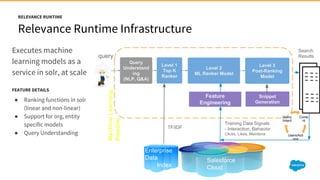
1) Jayesh Govindarajan presented on improving enterprise search and findability at Salesforce. He discussed how enterprise search differs from consumer search, challenges with enterprise findability, and machine learning algorithms like LETOR that can be used.
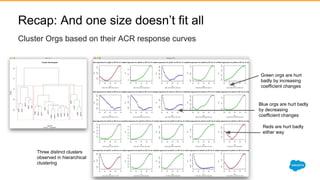
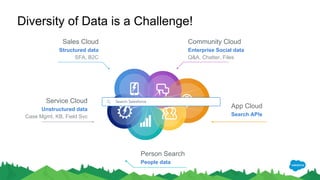
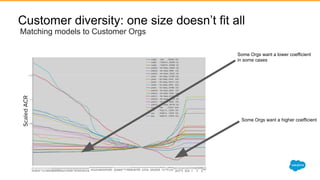
2) Govindarajan explained that diversity of data, intentions, and customers makes enterprise search more complex than consumer search. Most enterprise search relies on simple ranking functions that may not reflect relevance well.
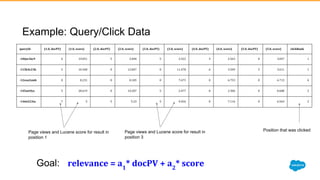
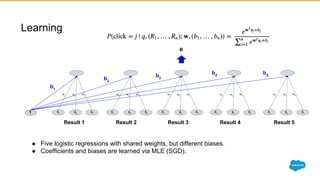
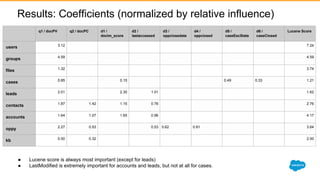
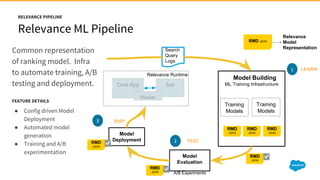
3) Machine learning algorithms like logistic regression and learning to rank can learn relevance from user behavior data like clicks and views. These algorithms output ranking models that can be deployed to search engines like Solr.









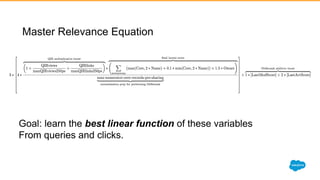
![Most ranking functions start off with a few boosts
and end up like….this
Form
1. Query independent signals - multiplicative boosts in range [1-3]
2. Entity specific signals - additive boosts in the range of [1-12]
a. Accounts, Contacts, Leads - LastActivityScore, LastModifiedScore
b. Cases - CaseStatus, CaseEscalationScore
3. ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jayeshgovindarajanimprovingenterprisefindabilityrev2016-161104162452/85/Improving-Enterprise-Findability-Presented-by-Jayesh-Govindarajan-Salesforce-12-320.jpg)