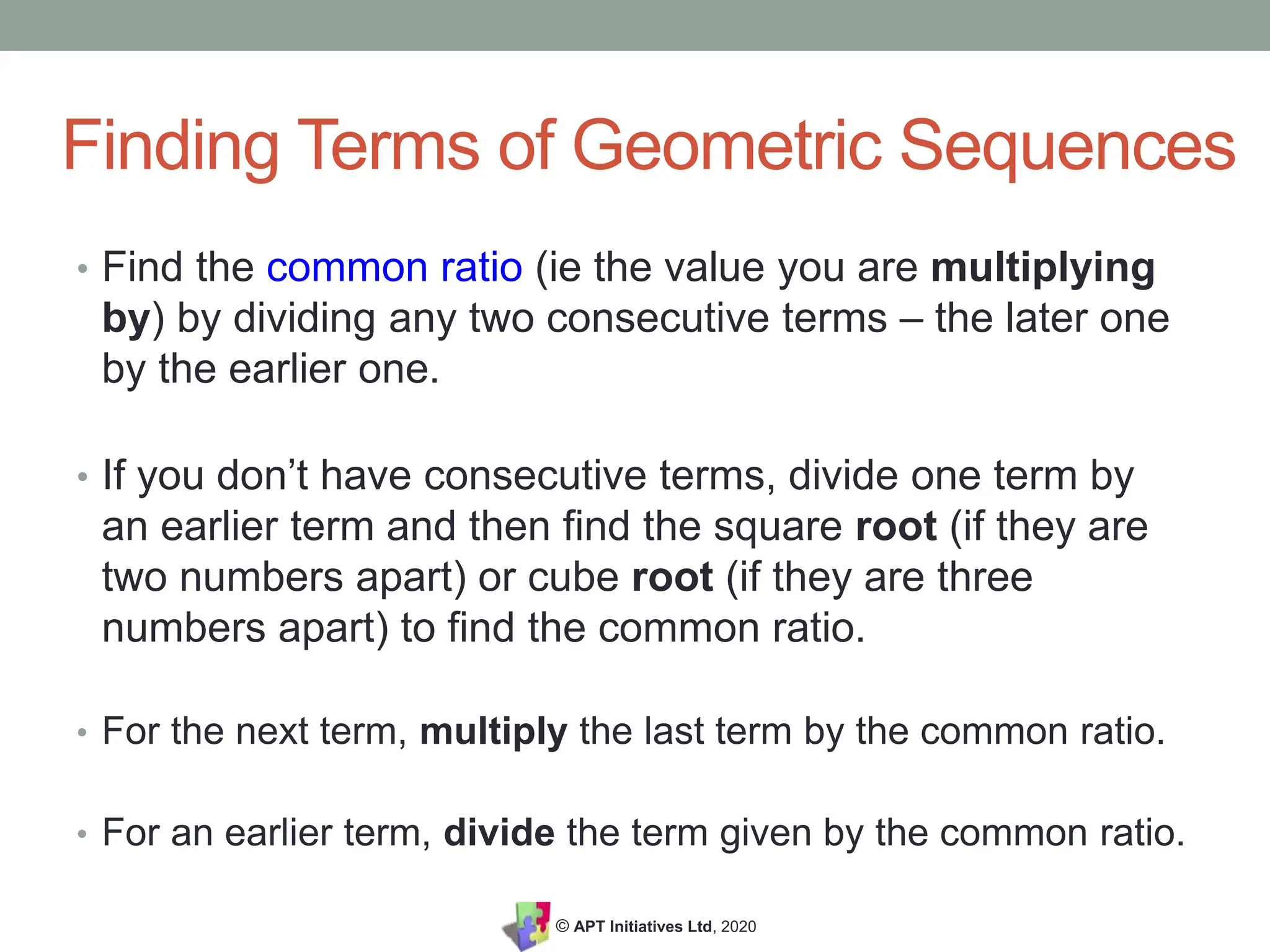
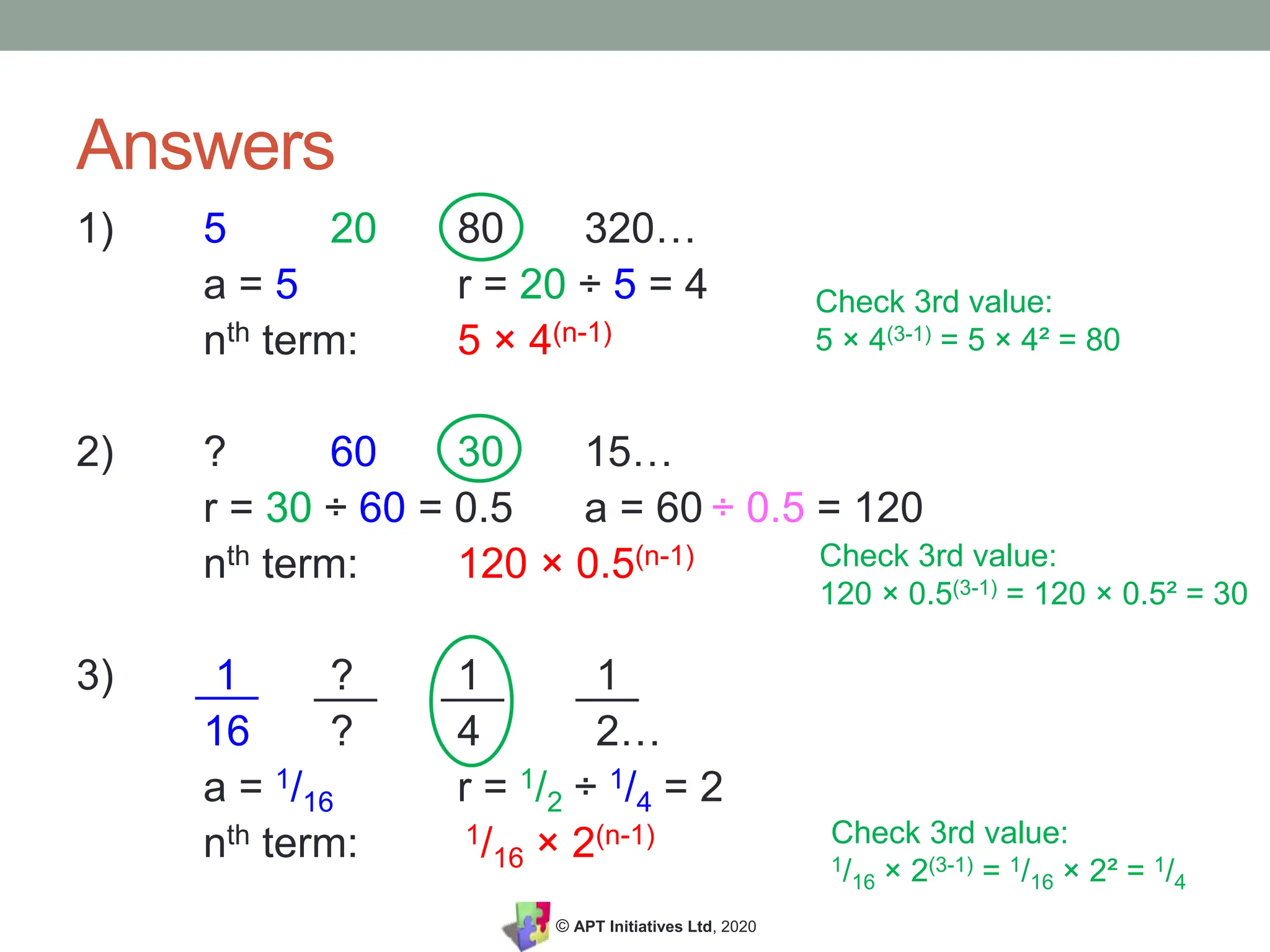
The document provides an educational overview of geometric sequences, detailing how to identify and calculate terms, including finding the common ratio and determining the nth term using a formula. It contrasts geometric sequences with other types like arithmetic, quadratic, and Fibonacci sequences while offering practice problems and solutions. The content is aimed at supporting students in GCSE and Key Stage 3 mathematics to better understand the concept of sequences.