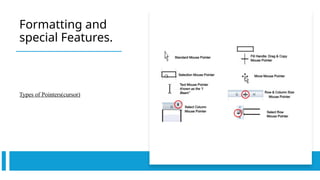
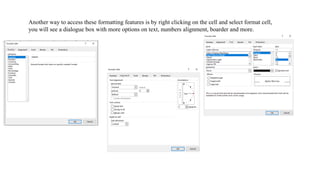
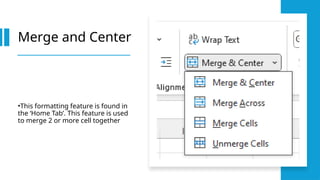
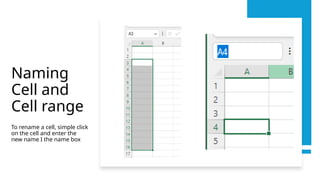
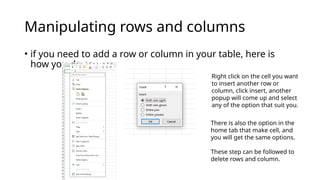
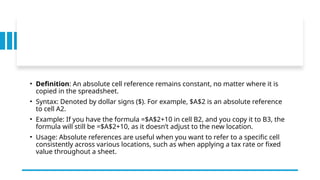
A spreadsheet is a digital tool organized in rows and columns, used to store and manipulate data, often for financial calculations and data analysis. Cells are the basic units that hold data, which can include text, numbers, or formulas, while various features allow for text formatting and data management. Spreadsheets often support operations like sorting, filtering, and using relative or absolute cell referencing for calculations.