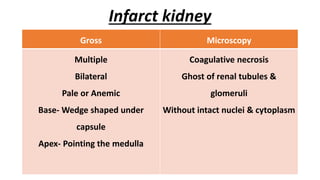
This document discusses infarcts, which are areas of ischemic necrosis caused by occlusion of the arterial supply or venous drainage. It defines infarcts and lists common causes like thrombotic occlusion. It describes different types of infarcts based on color, age, and presence of infection. Pathogenesis involves local hyperemia, edema, hemorrhage, and cellular changes leading to necrosis replaced by fibrous tissue. Gross morphology shows wedge-shaped lesions pointing toward the occluded vessel. Microscopy typically shows coagulative necrosis and inflammatory reaction at the periphery replaced by fibrous tissue. Commonly affected organs and outcomes are also outlined.