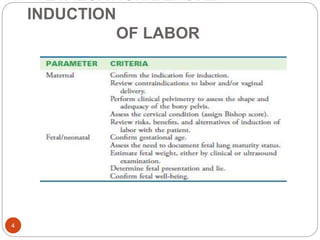
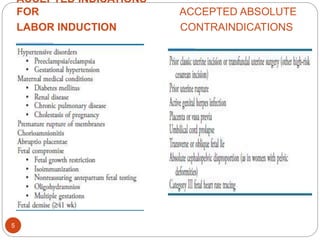
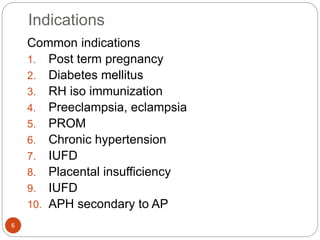
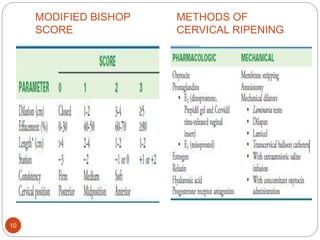
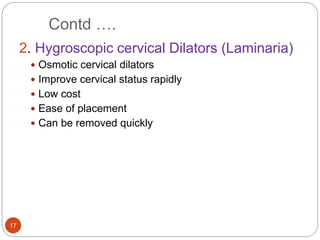
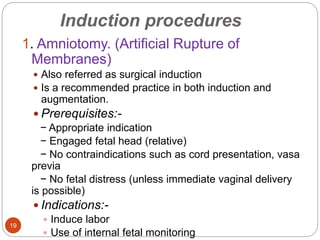
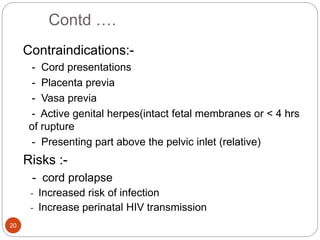
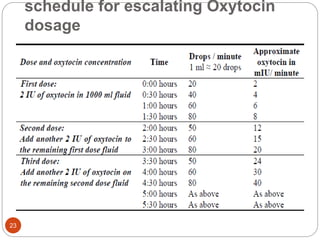
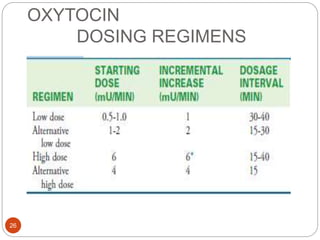
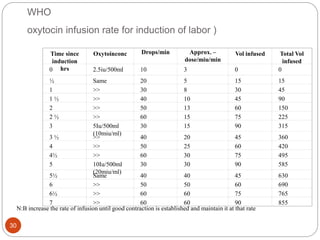
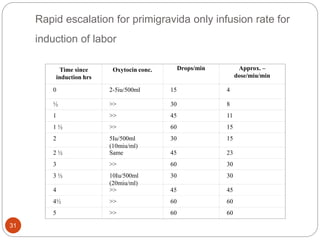
Induction and augmentation of labor can be done when the benefits outweigh continuing the pregnancy. Induction requires no contraindications and an assessment of cervical readiness. Common induction methods include prostaglandins like misoprostol or dinoprostone for cervical ripening, and oxytocin infusion to stimulate contractions. Risks include failed induction requiring C-section, uterine hyperstimulation, and fetal distress. Oxytocin must be carefully titrated to achieve effective contractions without overstimulation.