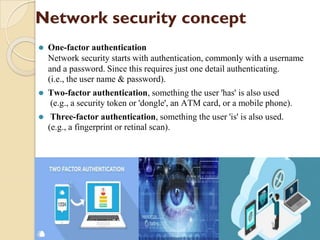
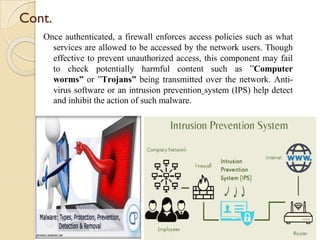
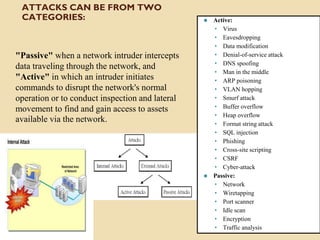
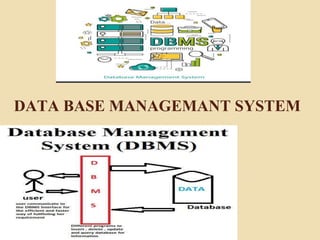
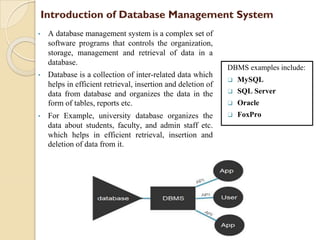
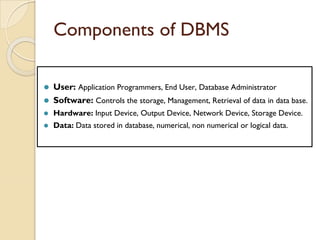
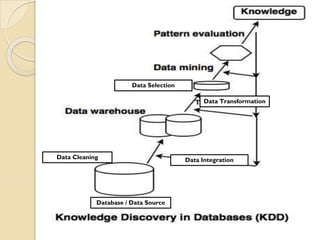
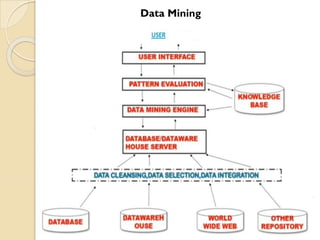
The document provides an overview of Information Technology (IT) and its integral role in modern business, including its applications in communication, data storage, and information management. It also discusses the significance of Database Management Systems (DBMS), data mining, and business intelligence in enhancing decision-making processes. Furthermore, it highlights trends in e-governance and the various sectors involved in government interactions with citizens, businesses, and employees.