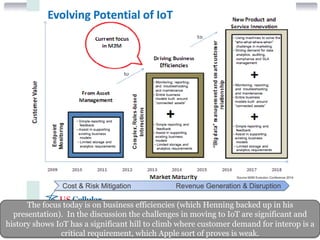
The IIT Real-Time Communication Conference highlighted advancements and challenges in telecommunications, particularly with WebRTC and IoT integration. Notable discussions included the importance of security and privacy for WebRTC applications alongside the impact of cloud technology on traditional PSTN services. The conference emphasized the need for interoperability and the evolving landscape of RTC in both mobile and cloud environments, suggesting a future where real-time communication is ubiquitous and embedded in various applications.
































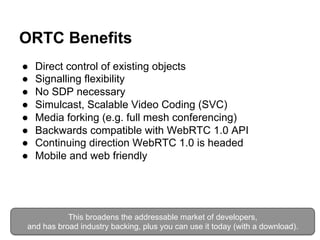
![WebRTC, Mobility, Cloud, and More...
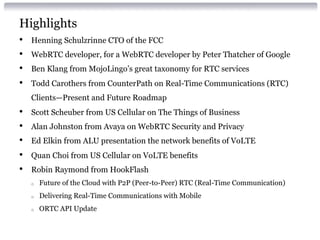
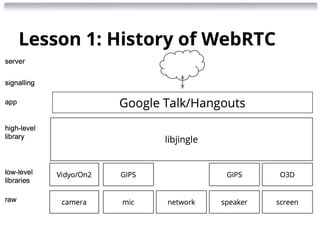
IIT REAL-TIME COMMUNICATIONS
Conference & Expo Sept 30 - Oct 2, 2014 Chicago
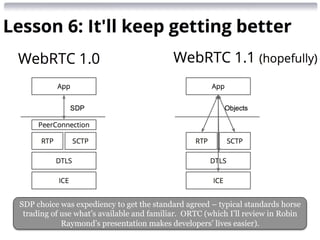
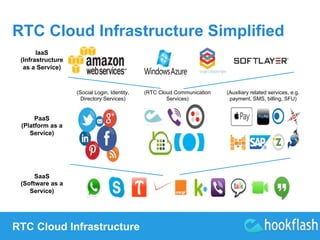
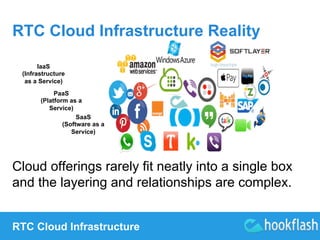
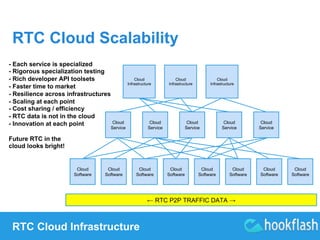
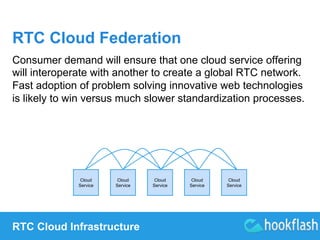
Future of the Cloud with P2P
(Peer-to-Peer) RTC (Real-Time
Communication)
Presented by Robin Raymond [http://about.me/robinraymond]
Chief Architect
Hookflash.com / OpenPeer.org
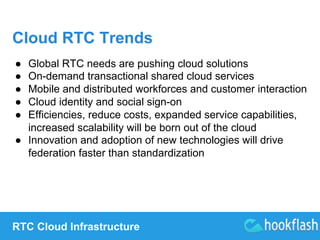
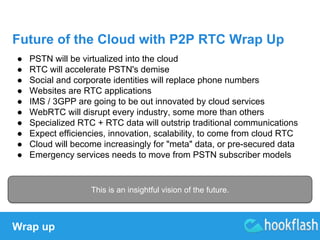
Robin gave several nice presentations, I review a couple here, first on Cloud and
2014-09-30 9:30am WEST: Alumni Lounge
RTC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iitrtcconf2014summary-141002143818-phpapp01/85/IIT-RTC-Conference-2014-summary-48-320.jpg)





















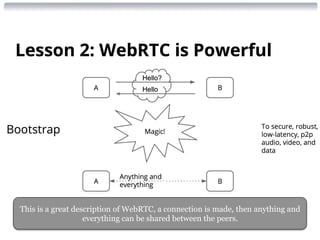
![WebRTC, Mobility, Cloud, and More...
IIT REAL-TIME COMMUNICATIONS
Conference & Expo Sept 30 - Oct 2, 2014 Chicago
Delivering Real-Time
Communications with Mobile
Presented by Robin Raymond [http://about.me/robinraymond]
Chief Architect
Hookflash.com / OpenPeer.org
2014-10-01 9:00am WEST: Alumni Lounge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iitrtcconf2014summary-141002143818-phpapp01/85/IIT-RTC-Conference-2014-summary-76-320.jpg)