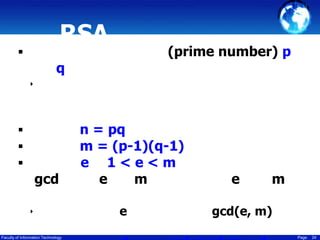
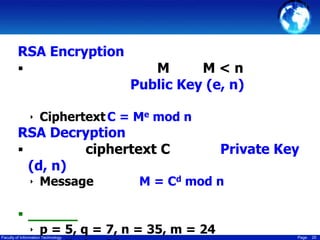
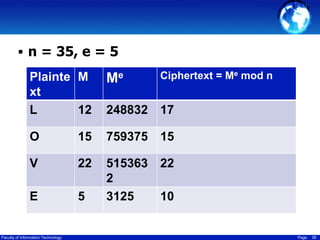
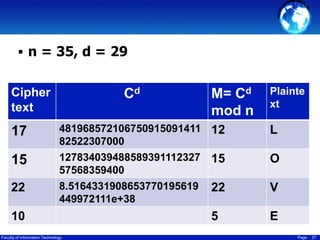
This document discusses cryptography techniques including symmetric key cryptography, stream ciphers, the one-time pad cipher, RC4 stream cipher, and asymmetric key cryptography. Symmetric key cryptography uses the same key for encryption and decryption, while asymmetric key cryptography uses public and private key pairs. Specific techniques covered include DES, AES, RC4 stream cipher, one-time pad, and the RSA algorithm for asymmetric encryption.







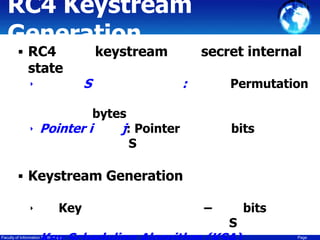
![Key Scheduling
Algorithm (KSA)
KSA
S
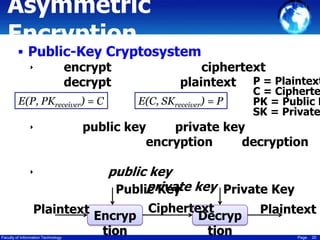
‣
byte
for i from 0 to 255
S[i]
S[1] := i
endfor
S
S[0]
,
,
Identity Permutation
‣
for i from 0 to 255
j := (j + S[i] + key[i mod keylength]) mod 256
swap S[i] and S[j]
Permute
S
Key
endfor
Faculty of Information Technology
Page](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9164it346-wk4-cryptography-2-131015153818-phpapp01/85/Information-system-security-wk4-cryptography-2-11-320.jpg)

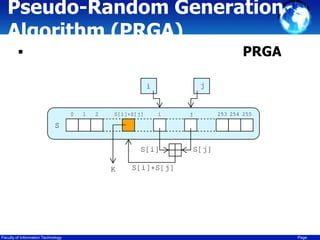
![Pseudo-Random Generation
Algorithm (PRGA)
PRGA
pointer i
‣
‣
i
•
j
•
•
•
(S[i]
Faculty of Information Technology
S[i]
j
PRGA
S[i]
i := 0 , j := 0
S[j]
while
S[i]
S[j] :=GeneratingOutput:
i
(i + 1) mod 256
Keystream (j + S[i]) mod 256
j :=
swap S[i] and S[j]
S
+ S[j]) mod K := S[(S[i] + S[j]) mod 256]
256
output K
endwhile
Page](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9164it346-wk4-cryptography-2-131015153818-phpapp01/85/Information-system-security-wk4-cryptography-2-13-320.jpg)