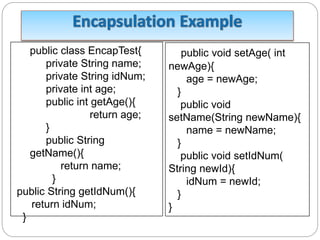
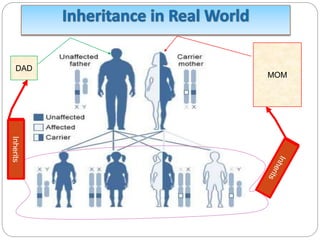
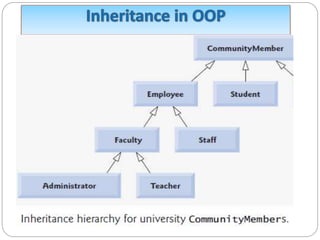
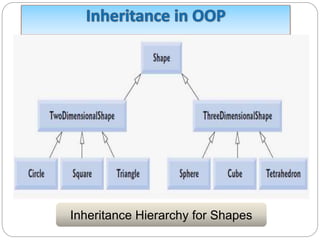
This document discusses object-oriented programming principles like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, abstract classes, and interfaces. It provides examples of how each principle is implemented in Java code. Encapsulation involves making fields private and providing public getter and setter methods. Inheritance allows new classes to inherit attributes and behaviors from existing classes in a hierarchy. Polymorphism allows a parent class reference to refer to child class objects. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated while interfaces contain only abstract methods and are implemented by classes.



![ The public methods are the access points to this class’s
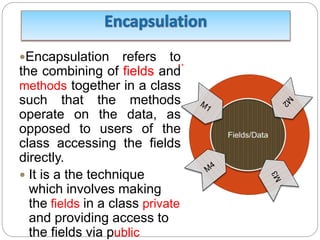
fields from the outside java world.
Normally these methods are referred as getters and
setters. Therefore any class that wants to access the
variables should access them through these getters and
setters.
The variables of the EncapTest class can be accessed
as below:
public class RunEncap{
public static void main(String args[]){
EncapTest encap = new EncapTest();
encap.setName("James");
encap.setAge(20);
encap.setIdNum("12343ms");
System.out.print("Name : " + encap.getName()+ " Age : "+
encap.getAge());
}
}
Out Put:
Name : James Age : 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-7-320.jpg)





![ We can assure that Mammal is actually an Animal with
the use of the instance operator.
public class Dog extends Mammal{
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a = new Animal();
Mammal m = new Mammal();
Dog d = new Dog();
System.out.println(m instanceof Animal);
System.out.println(d instanceof Mammal);
System.out.println(d instanceof Animal);
}
} This would produce following result:
true
true
true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-17-320.jpg)





![public class B extends A{
int d;
B(int l, int m, int n, int o){
super(l, m, n);
d=o;
}
void Show(){
super.show()
System.out.println("d = " + d);
}
public static void main(String args[]
){
B b = new B(4,3,8,7);
b.Show();
}
}
Output
a =
4
b =
3
c =
8
d =
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-23-320.jpg)

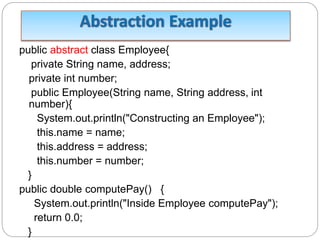

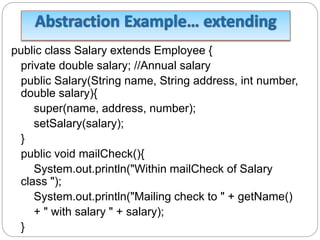

![ Here we cannot instantiate a new Employee, but if we
instantiate a new Salary object, the Salary object will
inherit the three fields and seven methods from Employee.
public class AbstractDemo{
public static void main(String [] args) {
Salary s = new Salary("Mohd ", "Ambehta, UP“, 3,
3600.00);
Salary e = new Salary("John ", "Boston, MA", 2,
2400.00);
System.out.println("Call mailCheck using Salary
reference --");
s.mailCheck();
System.out.println("n Call mailCheck using Employee
reference--");
e.mailCheck();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-29-320.jpg)





![ A class uses the implements keyword to implement an
interface.
The implements keyword appears in the class declaration
following the extends portion of the declaration.
interface Animal { public void eat(); public void travel(); }
public class MammalInt implements Animal{
public void eat(){ System.out.println("Mammal eats"); }
public void travel(){ System.out.println("Mammal travels"); }
public int noOfLegs(){ return 0; }
public static void main(String args[]){
MammalInt m = new MammalInt();
m.eat();
m.travel();
}
}
Output:
Mammal eats
Mammal travels](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-37-320.jpg)




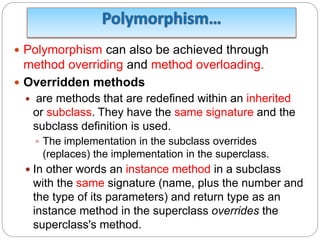
![public class Rectangle extends Shape{
private double width;
private double height;
public Rectangle(double w, double h){this.width =
0;this.height = 0;}
public double computeArea(){ return this.width *
this.height; }
public double computeCircum(){return 2*(this.width
*this.height);}
}
public class ShapeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[3];
shapes[0] = new Circle(4.0);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-43-320.jpg)
![double totalArea = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<shapes.length;i++){
totalArea+=shapes[i].computeArea();
}
System.out.println(“Total area = “ +totalArea);
}
}
Out Put: Total area = 60.44424265506762
A reference variable of type Shape is used to refer
objects of types of its subclasses (Circle and
rectangle)
What is the output of the above code if you comment
out computeArea() method in Circle and Rectangle
classes?
Out Put: Total area = -3.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-44-320.jpg)
![ To know which subclass’s object (or any of subclass’s
subclass objects) is stored in a supperclass reference,
use instanceOf operator.
And if it is the type of the subclass in question,
downcast it explicitly.
For Example if a Rectangle class had getDiagonal()
method and if we want to use this method we must first
downcast it.
if(shap[1] instanceOf Rectangle)
Rectangle r = (Rectangle)shapes[1];
We cannot treat a superclass object as a subclass
object because a superclass object is not an object of
any of its subclasses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-46-320.jpg)
![ It is possible to display each shape’s type as a
string.
for(int i = 0;i<shapes.length;i++){
System.out.printf( “Shape %d is a %sn", i,
shapes[ i] .getClass().getName());
}
The output is
Shape 0 is a Circle
Shape 1 is a Rectangle
Shape 2 is a Circle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-47-320.jpg)








![public static void main(String args[]){
MammalInt m = new MammalInt();
m.eat();
m.travel();
}
}
Now you compile these two files and put them in a
sub-directory called animals and try to run as follows:
$ mkdir animals
$ cp Animal.class MammalInt.class animals
$ java animals/MammalInt
Mammal eats
Mammal travels](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-58-320.jpg)


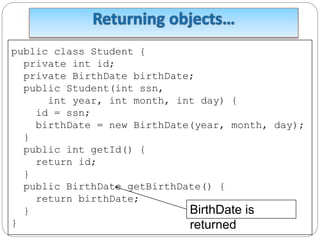
![ Passing by value for primitive type value
the value is passed to the parameter
Passing by value for reference type value
the value is the reference to the object
Example
public class TestPassObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
radius 1 Circle3 myCircle = new Circle3(1);
int n = 5;
printAreas(myCircle, n);
System.out.println("n" + "Radius is " +
myCircle.getRadius());
System.out.println("n is " + n);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-61-320.jpg)


![public class Test {
public static void main(String[]args{
Student student = new
Student(111223333, 1970, 5, 3);
BirthDate date =
student.getBirthDate();
date.setYear(2010);
// Now the student birth year is changed!
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5oopprinciples-230928041356-f7fa63c8/85/Chapter-5-OOP-Principles-ppt-65-320.jpg)
