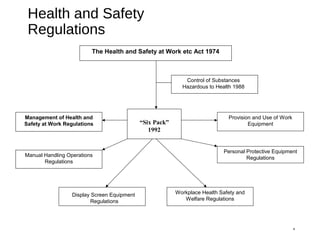
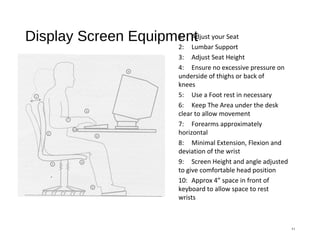
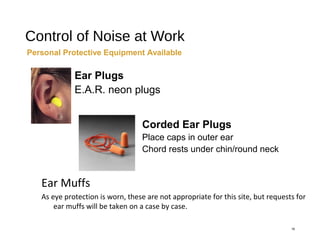
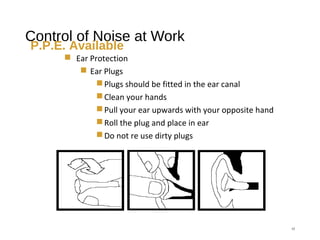
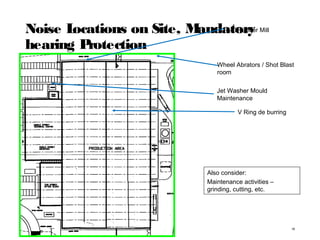
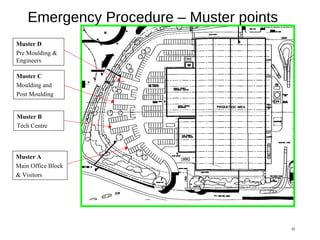
The document discusses health and safety regulations and procedures at an employee site induction. It covers the Health and Safety at Work Act of 1974 which requires employers to ensure a safe work environment and employees to take reasonable care of their own safety. It also summarizes regulations around hazardous chemicals, noise protection, machinery safety, fire safety, and the responsibilities of both employees and employers.