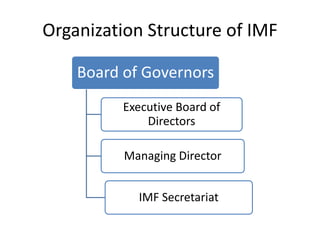
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 189 countries that works to foster global monetary cooperation and financial stability. It aims to facilitate international trade, promote employment and economic growth, and reduce poverty. The IMF provides loans to countries experiencing temporary balance of payments issues, offers technical assistance, and monitors economic policies. It is governed by a Board of Governors and Executive Board and led by a Managing Director. The IMF also issues Special Drawing Rights to supplement global reserve assets.