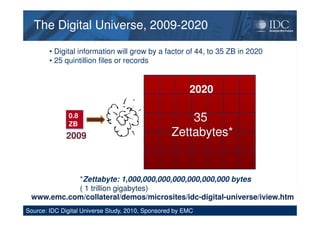
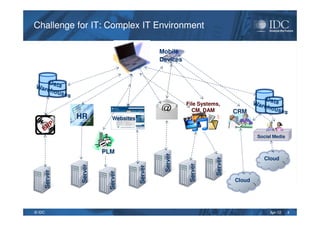
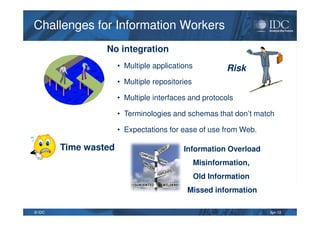
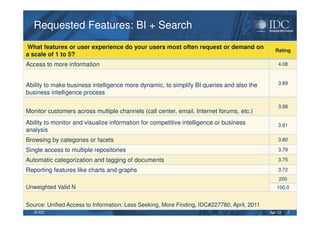
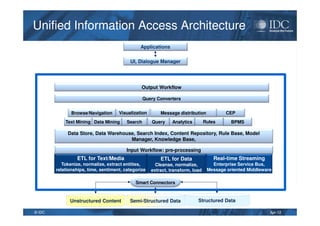
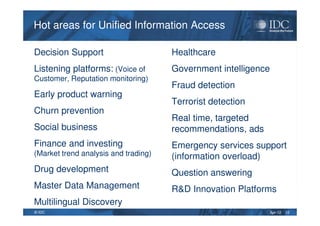
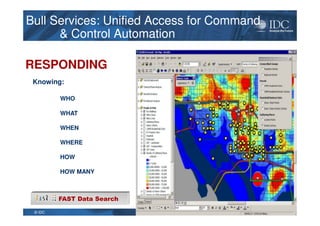
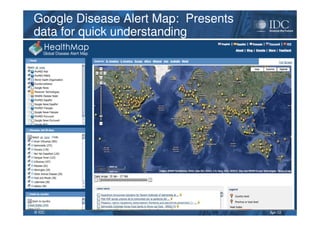
This document discusses unified information access, which provides a single point of access that integrates information from multiple heterogeneous sources. It defines unified information access and platforms that can integrate unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data through search, analytics, and visualization tools. Examples are given of how unified information access can be used in vertical industries like publishing, manufacturing, healthcare, and government for tasks like decision support, social media monitoring, and fraud detection.