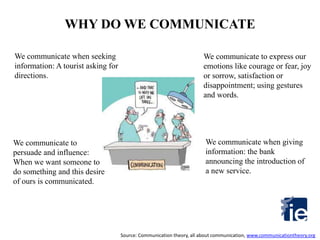
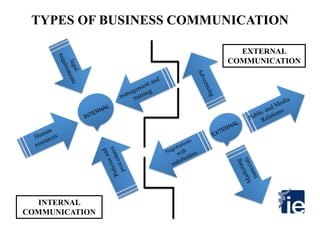
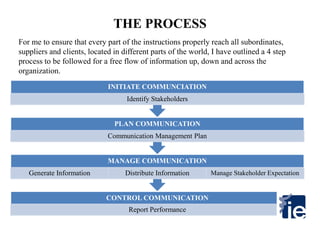
1) The document outlines a 4-step process to ensure proper communication of instructions from a meeting with the superior to all subordinates, suppliers, and clients worldwide.
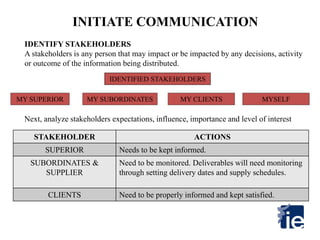
2) The first step is to identify stakeholders - the superior, subordinates, clients, suppliers, and myself. Their expectations, influence, importance, and interest are then analyzed.
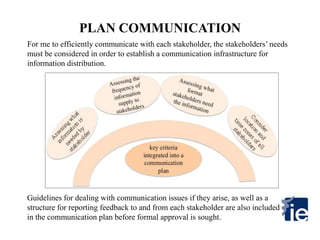
3) A communication plan is developed considering stakeholders' needs and including guidelines for issues and feedback reporting.
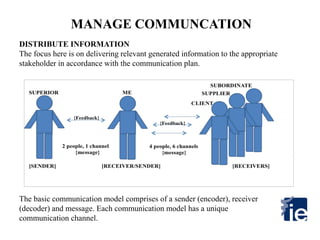
4) The plan is then implemented by generating, distributing, and confirming receipt of information through various channels to each stakeholder. Performance reports are presented to the superior.