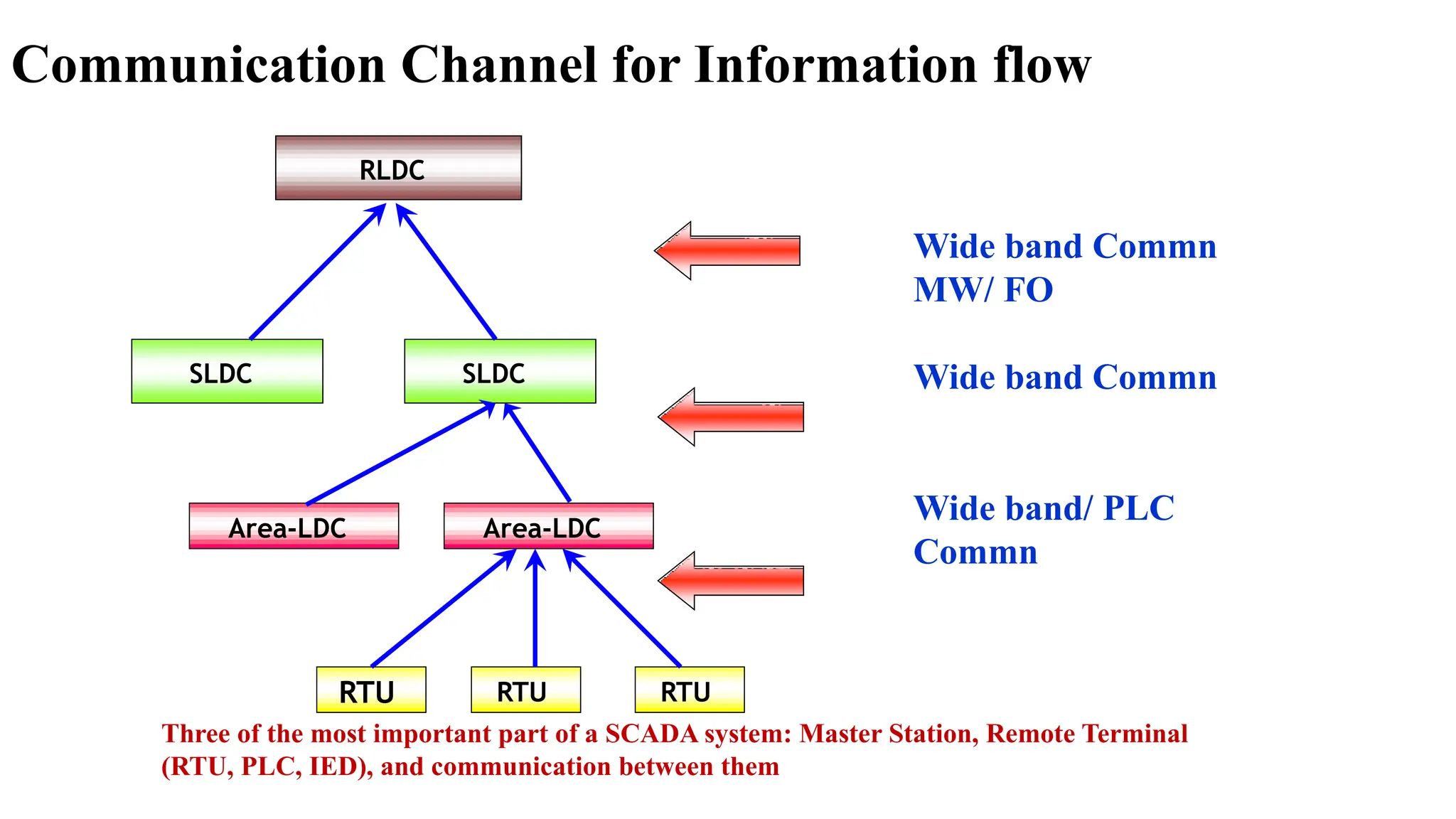
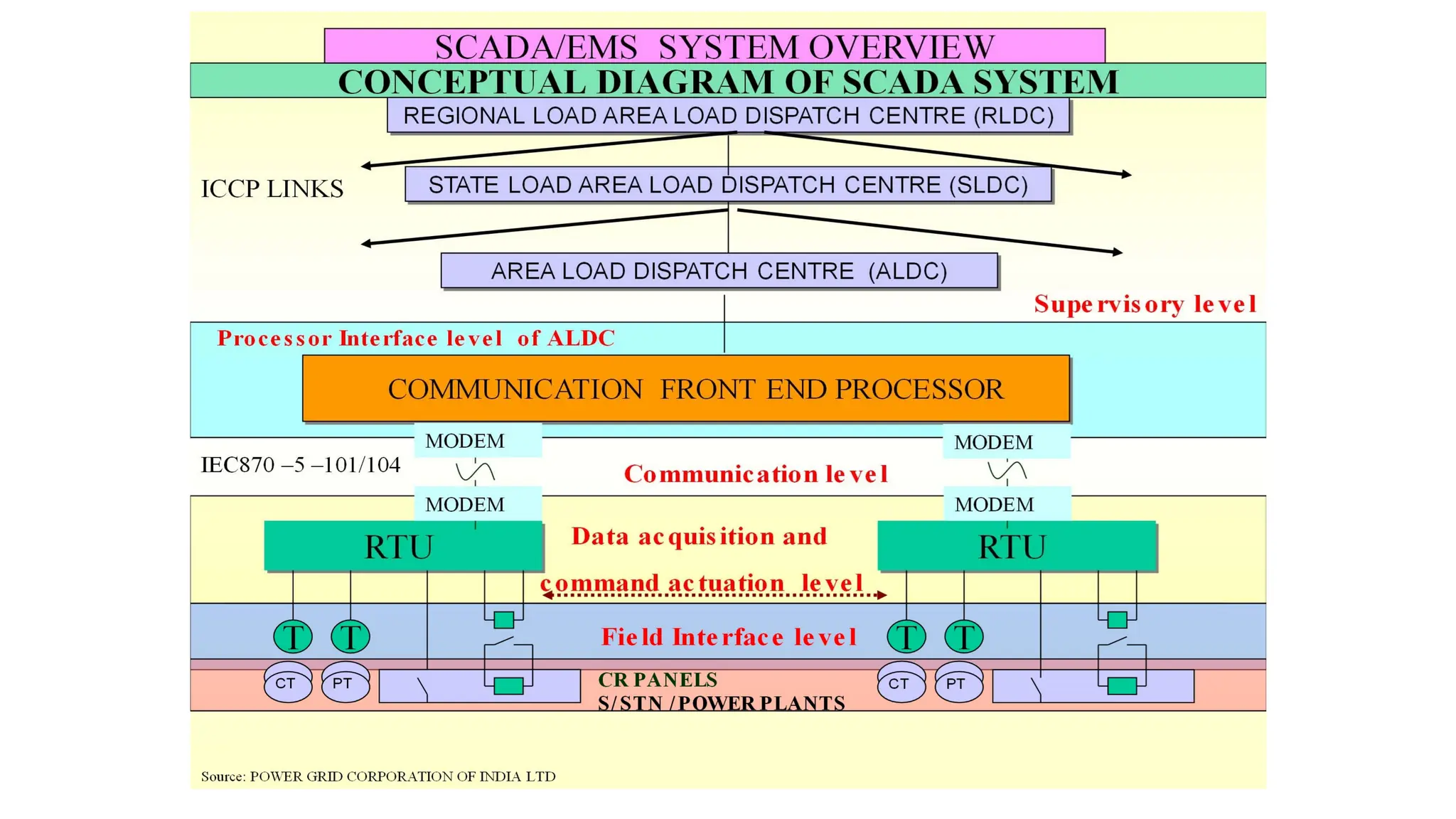
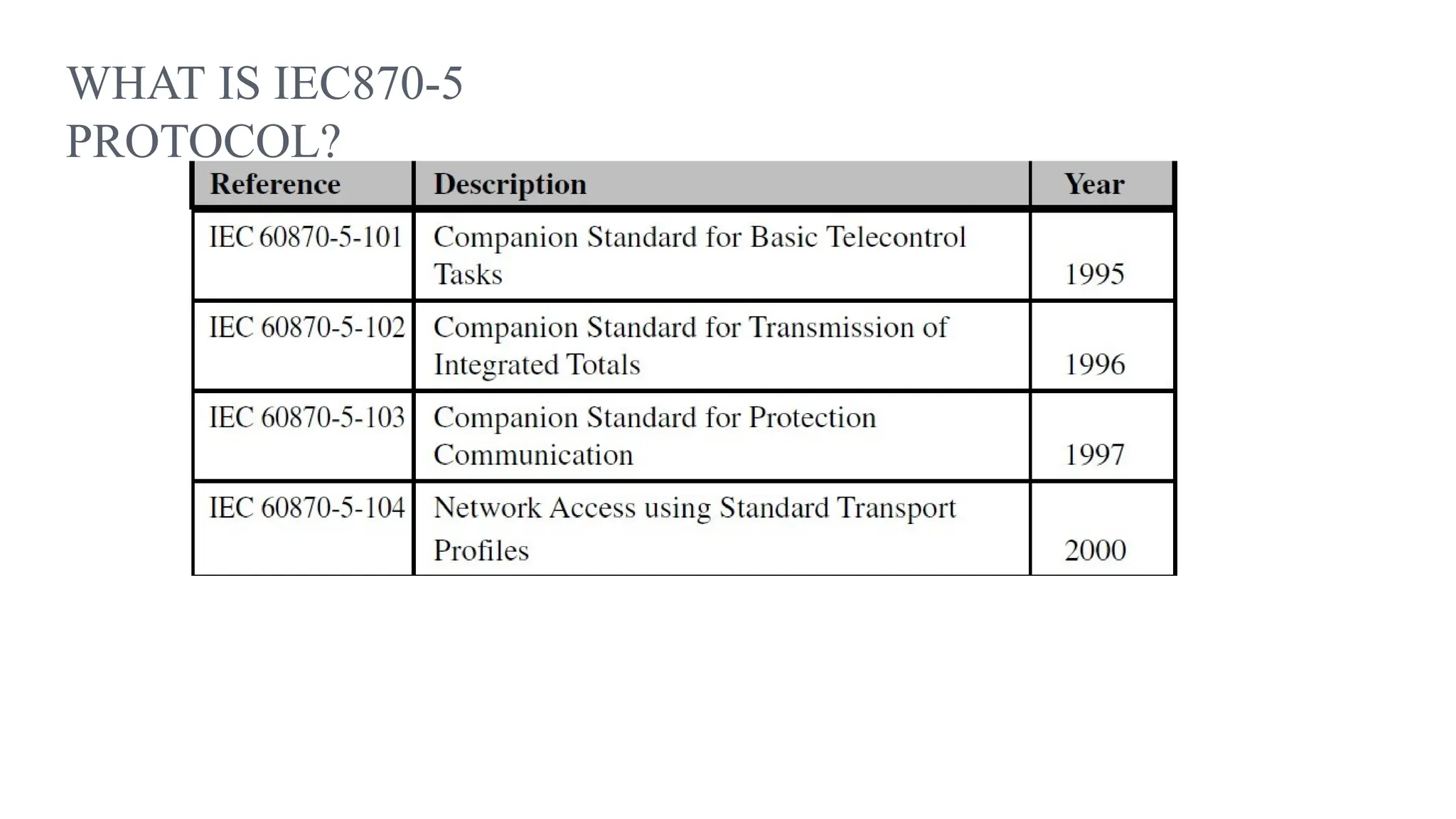
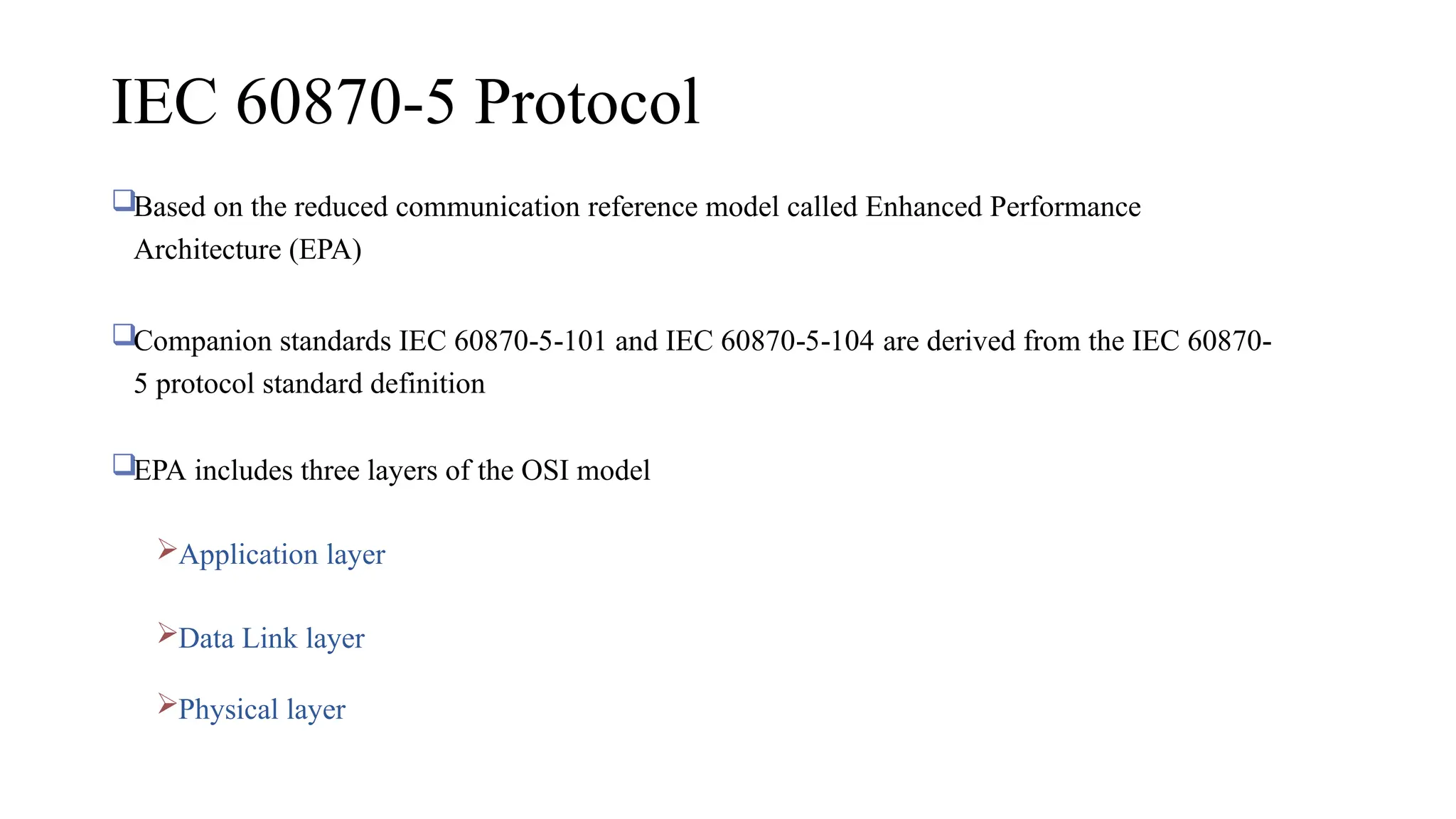
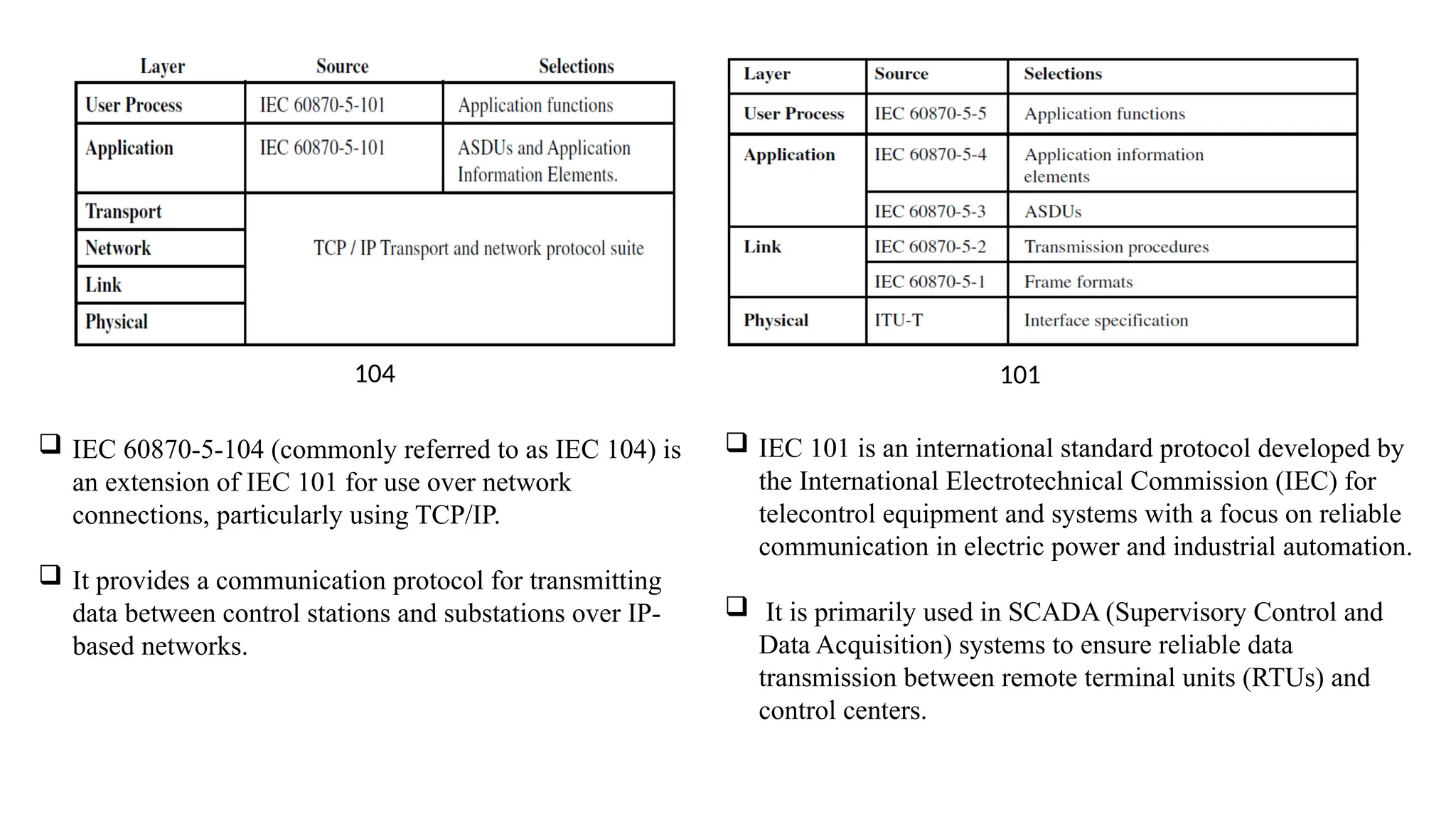
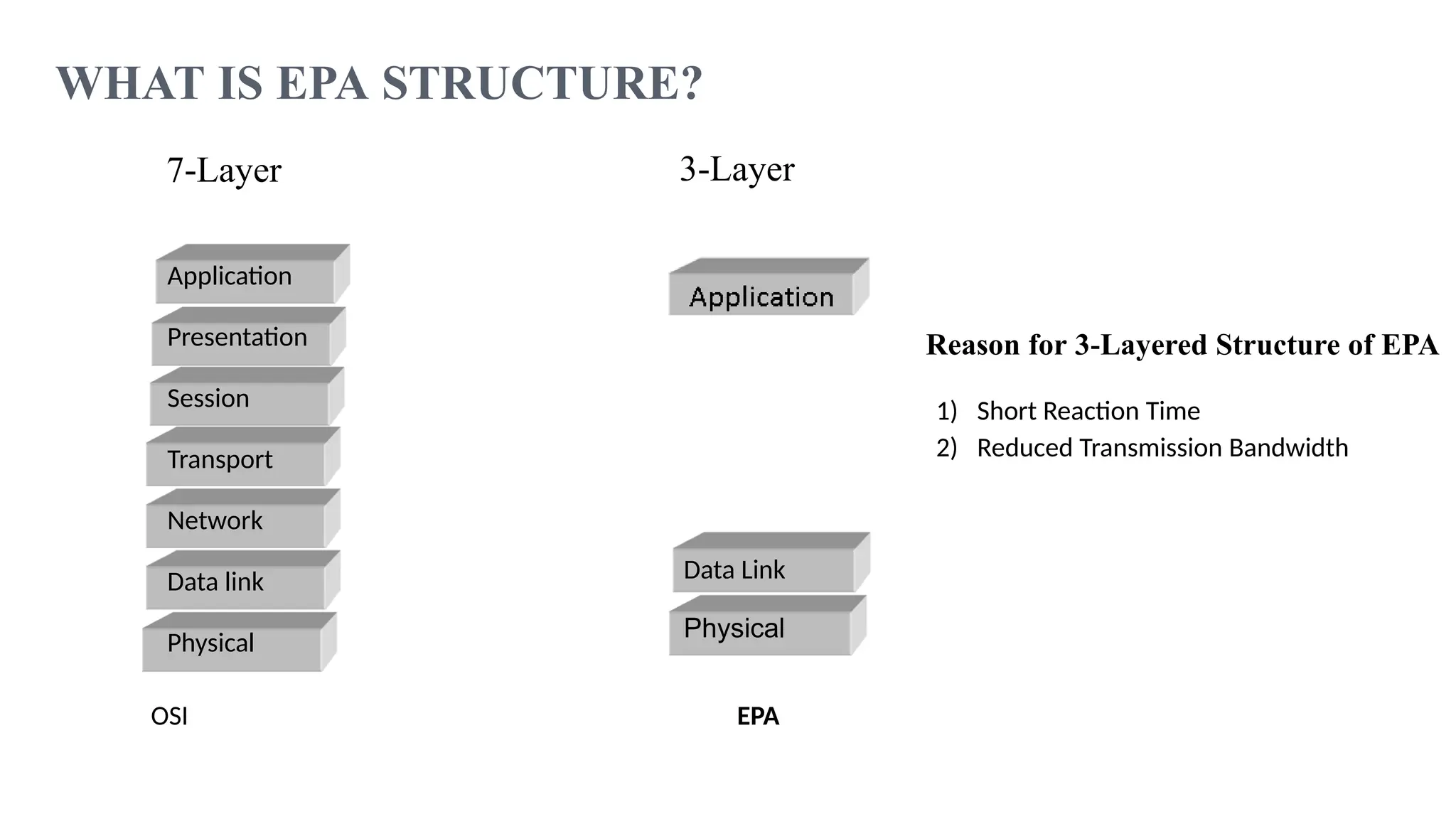
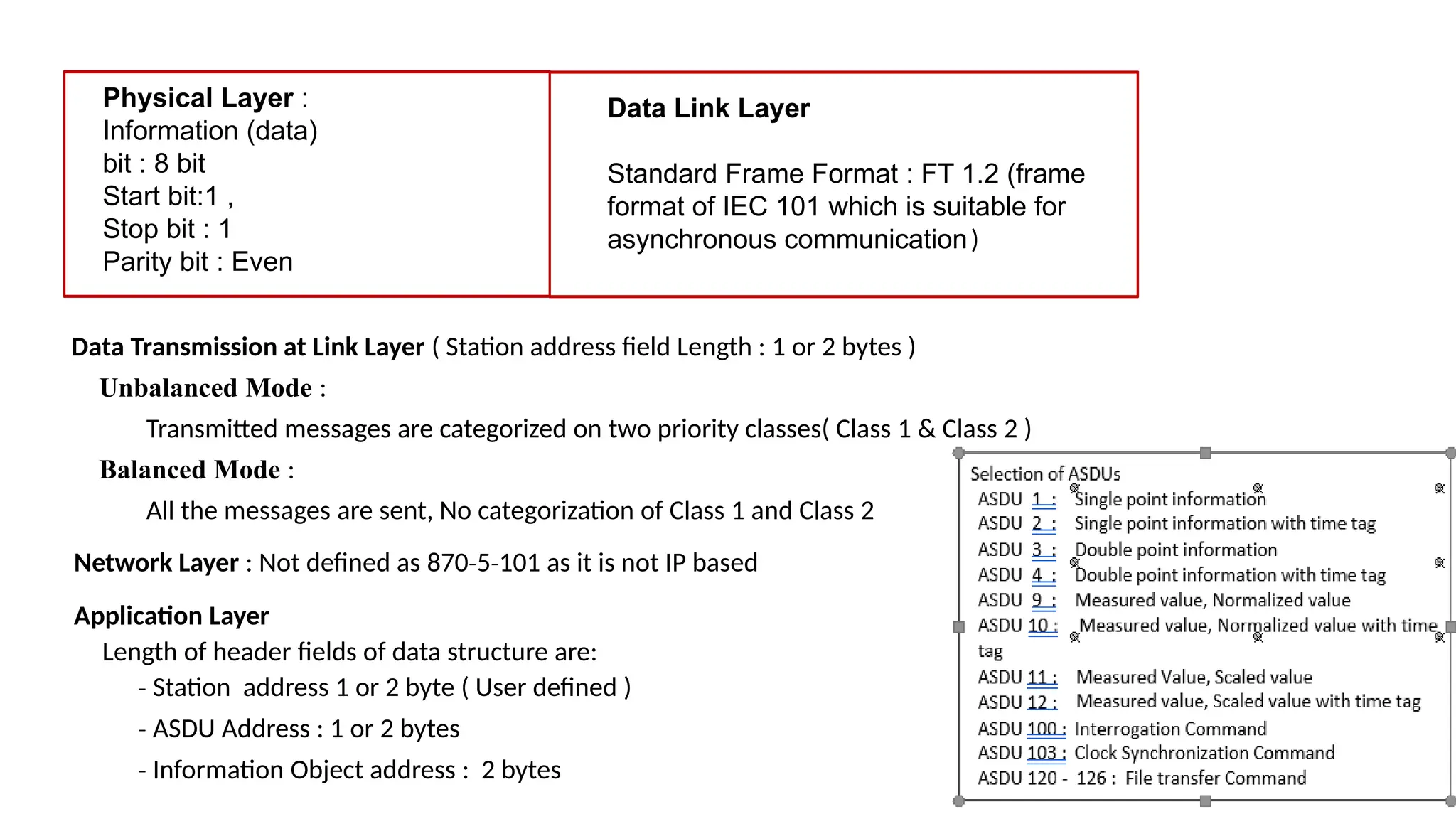
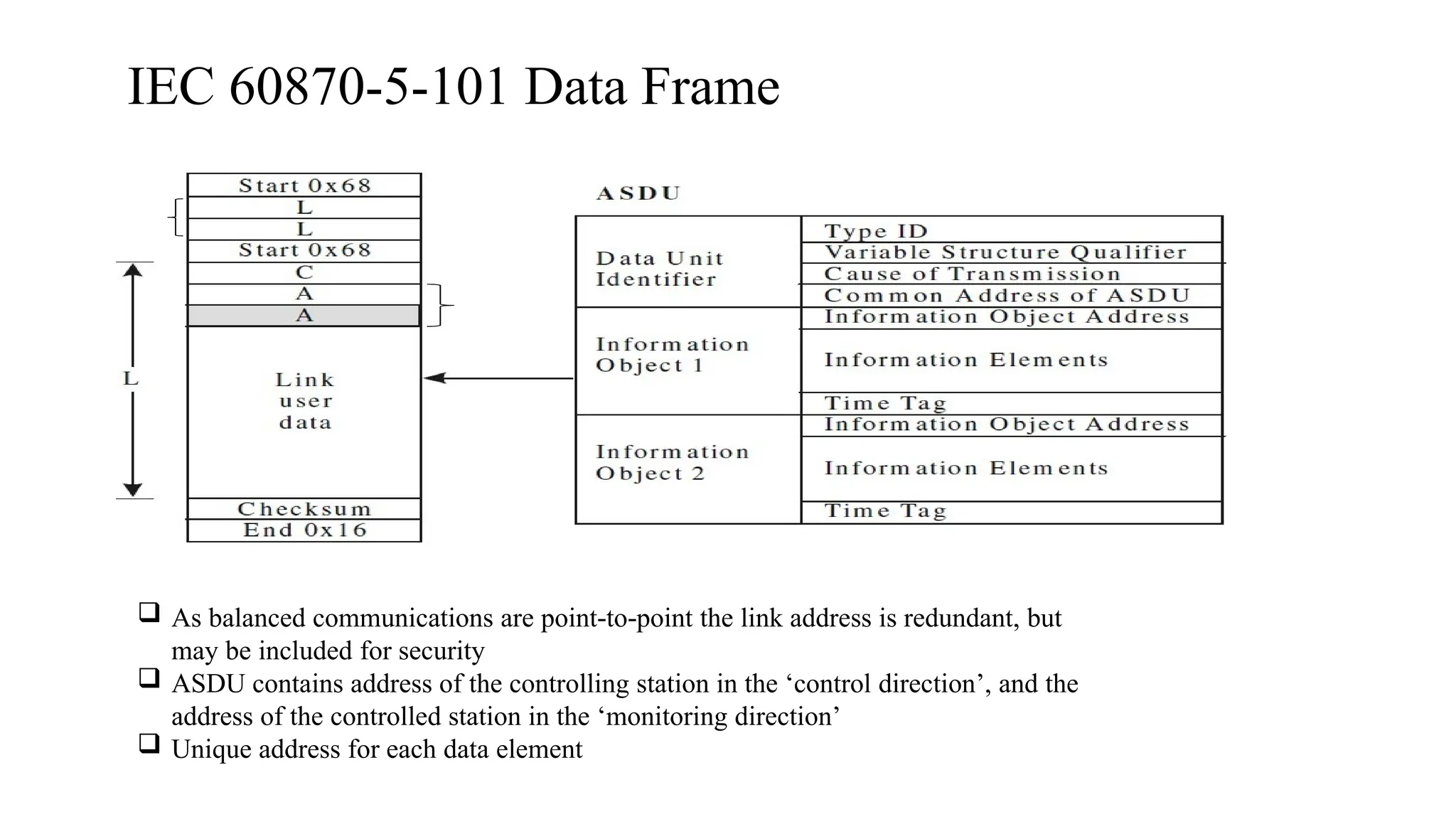
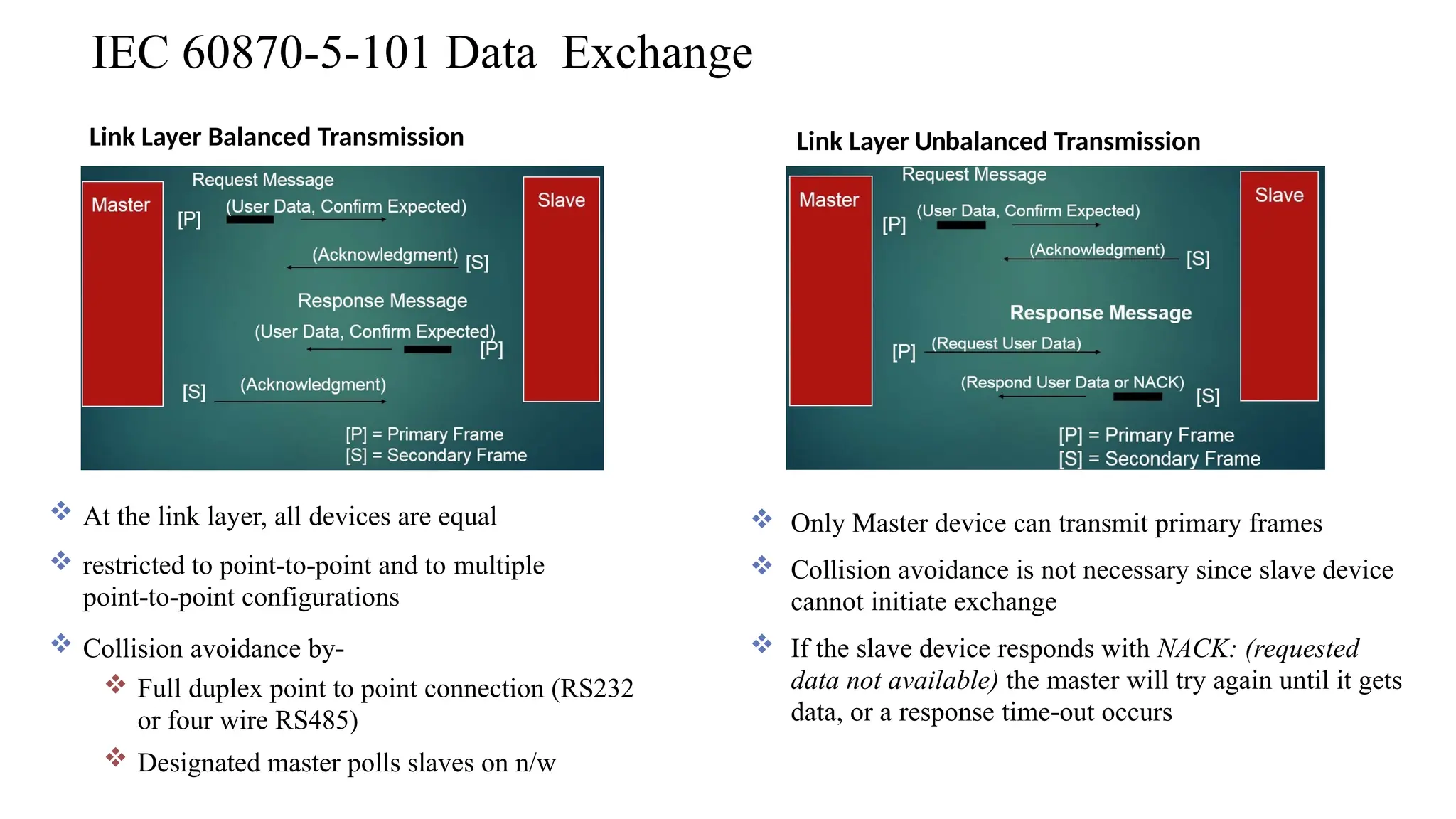
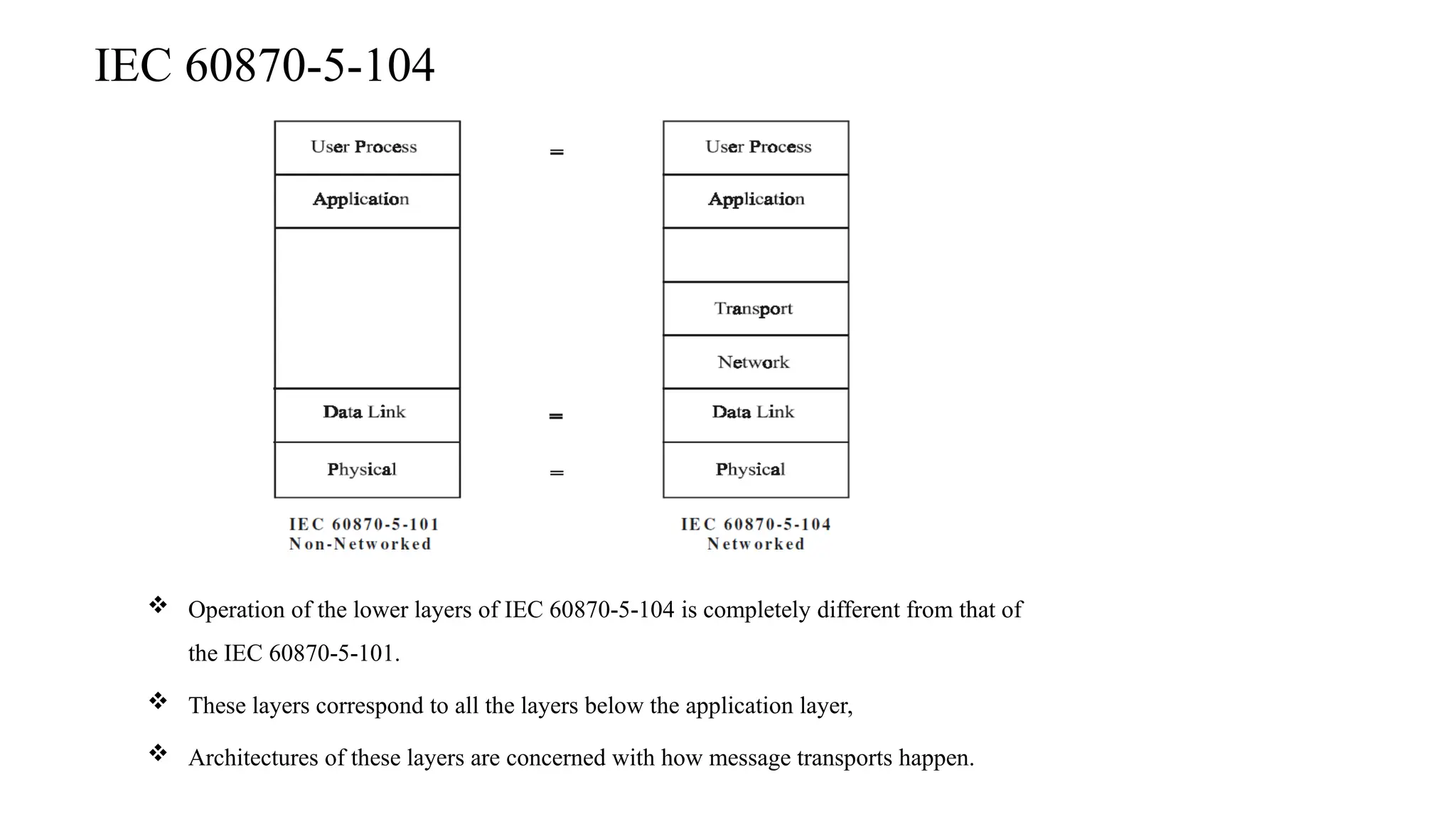
The document outlines various communication protocols, specifically focusing on IEC 60870 standards for telecontrol in electrical systems, including IEC 101 and IEC 104 for reliable data transmission. It explains the layers of the Enhanced Performance Architecture (EPA) model used in these protocols, detailing the application, data link, and physical layers, as well as transmission mechanisms. Key differences between IEC 101 and IEC 104 are highlighted, particularly their use cases in SCADA systems and network communications.