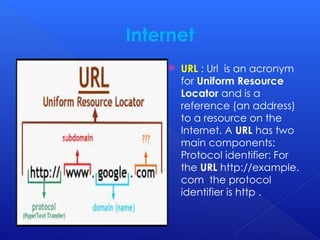
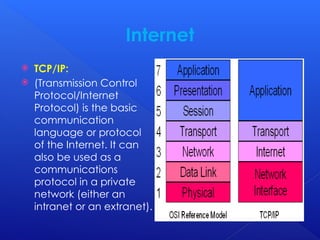
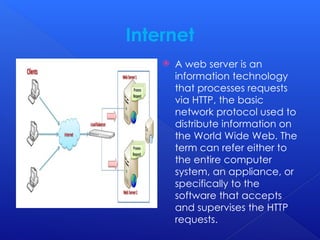
The document provides an overview of key concepts related to the World Wide Web, including web browsers, HTTP, URLs, HTML, IP addresses, TCP/IP, email attachments, web servers, internet surfing, chatting, and e-commerce. It explains how these elements interact and function within the internet environment. The content is focused on the foundational technologies and practices that enable web-based communication and information sharing.
![Internet
WWW:
The World Wide Web
(www,
W3 [citation needed]
) is an
information space where
documents and other
web resources are
identified by URLs,
interlinked by hypertext
links, and can be
accessed via the Internet.
It has become known
simply as the Web.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/differentterminology-240803134211-fd76a8e4/75/Information-on-Internet-Its-Terminology-pptx-1-2048.jpg)