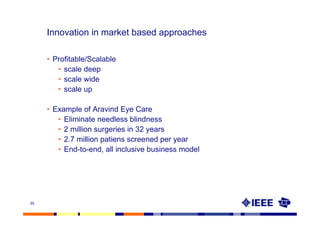
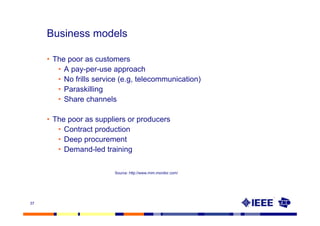
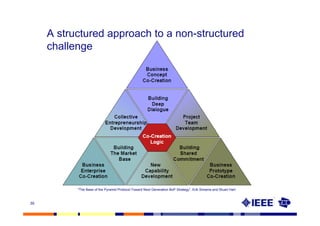
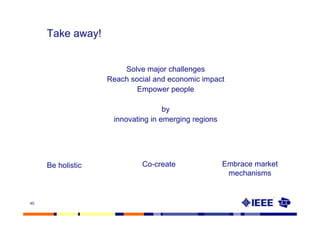
This document provides an overview of innovation for development. It discusses what innovation is, why it is relevant for emerging regions, and guidelines for innovating in these markets. Examples are provided of innovations in products/services like the ICT sector in Africa as well as market-based approaches like social enterprises solving health challenges through portable technologies. Co-creation with local stakeholders is emphasized as important for developing holistic solutions.