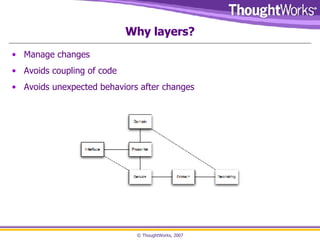
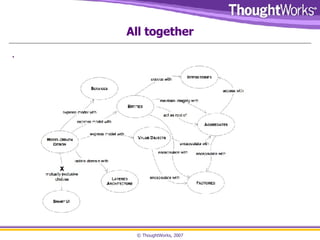
The document discusses the importance of being driven in software design, emphasizing that it is an art that cannot be rigorously taught. It covers key concepts like Agile methodologies, Behavior Driven Development (BDD), Domain Driven Development, and the significance of refactoring and maintaining a clear domain language. The text also highlights the role of factories and repositories in managing object creation and data retrieval, advocating for a collaborative approach involving domain experts to enhance code readability and alignment with business needs.