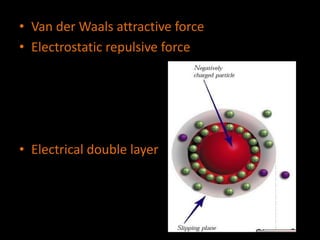
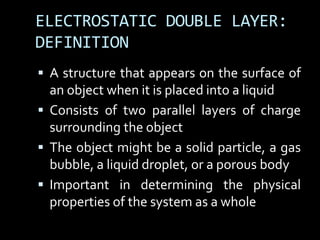
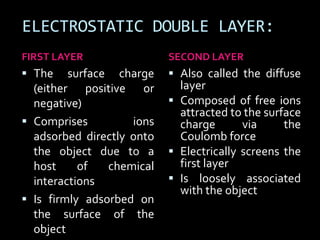
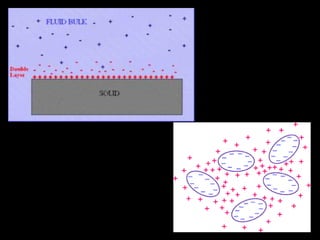
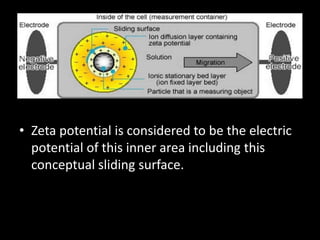
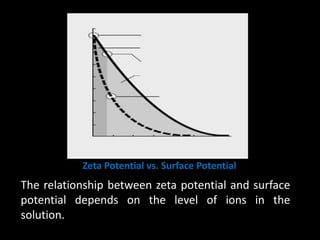
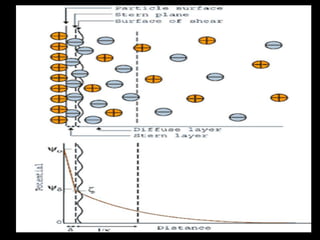
Electrostatic forces are caused by electric charges on particles and affect colloid stability. Colloidal particles often carry an electrical charge, causing them to attract or repel each other. The total interaction potential between particles can be calculated using the DLVO theory, which balances attractive van der Waals forces and repulsive electrostatic forces. The zeta potential, which indicates colloid stability, depends on factors like ionic strength, pH, and surface chemistry.












![Zeta potential [mV] Stability behavior of the
colloid
from 0 to ±5 Rapid coagulation or
flocculation
from ±10 to ±30 Incipient instability
from ±30 to ±40 Moderate stability
from ±40 to ±60 Good stability
more than ±61 Excellent stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imk209fantasia-101031033710-phpapp02/85/Imk209-fantasia-20-320.jpg)








