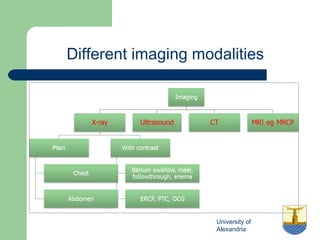
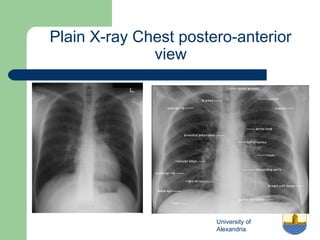
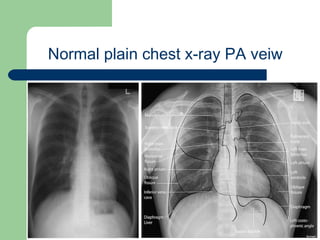
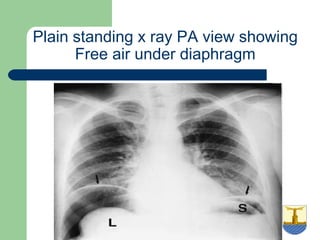
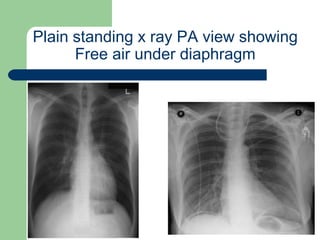
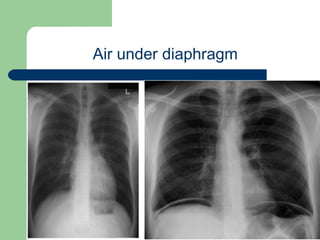
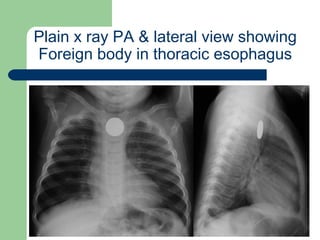
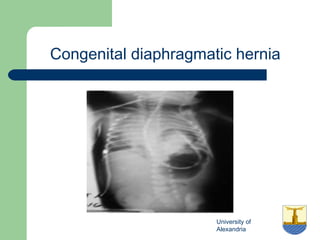
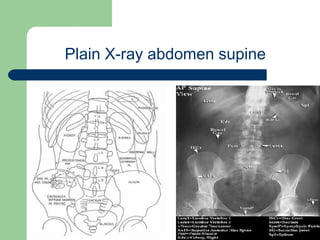
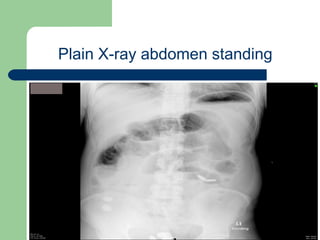
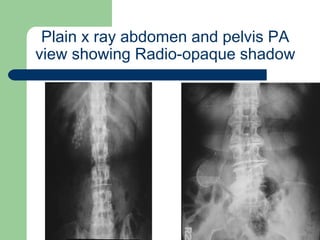
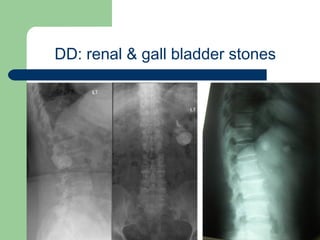
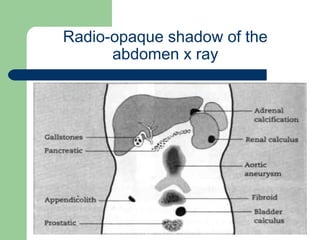
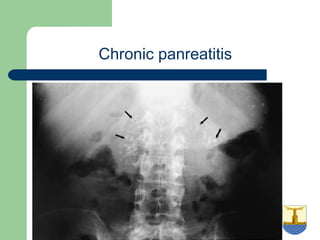
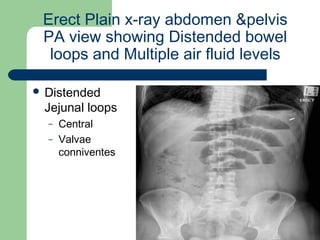
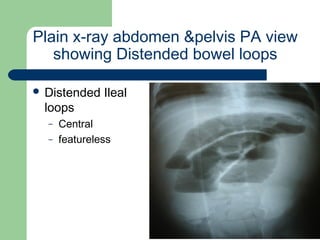
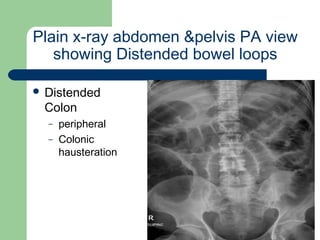
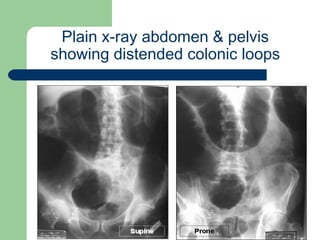
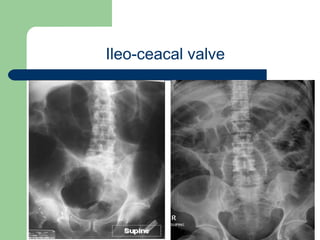
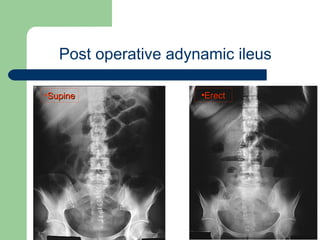
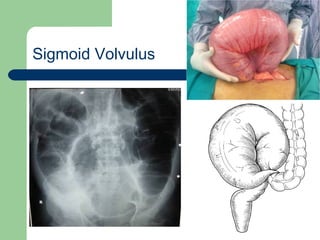
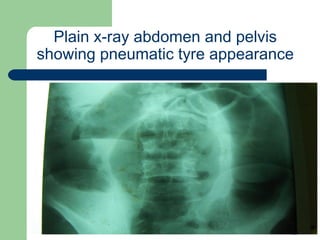
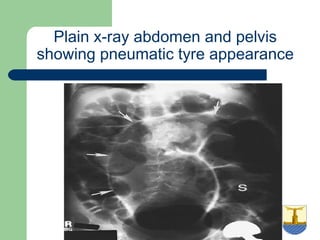
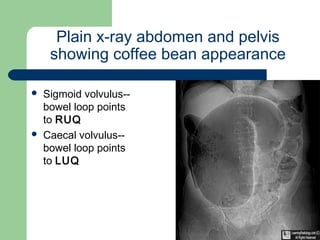
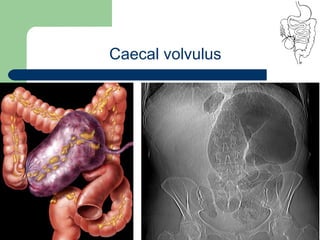
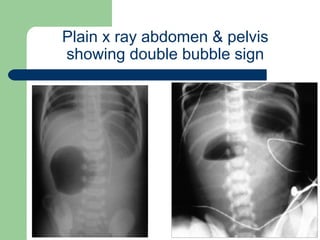
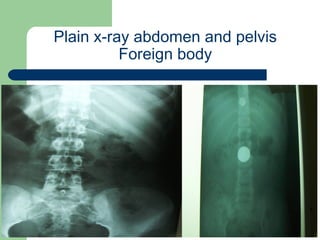
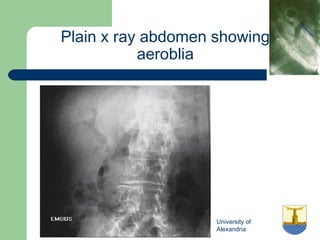
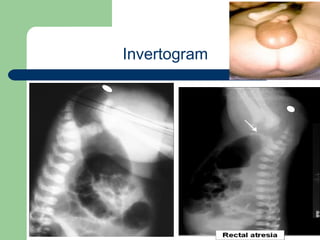
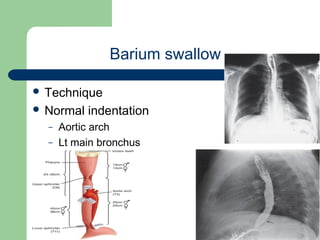
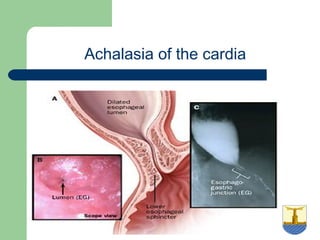
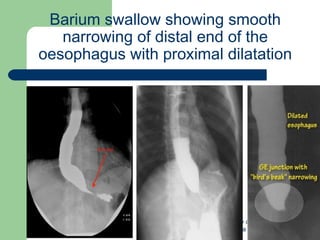
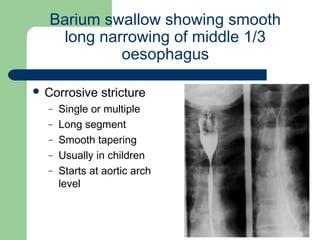
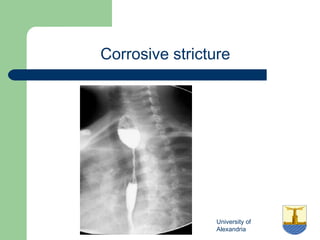
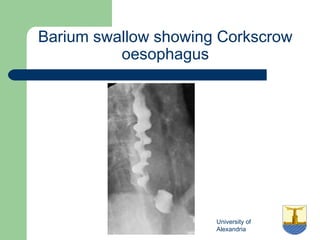
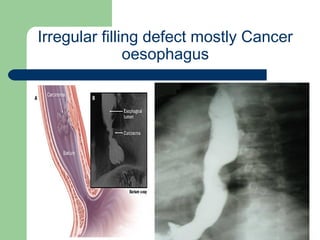
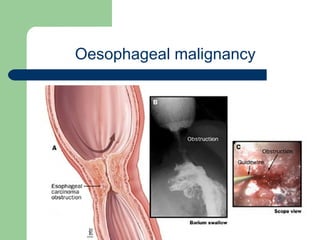
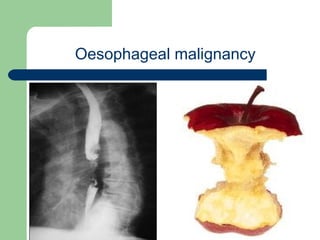
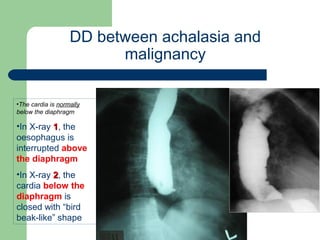
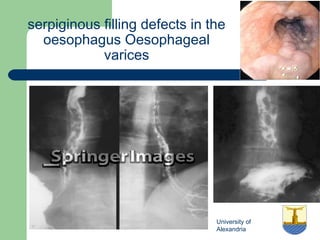
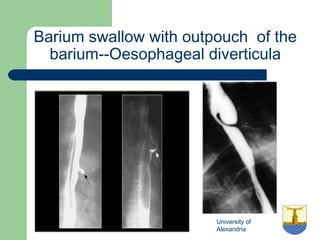
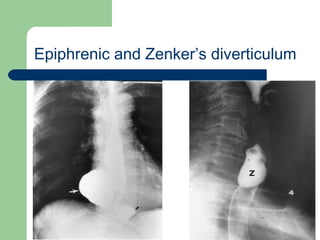
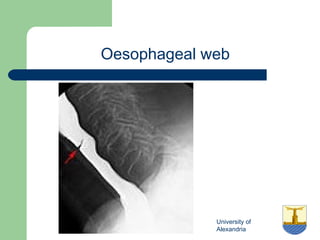
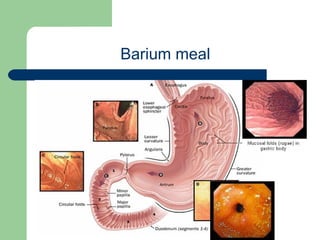
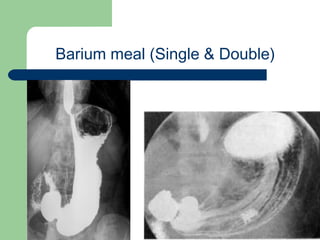
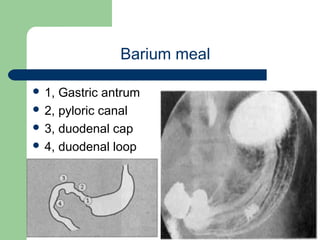
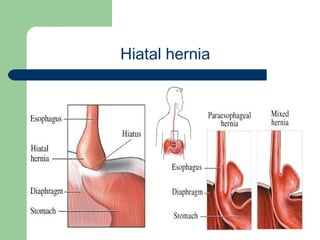
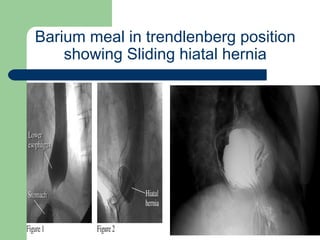
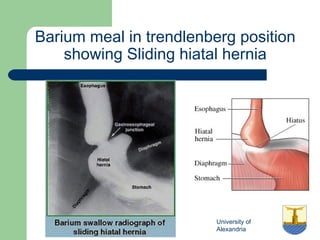
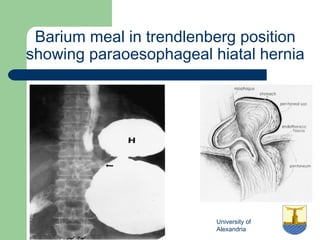
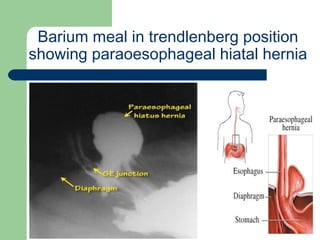
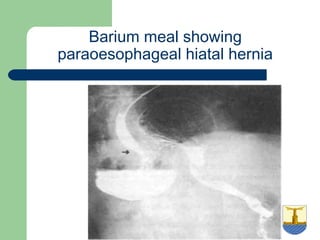
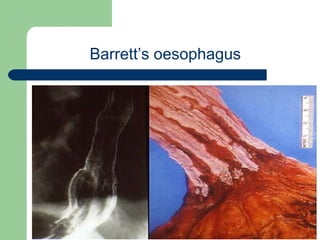
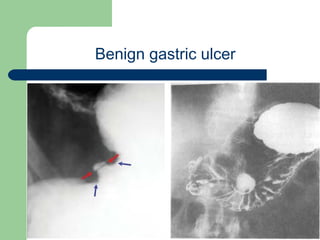
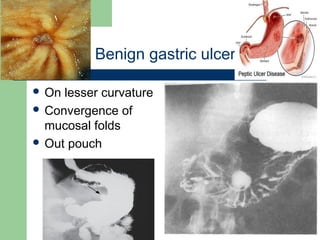
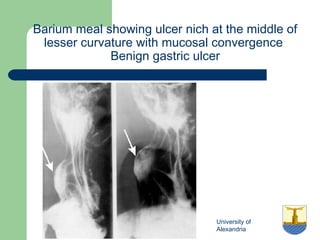
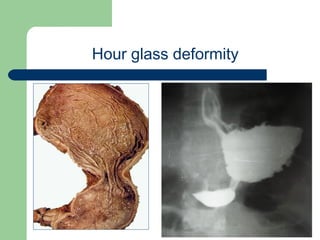
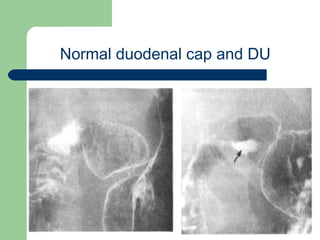
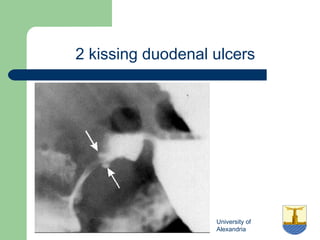
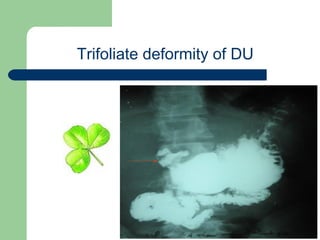
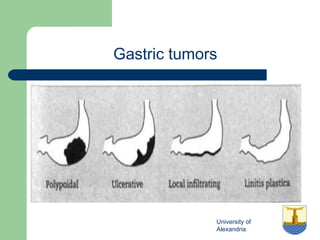
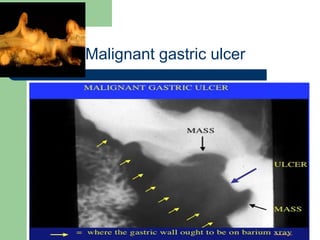
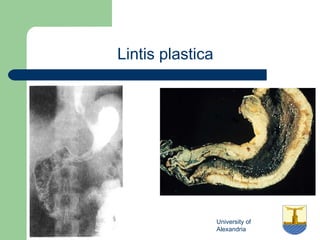
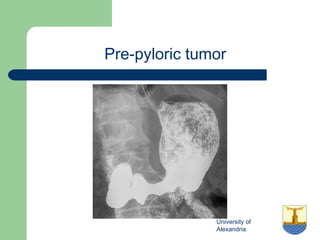
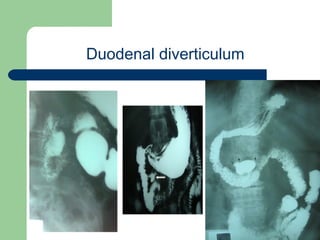
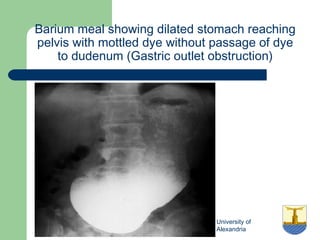
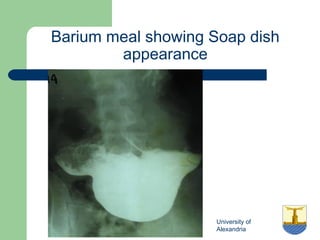
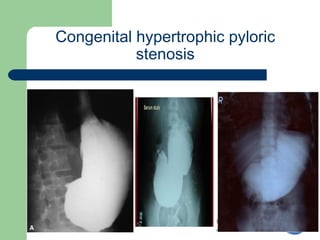
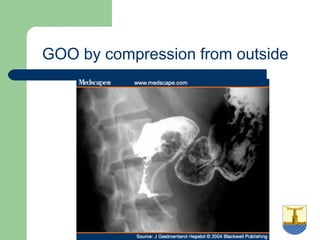
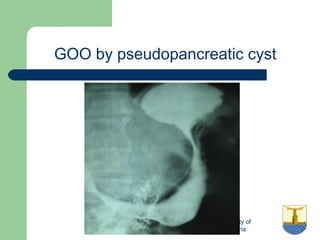
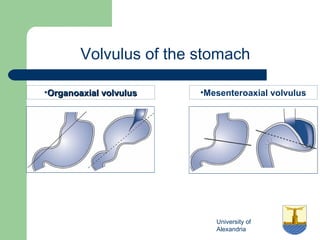
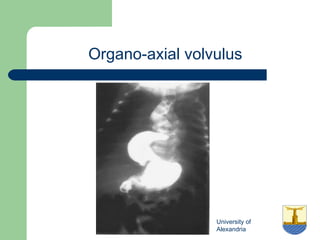
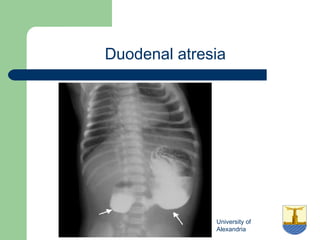
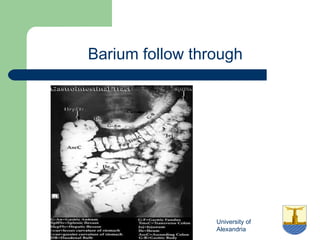
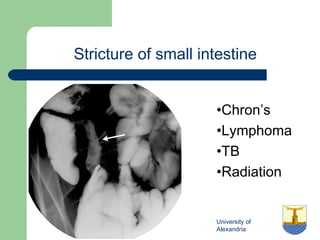
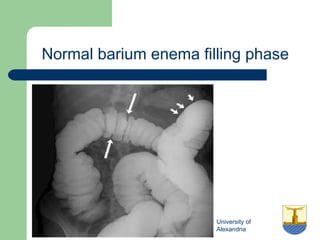
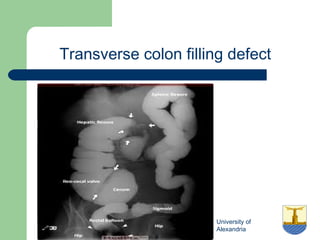
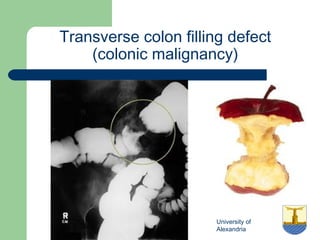
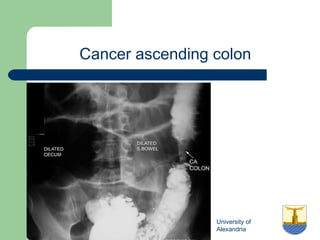
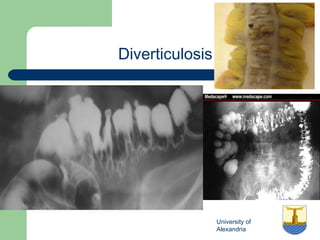
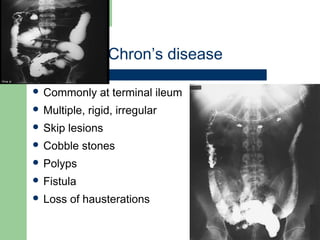
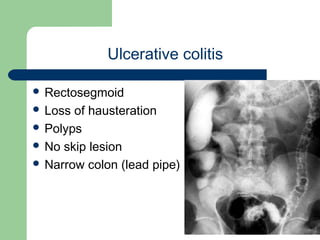
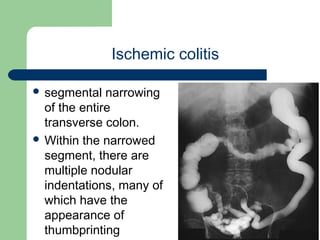
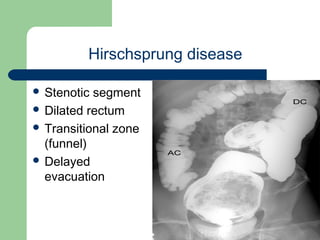
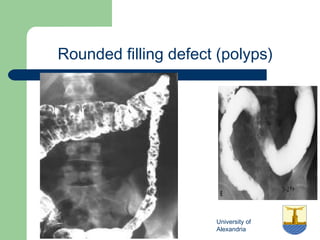
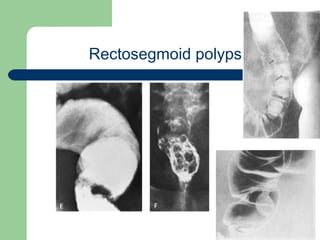
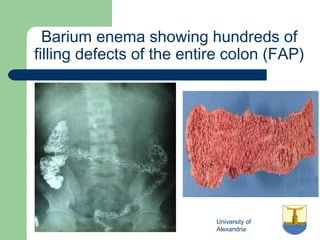
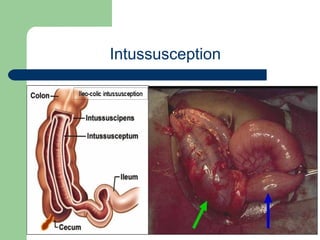
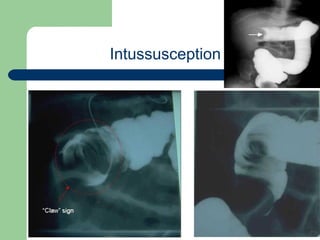
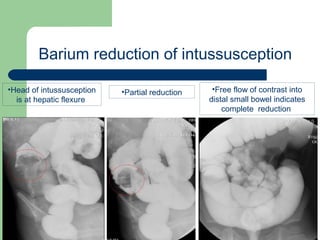
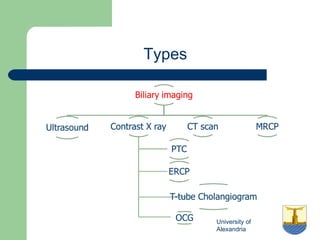
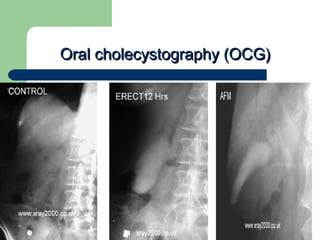
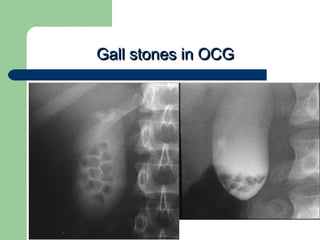
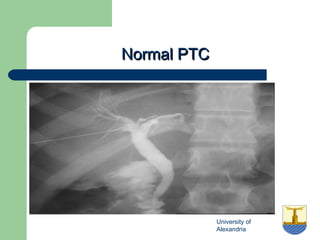
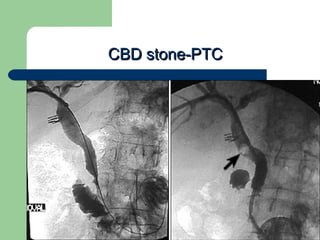
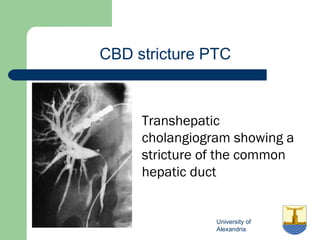
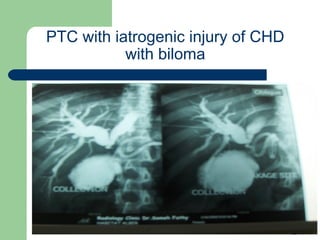
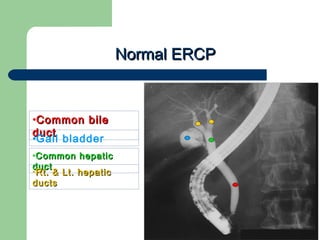
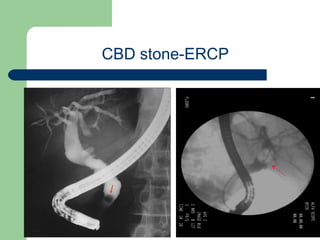
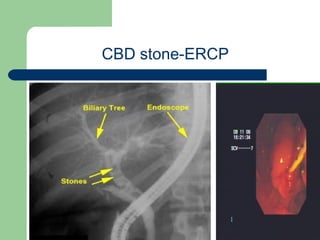
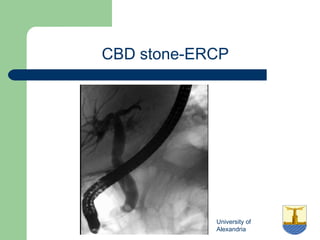
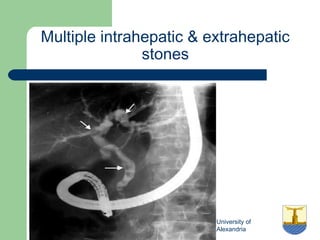
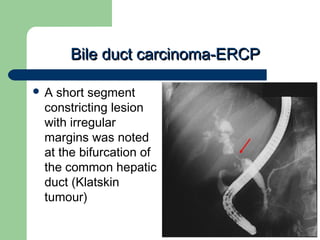
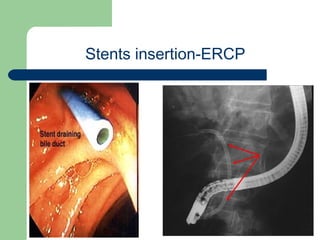
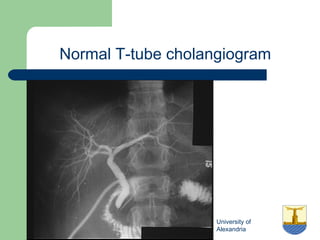
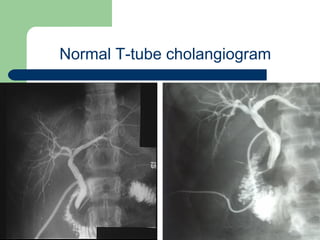
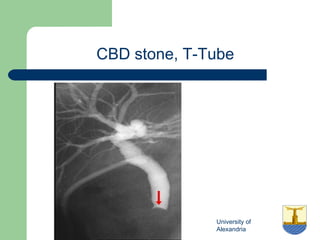
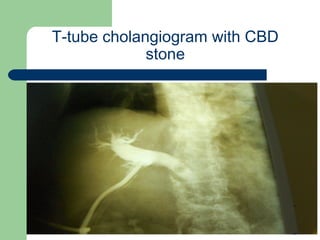
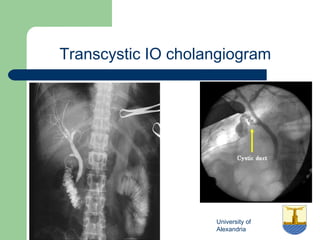
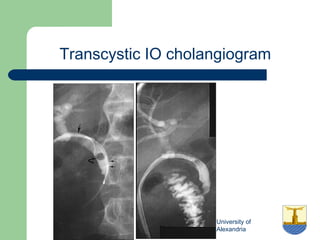
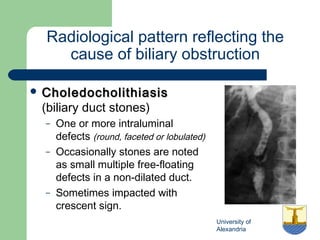
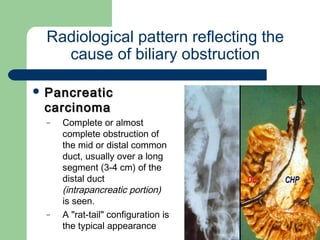
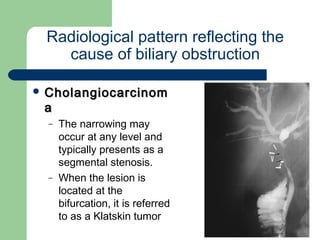
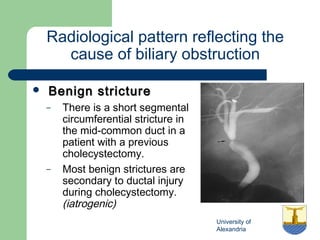
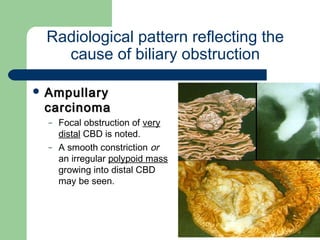
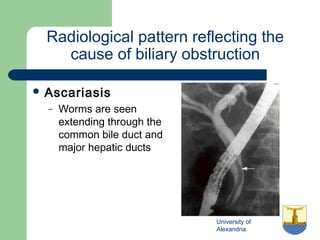
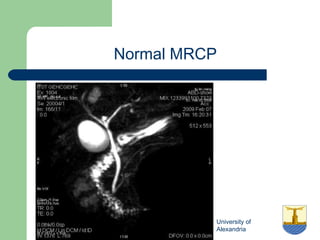
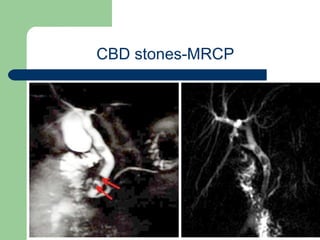
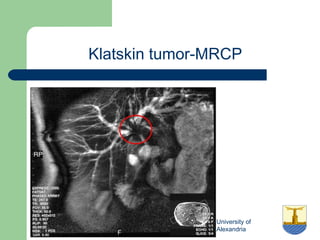
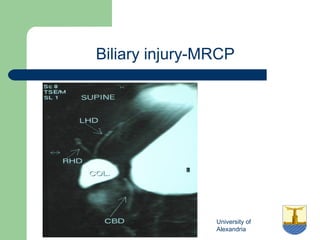
This document provides an overview of various imaging modalities used in gastrointestinal surgery at the University of Alexandria, including plain x-rays of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. It discusses normal anatomy and findings, as well as pathologies seen on barium swallow, barium meal, barium follow through, barium enema, oral cholecystography, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), T-tube cholangiography, and intraoperative cholangiography. Examples of findings for conditions like hiatal hernia, gastric and duodenal ulcers, gallstones, biliary strictures, and cholangiocarcin