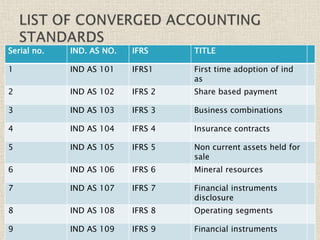
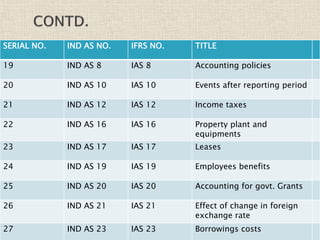
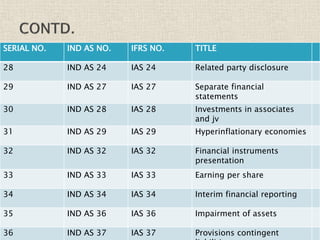
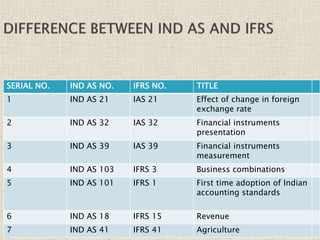
The document discusses the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and their adoption in India, highlighting the convergence of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) with IFRS as a strategic approach. It outlines the benefits of IFRS, including improved transparency and comparability in financial statements, and details the timeline for implementation by different companies based on their turnover. The document emphasizes the ongoing challenges in achieving full adoption and the collaborative efforts required among the government, ICAI, and SEBI to facilitate this transition.