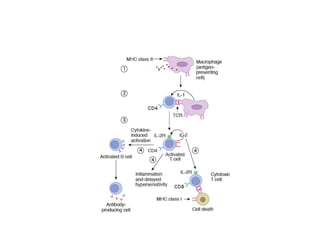
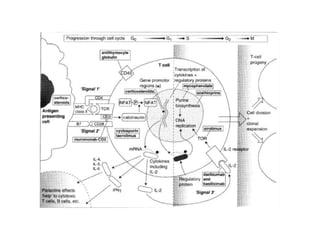
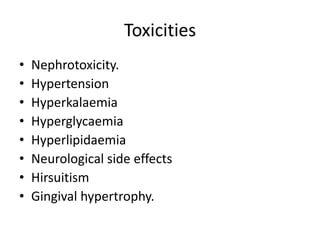
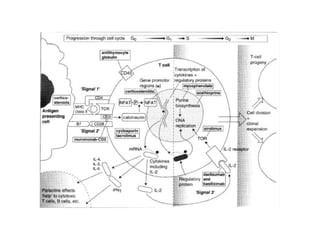
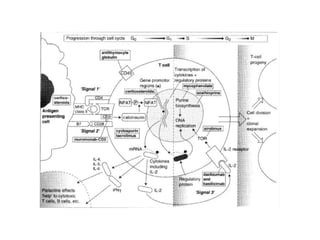
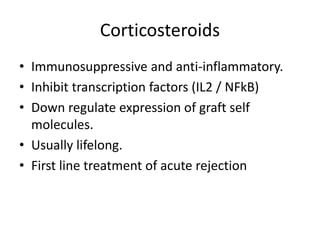
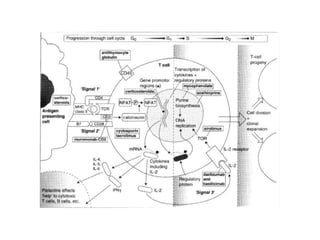
The document discusses immunosuppression in transplantation, detailing types of rejection (acute and chronic) and various immunosuppressive agents including calcineurin inhibitors, antimetabolites, corticosteroids, and monoclonal antibodies. It highlights specific drugs like cyclosporin A, tacrolimus, azathioprine, and mycophenolate, along with their mechanisms, toxicities, and monitoring requirements. The information is crucial for understanding post-transplant care and managing rejection in lung transplant patients.