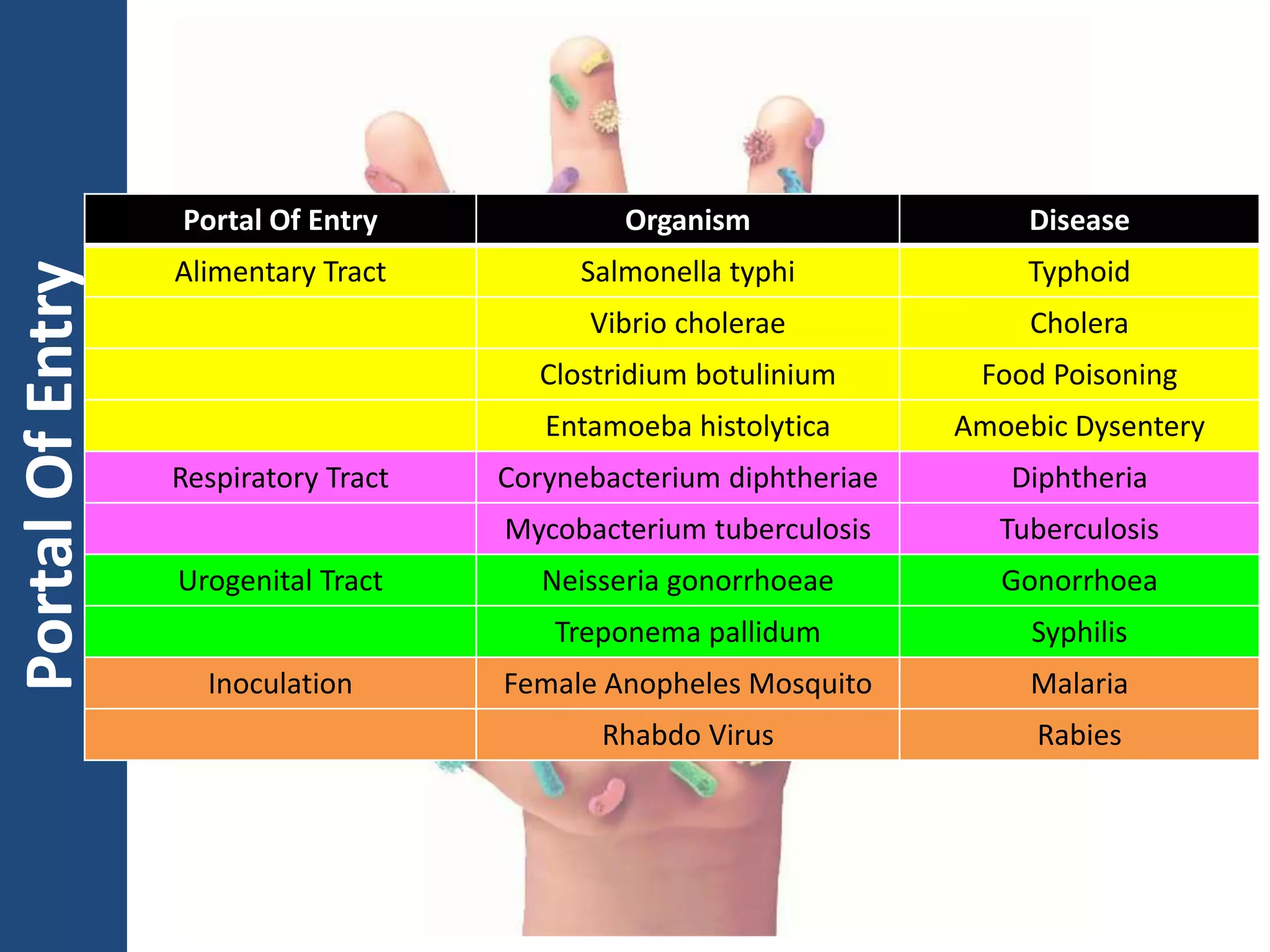
The document discusses various types of infections including primary, secondary, latent and opportunistic infections. It explains different modes of transmission for pathogens such as direct contact, droplet transmission, and indirect transmission through vehicles like contaminated water or food. Various organisms that cause diseases are described based on their portal of entry and exit from the host.