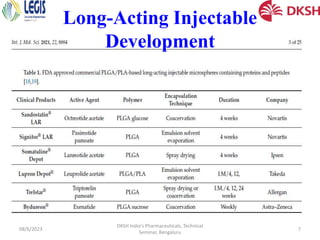
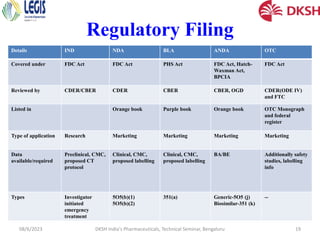
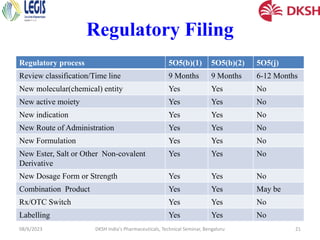
The document covers the development of injectable drugs, ophthalmic preparations, and controlled-release solid oral formulations, focusing on formulation strategies, stability requirements, and release mechanisms. It also discusses regulatory requirements for drug filings in various jurisdictions and the impact of intellectual property rights on generic drug approvals. The seminar, led by Dr. Basavaraj K. Nanjwade, includes detailed insights on both the technical aspects of drug formulation and the legal landscape surrounding pharmaceuticals.