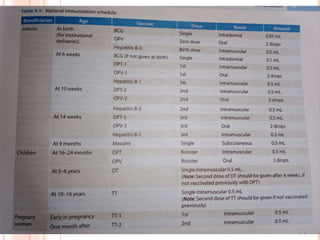
Immunization involves protecting individuals from disease by introducing live, killed, or attenuated organisms. It stimulates the body's immune system and is one of the most cost-effective health interventions. Immunization helps reduce communicable diseases' impact on health and has controlled or eliminated some diseases from certain areas. National immunization schedules tailored to community needs aim to protect children from six killer diseases.