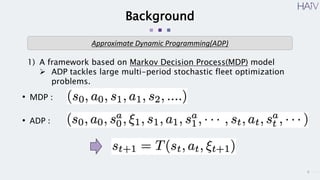
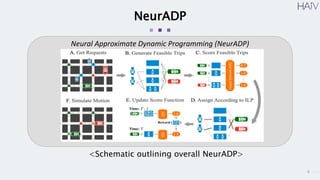
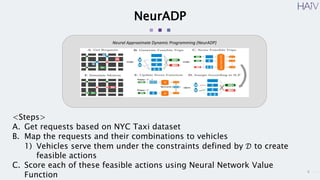
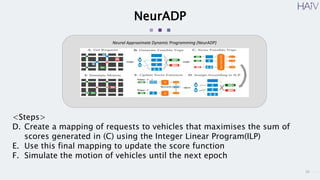
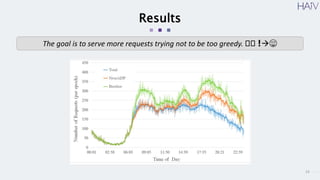
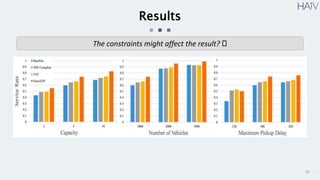
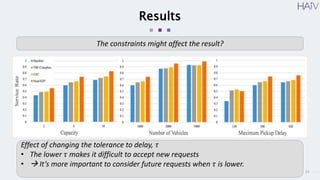
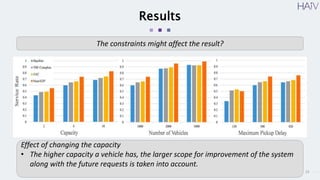
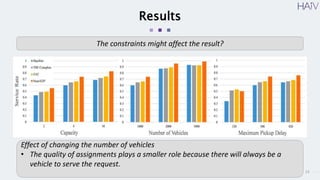
This document summarizes a research paper on using neural approximate dynamic programming (NeurADP) to solve the ride-pooling matching problem (RMP) of optimally assigning passenger requests to vehicles. The key contributions are developing NeurADP, which uses a neural network to approximate the value function within an ADP framework, and connecting it to reinforcement learning. This allows NeurADP to handle the complex RMP involving partially filled vehicles better than prior methods. The researchers test NeurADP on New York City taxi data and find that changing constraints like maximum wait time and vehicle capacity affects NeurADP's ability to serve more requests while avoiding myopic assignments.