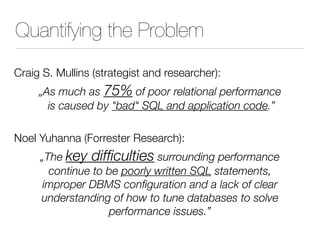
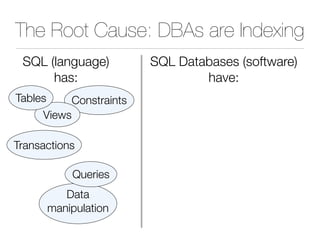
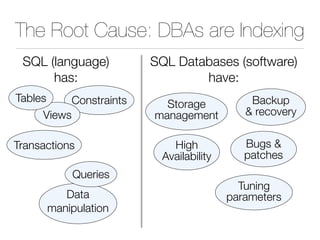
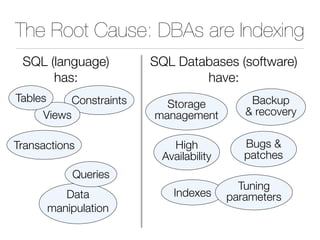
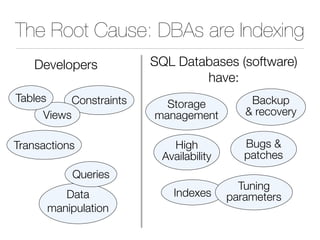
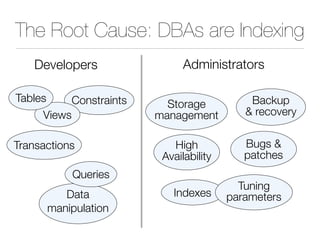
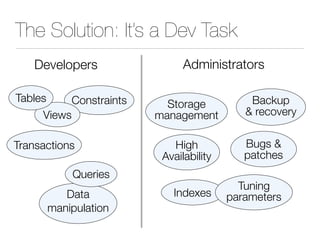
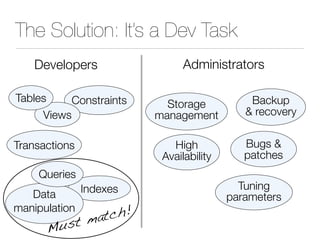
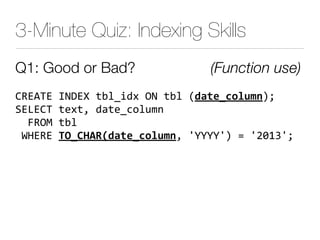
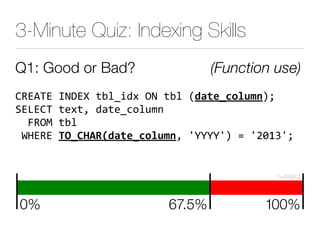
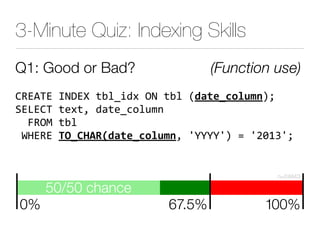
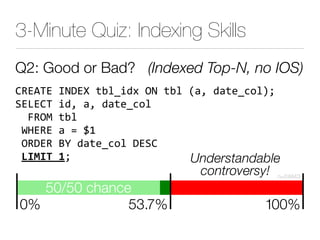
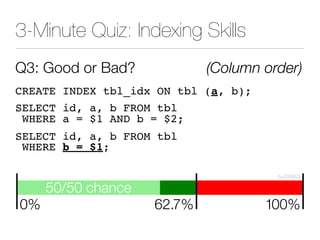
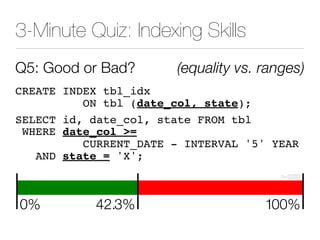
The document discusses improper index use as a common cause of poor database performance. It argues that indexing is often treated as an administrative task rather than a development task, but developers do not fully understand how to properly use indexes. As a result, indexes are not designed to match the overall needs of an application's queries. The document advocates that indexing should be viewed as a design task and that developers need to more fully learn how to utilize indexes to improve performance.