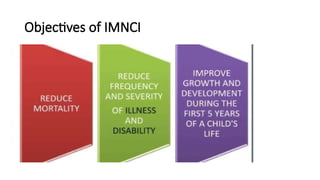
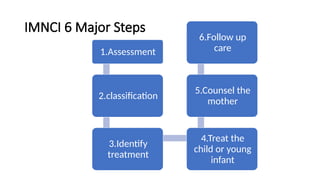
El manejo integrado de enfermedades neonatales y de la infancia (IMNCI) es una estrategia desarrollada por la OMS y UNICEF en 1992 para reducir la morbilidad y mortalidad en niños menores de cinco años mediante la gestión de enfermedades comunes, atención nutricional, inmunización y cuidados neonatales. Este enfoque implica un proceso de evaluación, clasificación, tratamiento y seguimiento del niño, involucrando a los cuidadores en la atención. La implementación del IMNCI ha mejorado significativamente la supervivencia infantil y neonatal al reducir tasas de mortalidad en varios países.