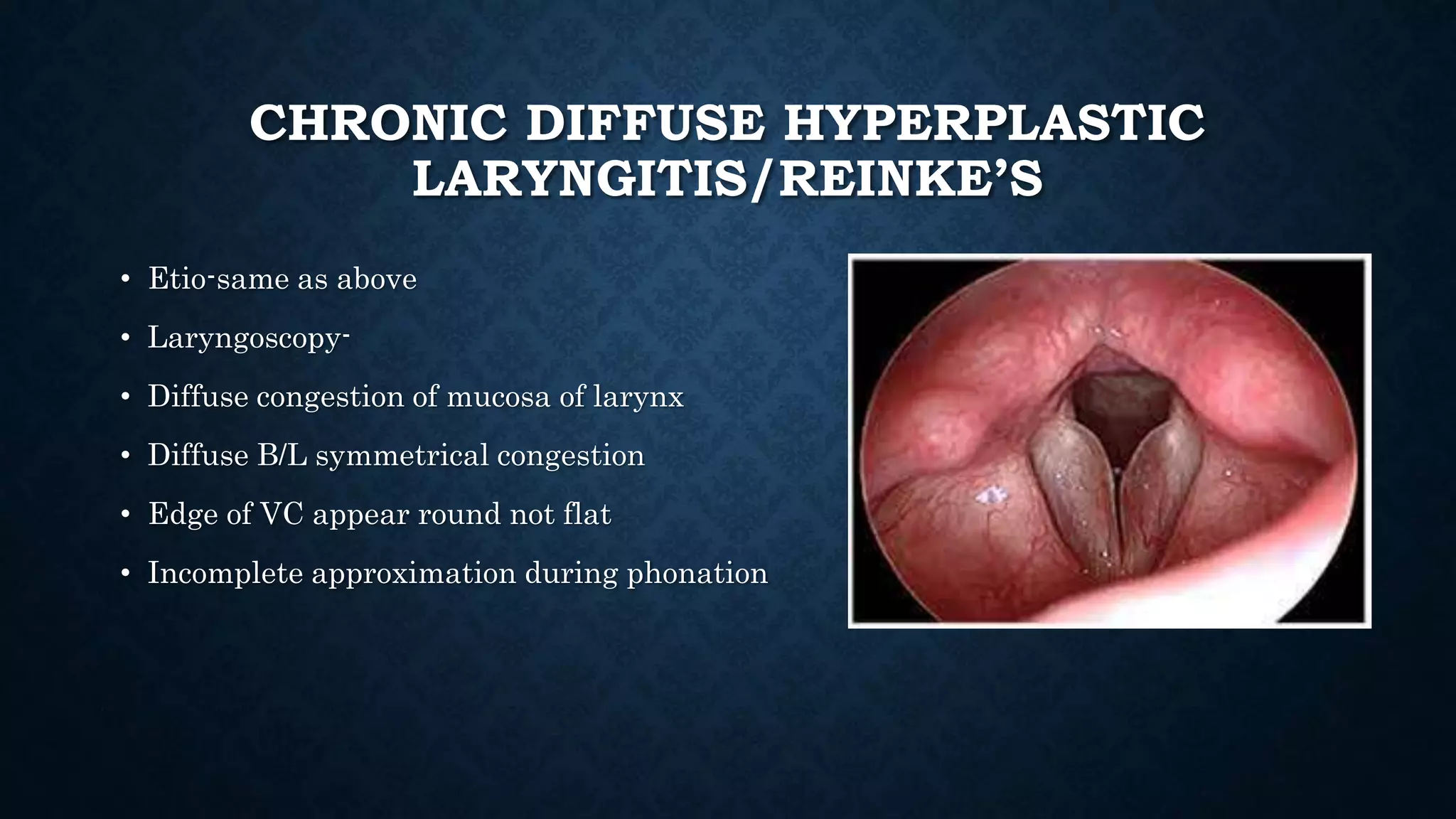
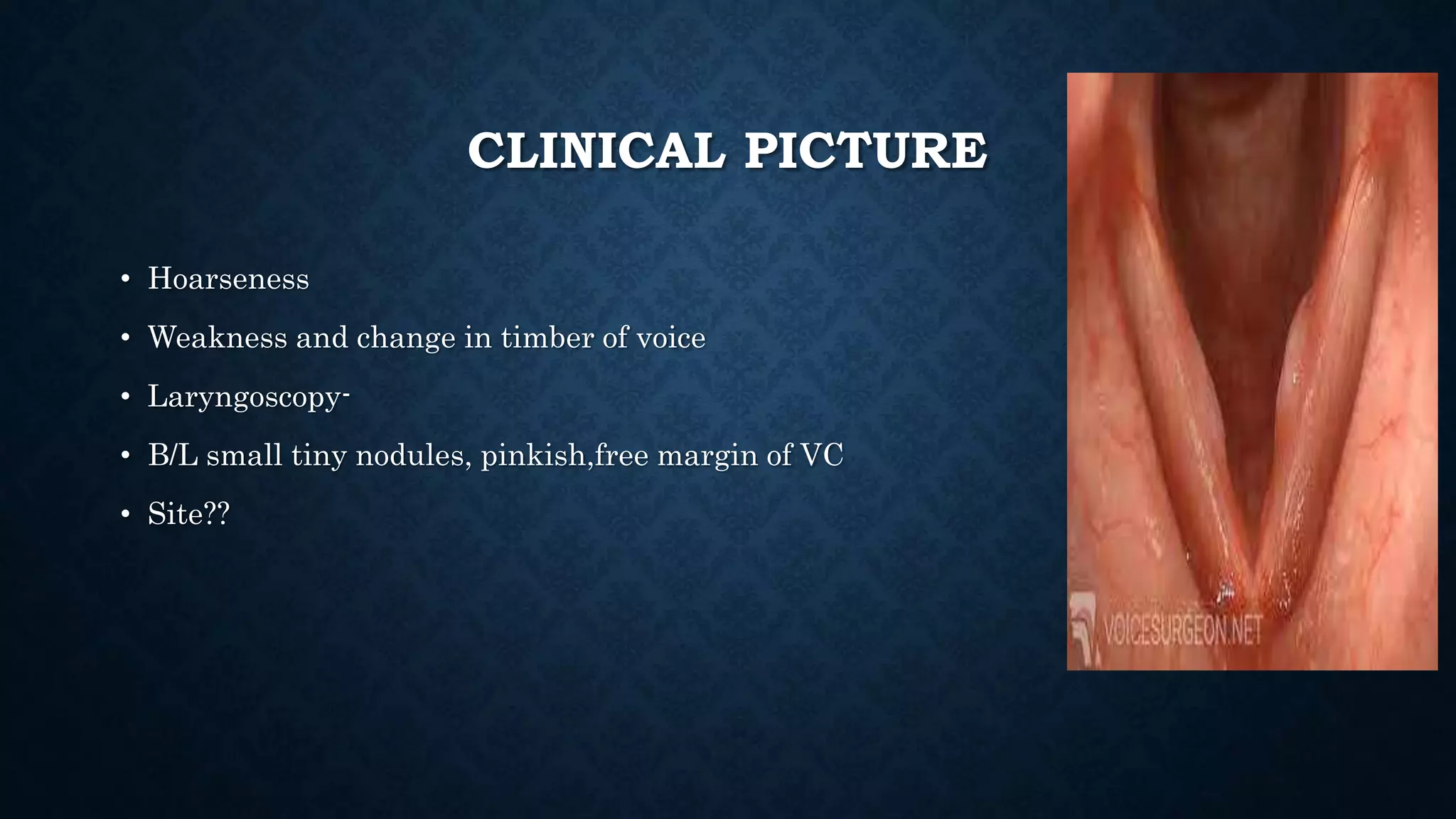
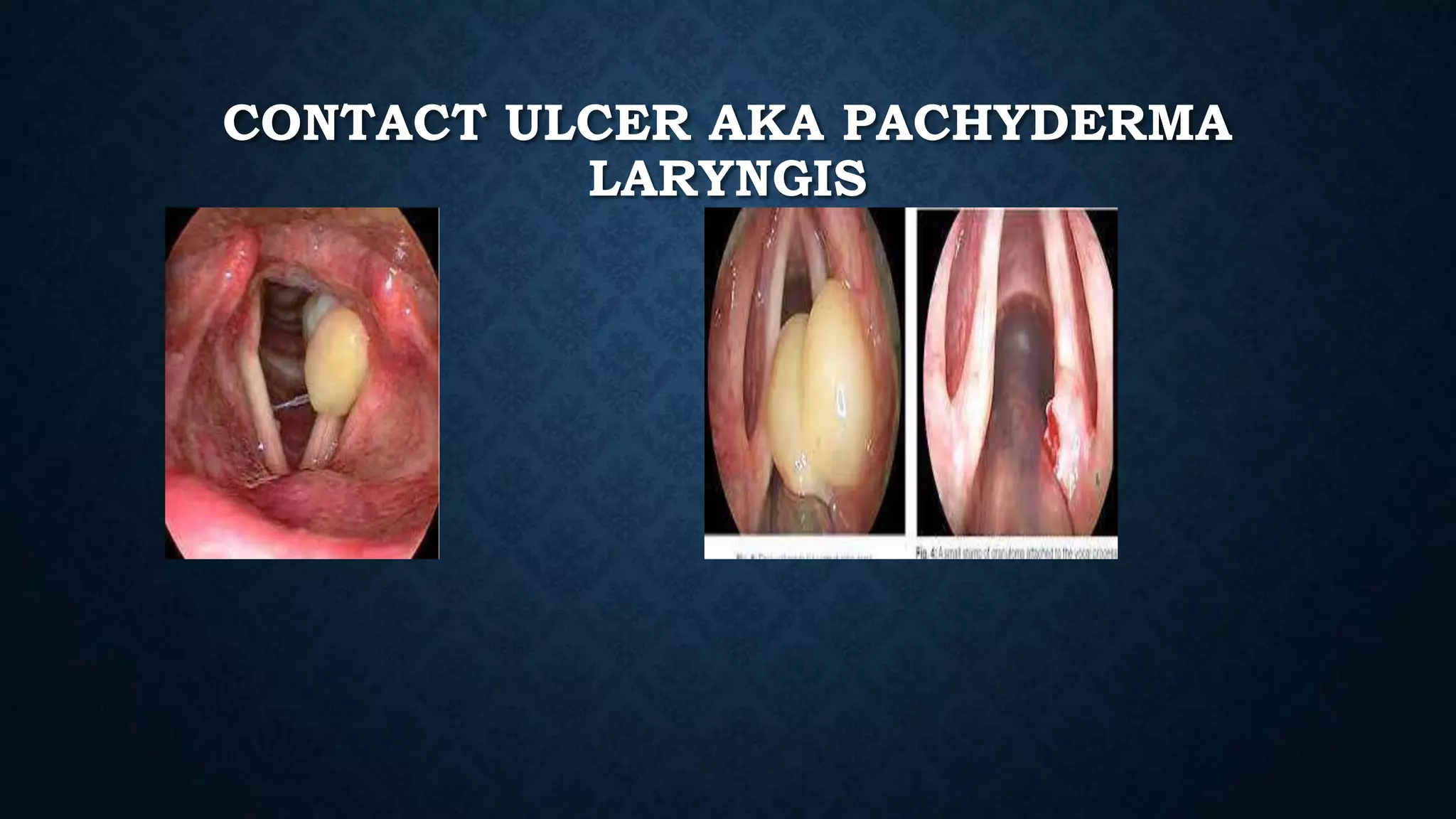
This document provides an overview of various inflammations of the larynx, including acute and chronic laryngitis, acute epiglottitis, laryngotracheobronchitis, and specific conditions like diphtheria, tuberculosis, and syphilis. It describes the causes, clinical features, examinations findings, and treatments for each condition. Key signs include hoarseness, cough, stridor, and dyspnea. Treatment involves voice rest, steam inhalation, antibiotics, steroids, and intubation or tracheostomy in severe cases to maintain an open airway. Chronic laryngitis is often caused by smoking, vocal abuse, or recurrent infections and may lead to nodules,