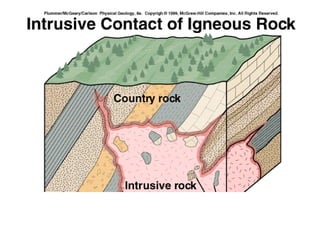
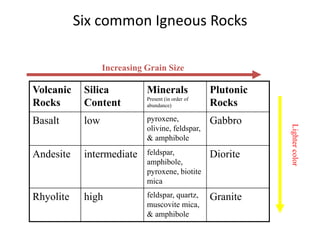
Igneous rocks form from the solidification of molten magma, classified into intrusive (solidifying underground) and extrusive (solidifying at the surface) types. Their textures vary based on cooling rates, influencing grain sizes where fine-grained rocks cool quickly and coarse-grained rocks cool slowly. The chemical composition (silica content) further categorizes these rocks into mafic, intermediate, felsic, and ultramafic groups, each with distinct mineral compositions and colors.

![Petroleum Geology 2
Molten rock or liquid usually
mostly silica. The liquid may
contain dissolved gases as well
and some solid material
It forms by partial melting in the crust
and uppermost mantle to a depth of ~250
km at high temperature and low pressure
MAGMA
[Greek=“paste”] i.e., molten rock](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-210218203955/85/Igneous-rocks-2-320.jpg)