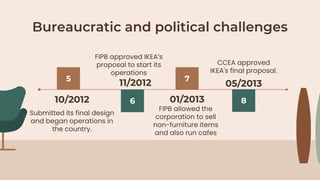
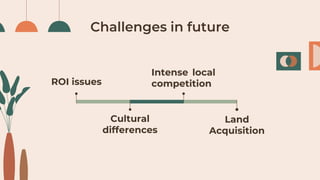
IKEA's business model focuses on eliminating the hassle of furniture shopping through low prices, convenient assembly, and a pleasant shopping experience. To enter the Indian market successfully, IKEA conducted market research, adapted its products and prices to Indian customers, and overcame bureaucratic challenges such as regulations favoring small local businesses. After opening its first store in 2018, IKEA has found success by addressing cultural preferences for heavier furniture, offering assembly services, and launching an online store in India.