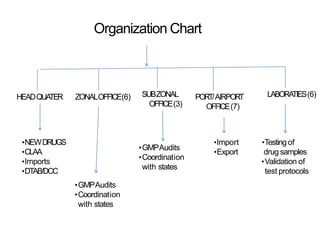
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the main regulatory body for pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and clinical trials in India. It is headed by the Drugs Controller General of India and has offices across the country. CDSCO is responsible for approving new drugs, medical devices, and clinical trials. It also regulates the import and manufacturing of drugs and medical devices through licensing and good manufacturing practice compliance.


![Drugs Controller General of India
[DCGI]
• He/she is aresponsible for approval of New
Drugs, Medical devices and Clinical Trailsto be
conducted in India.
• Heis appointed by the central governmentunder
the DCGIthe State drug control organization will
be functioning.
• TheDCGIis advised by the DrugTechnical
Advisory Board {DTAB}and the Drug Consultative
Committed {DCC}.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdsco-180730095653/85/Cdsco-3-320.jpg)