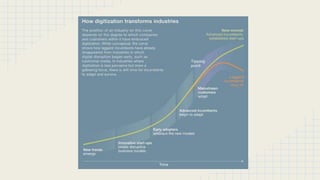
The document discusses embracing new technology in organizations. It defines organizational culture and explains how culture affects productivity, performance, and other factors. It states that product development and adapting to changing technology and consumer demands are crucial for organizational success. The document then provides examples of how different personalities, job satisfaction, leadership styles, and team dynamics are impacted by new technologies. It also discusses challenges like training and benefits like efficiency that organizations face when embracing new technologies.