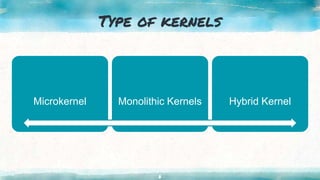
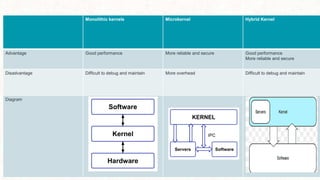
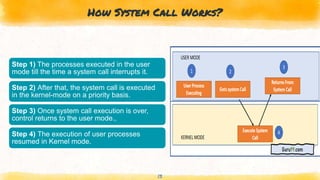
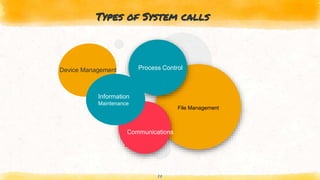
This document provides an overview of kernel APIs and system calls. It discusses that the kernel acts as an interface between user applications and hardware, and its objectives include managing communication between software and hardware, controlling tasks, and establishing communication. It describes different types of kernels like monolithic, micro, and hybrid kernels. It also explains important concepts like system calls, which allow processes to request services from the kernel, and examples of common system calls like wait, fork, exec, kill, and exit. Finally, it gives examples of kernel APIs for managing linked lists, including adding/removing entries and moving between lists.