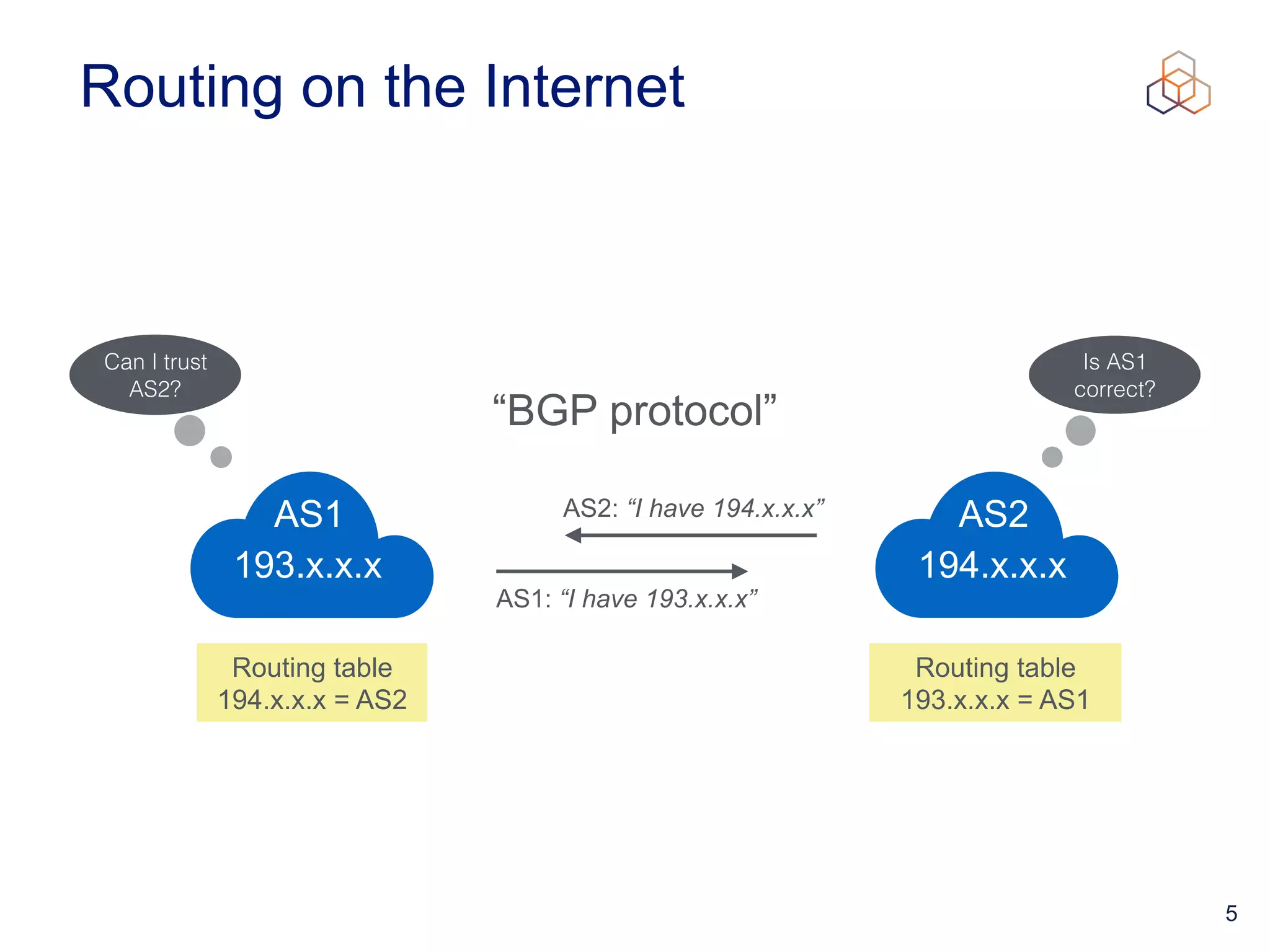
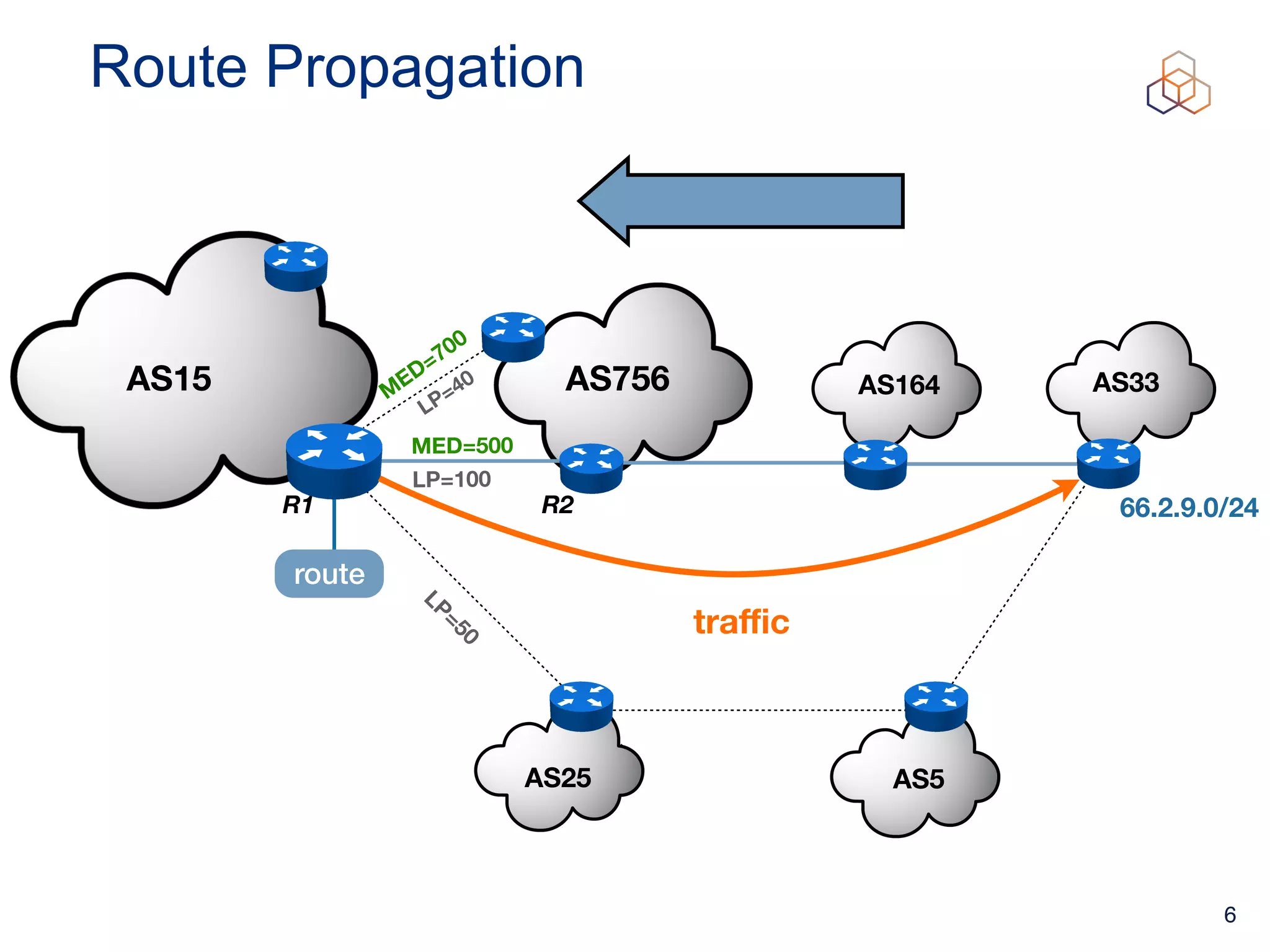
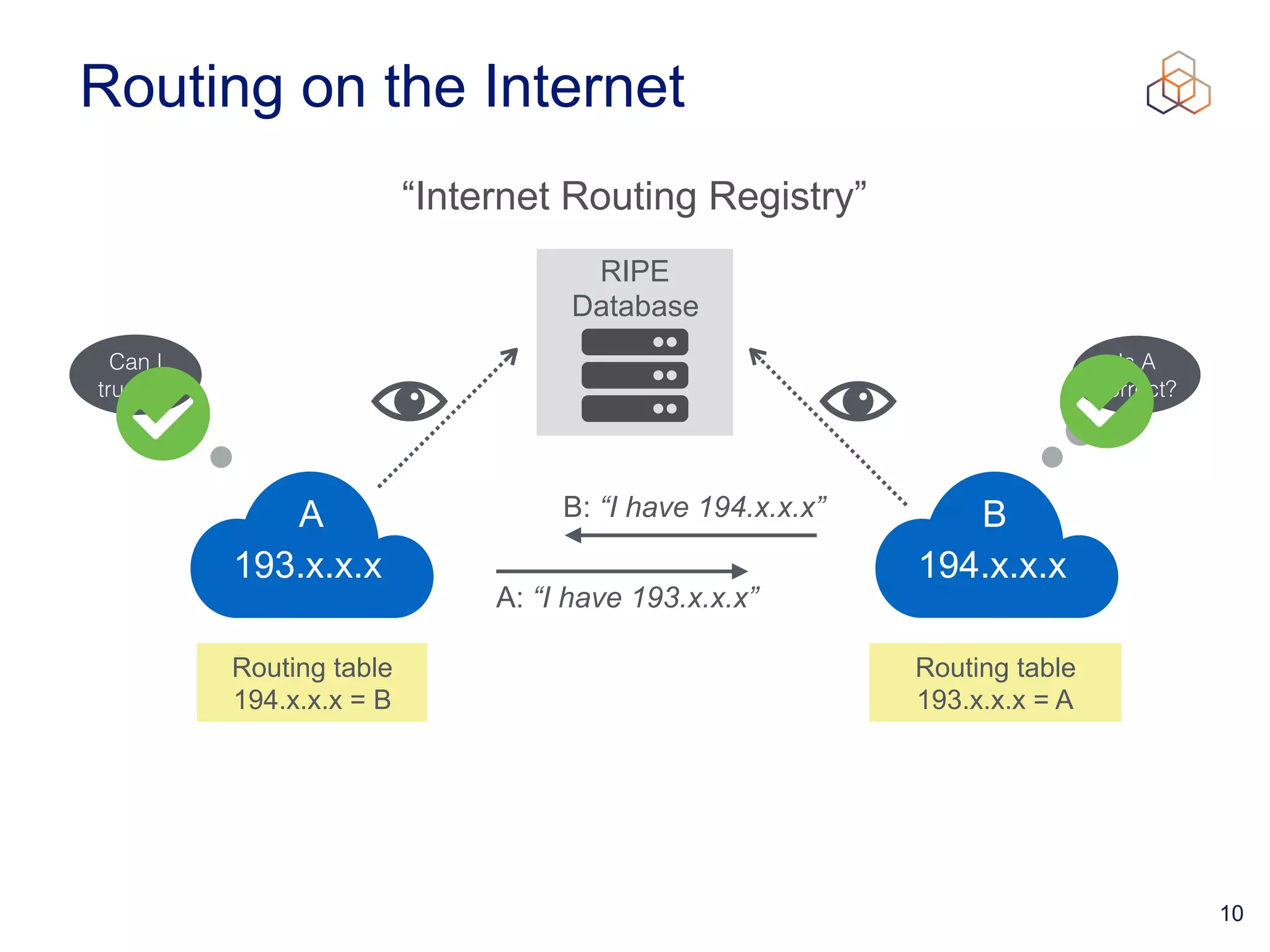
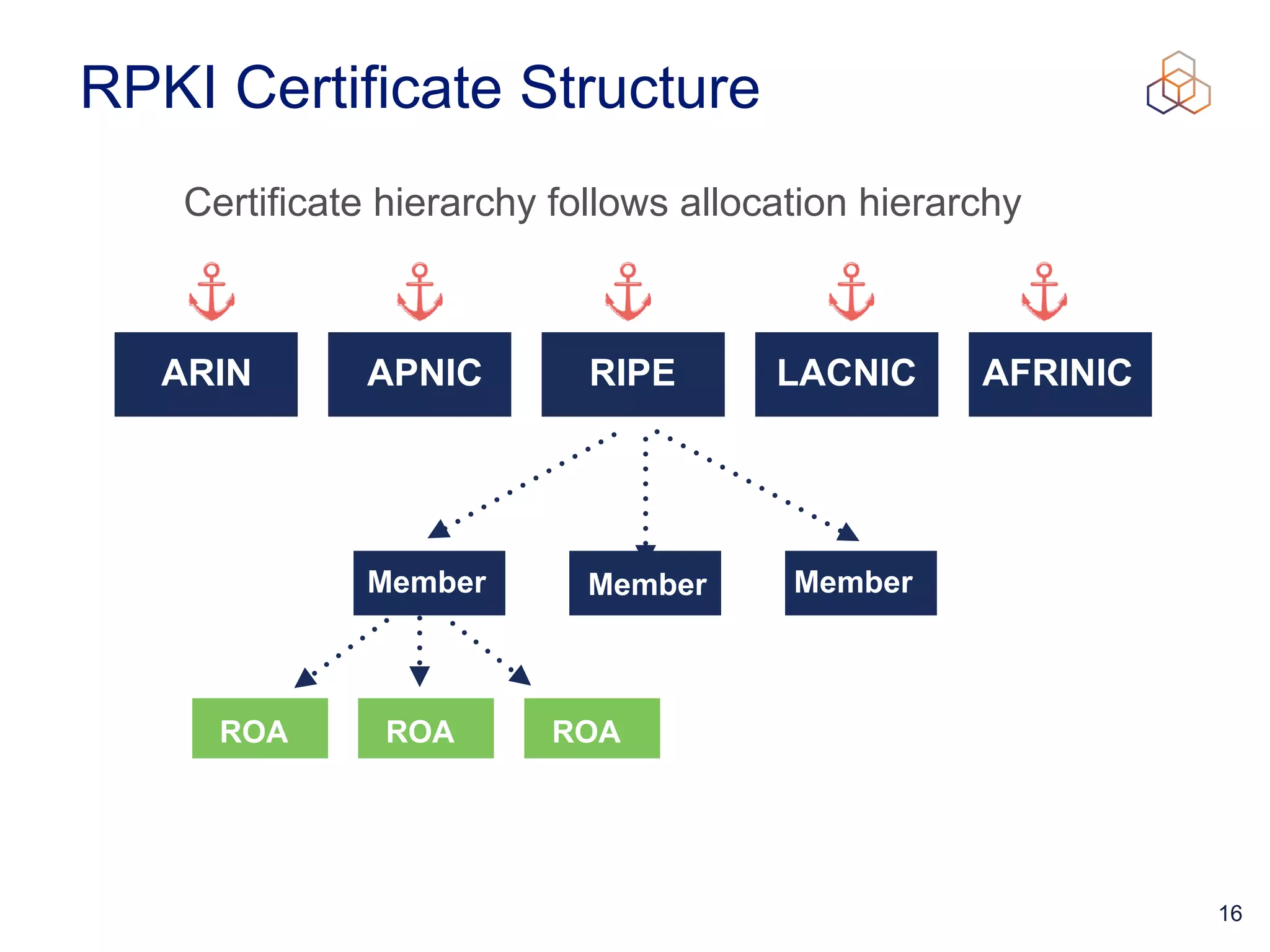
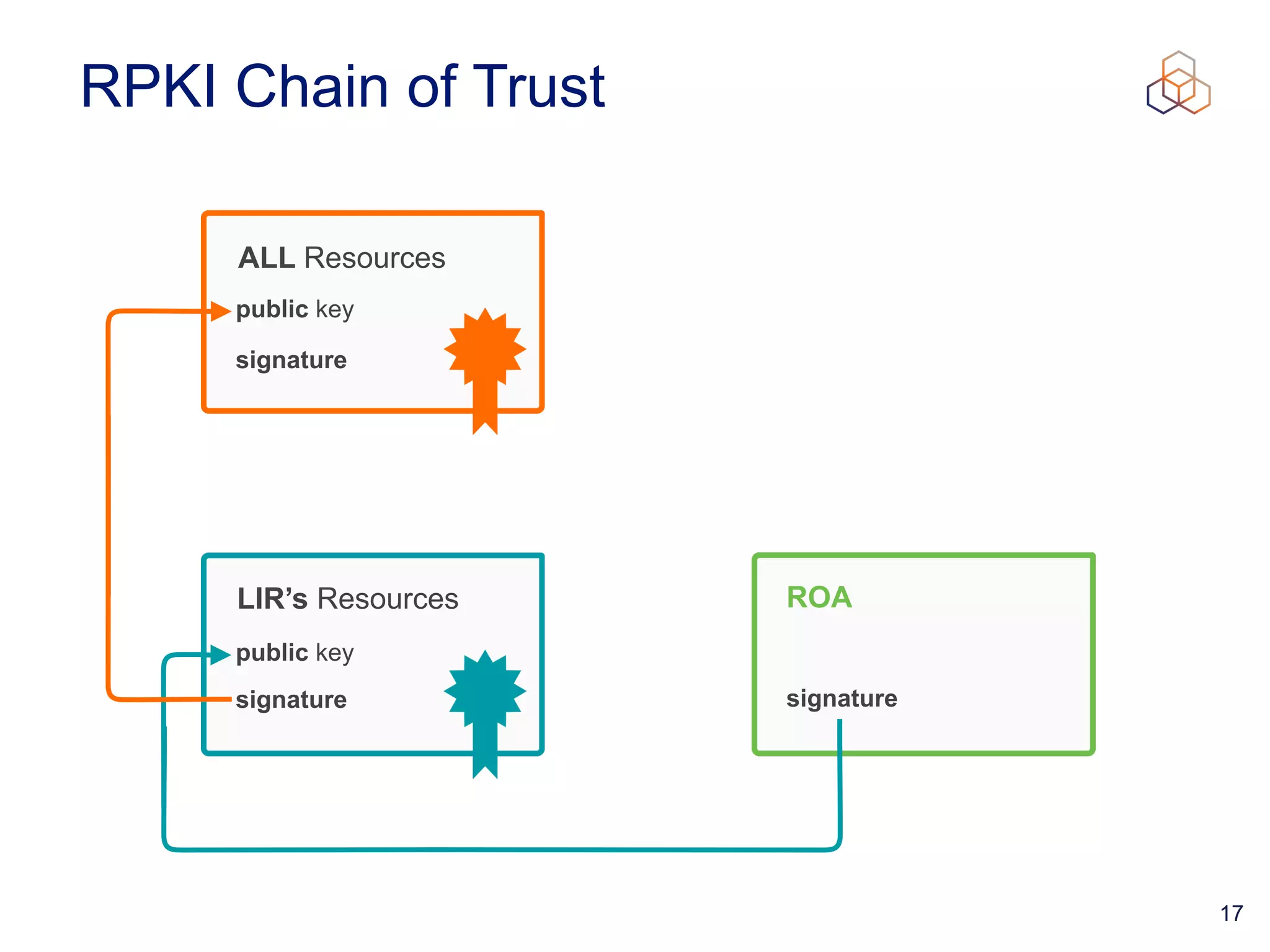
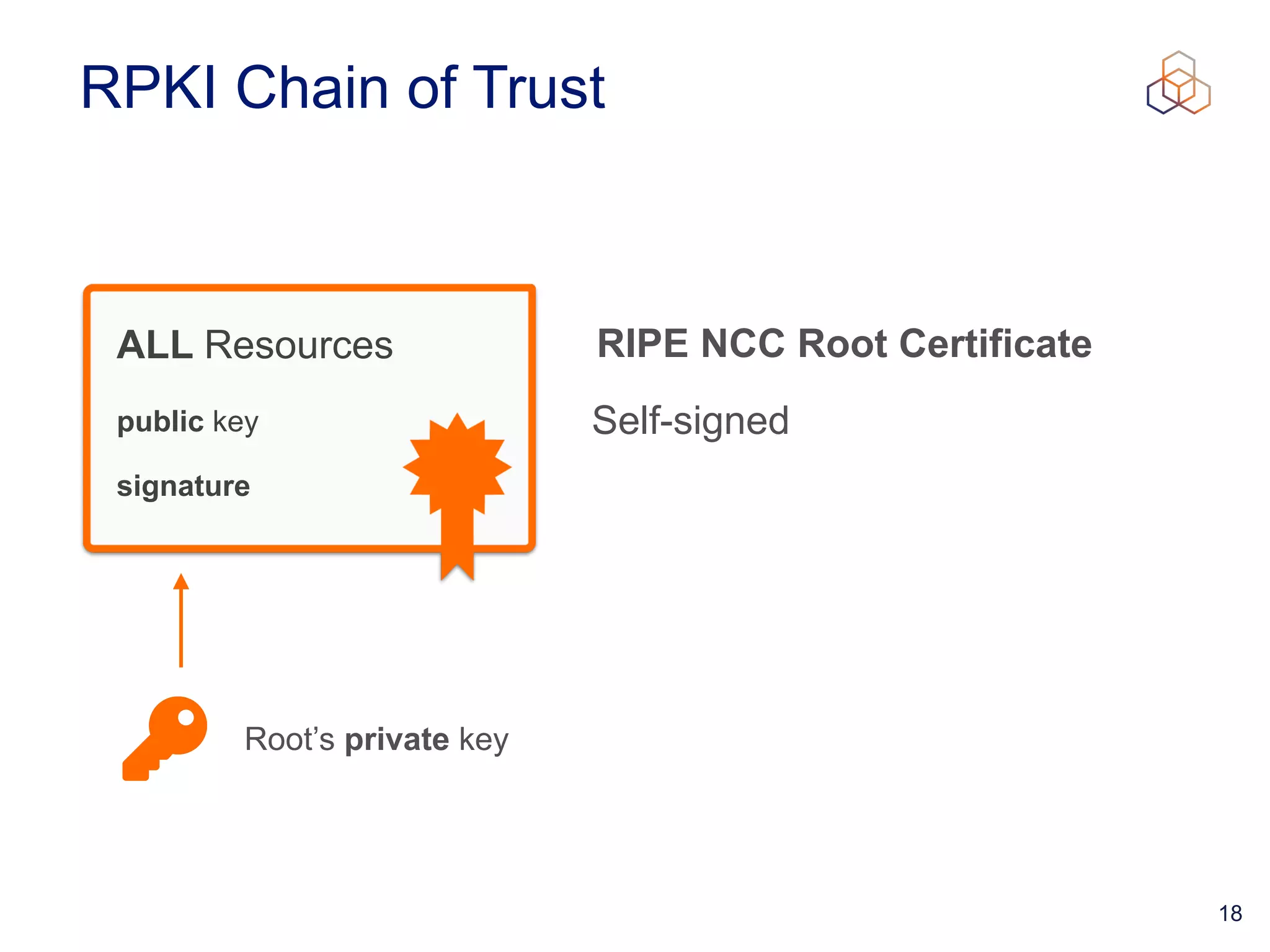
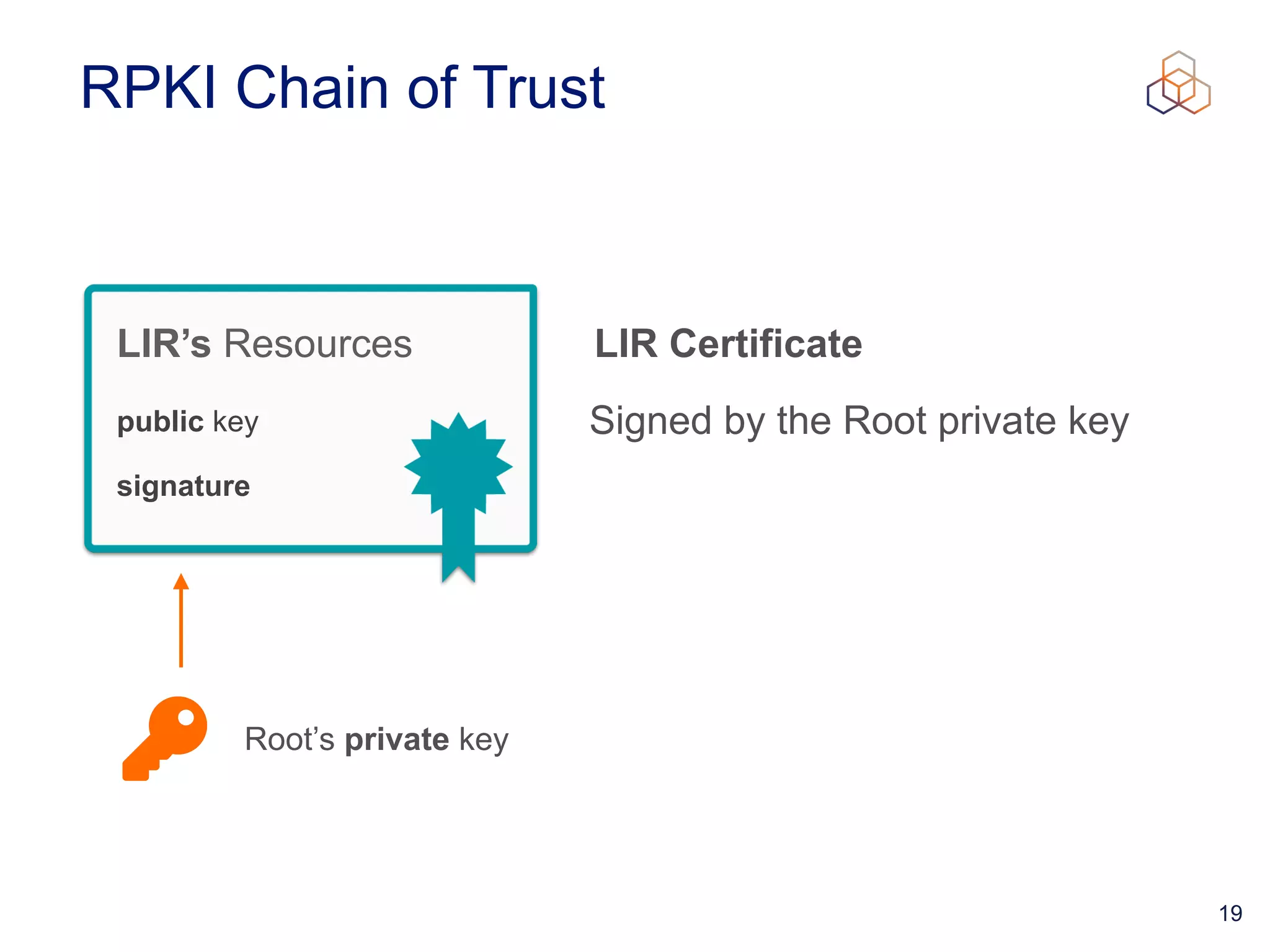
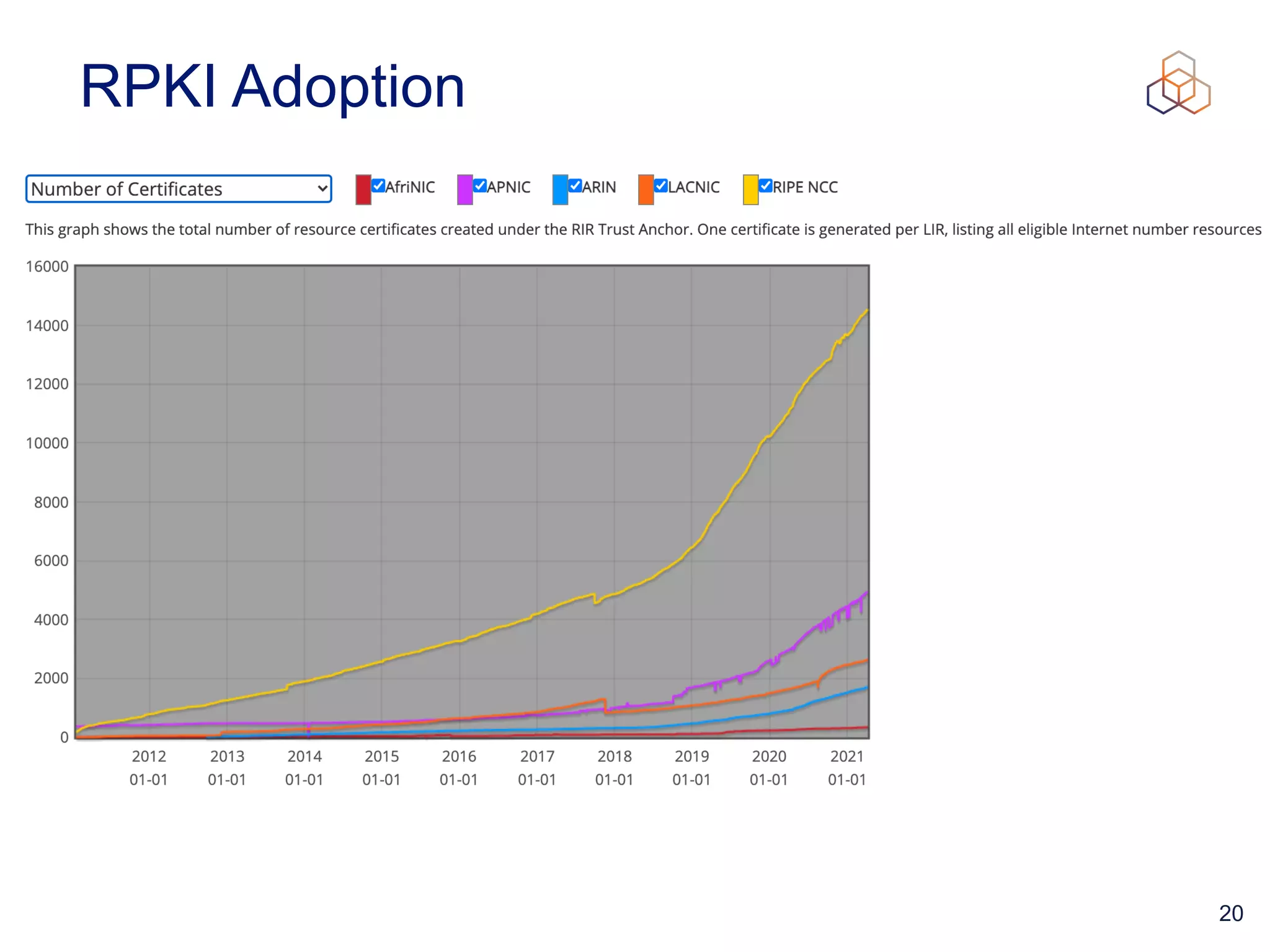
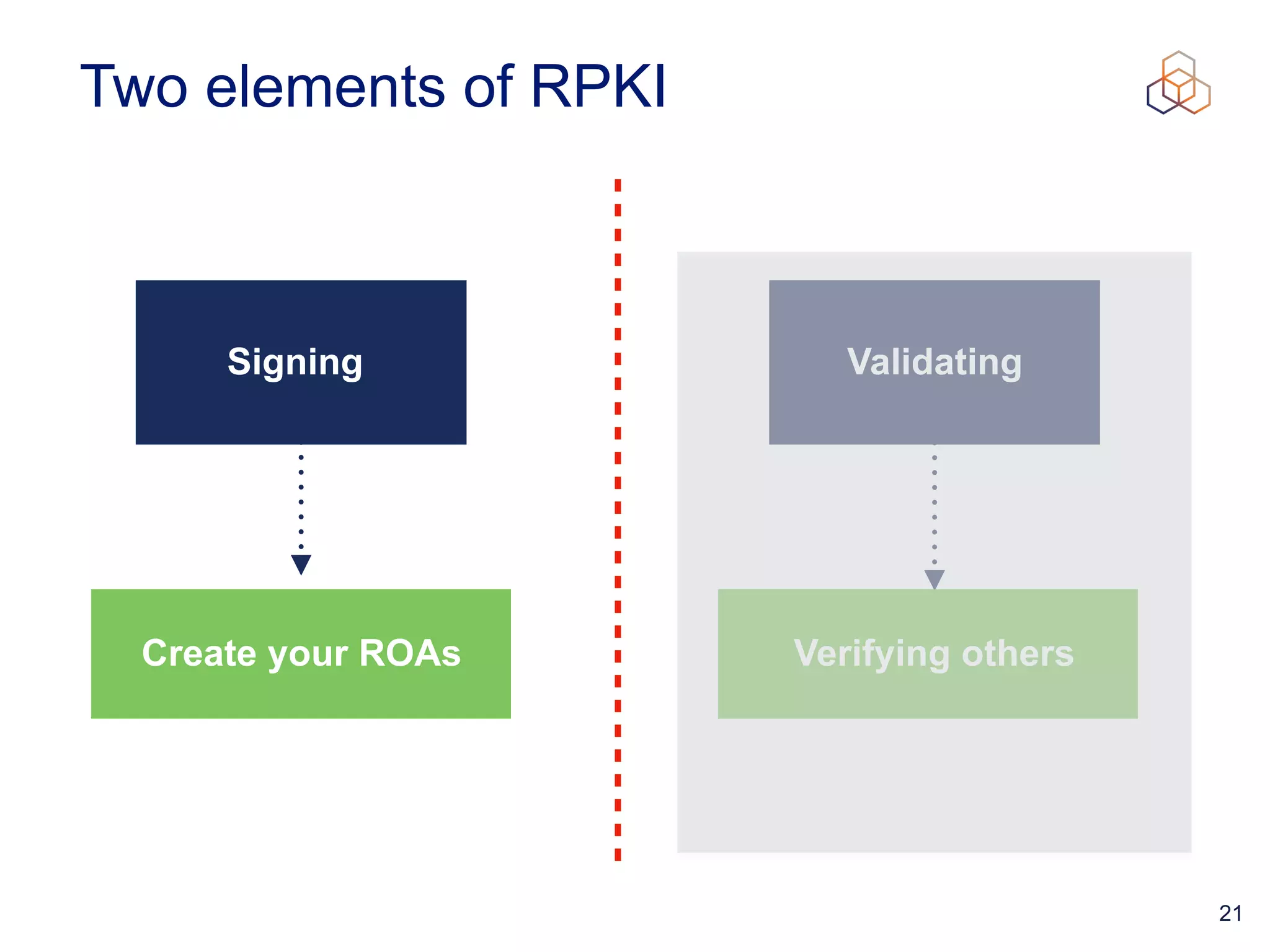
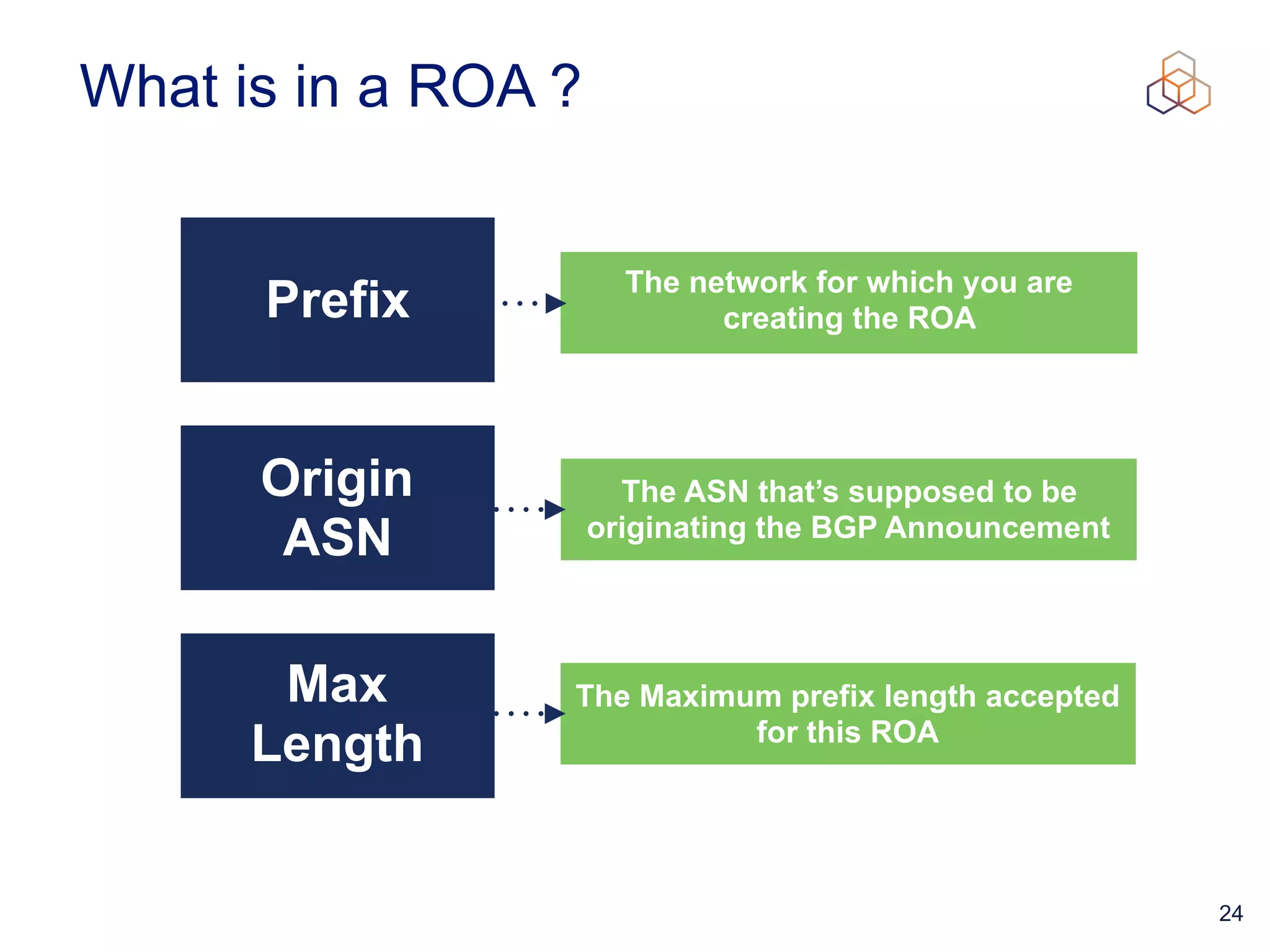
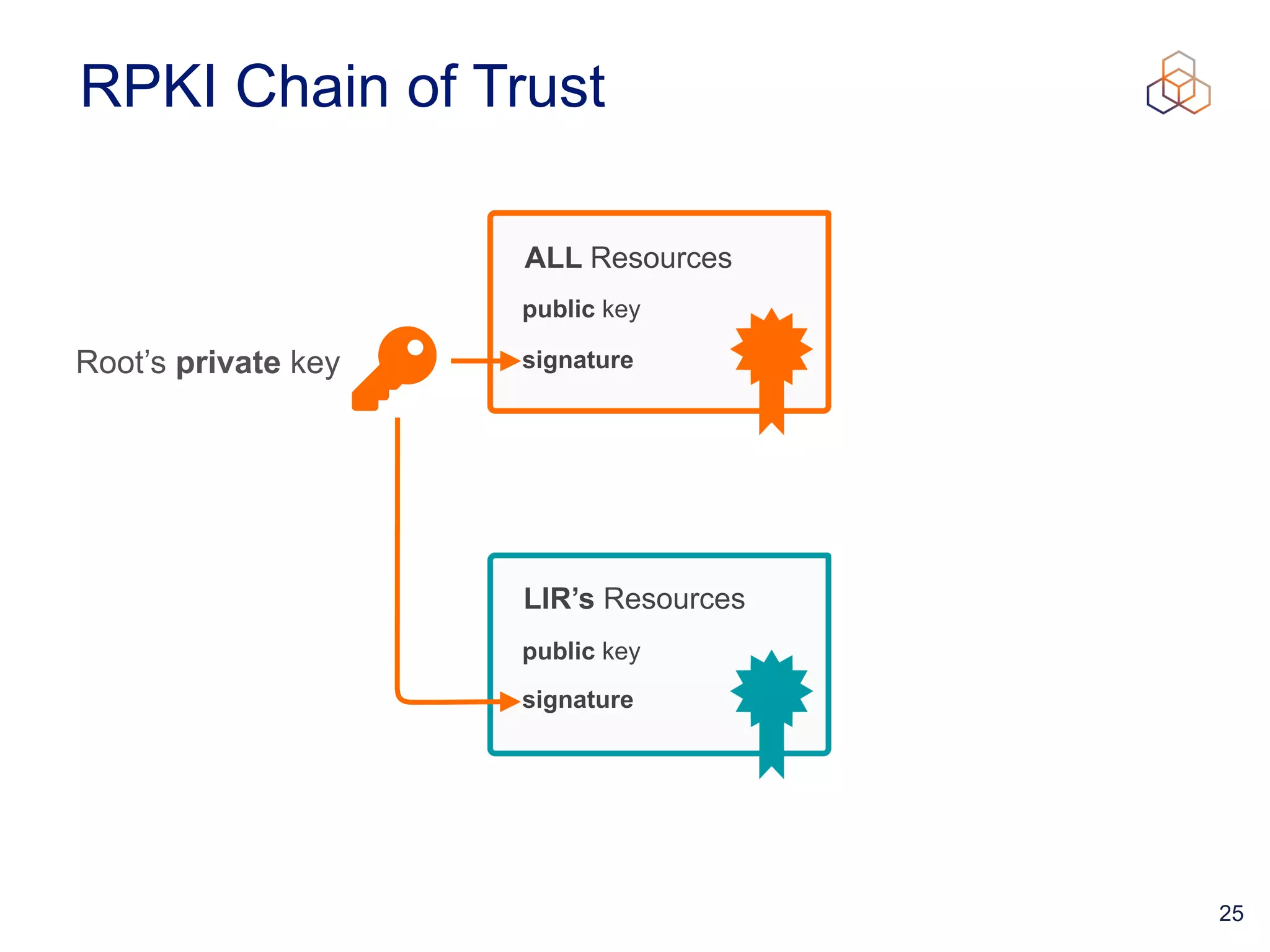
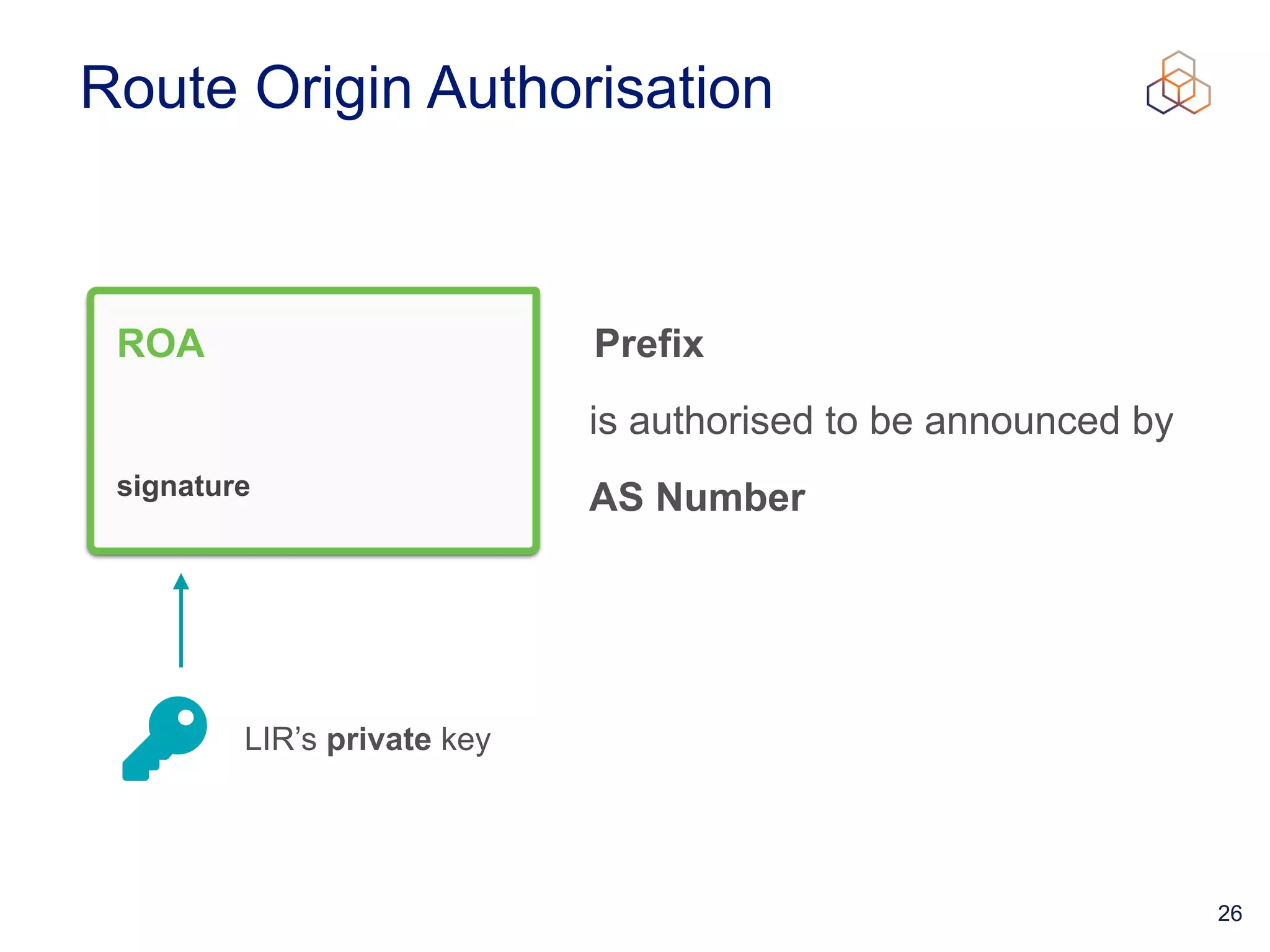
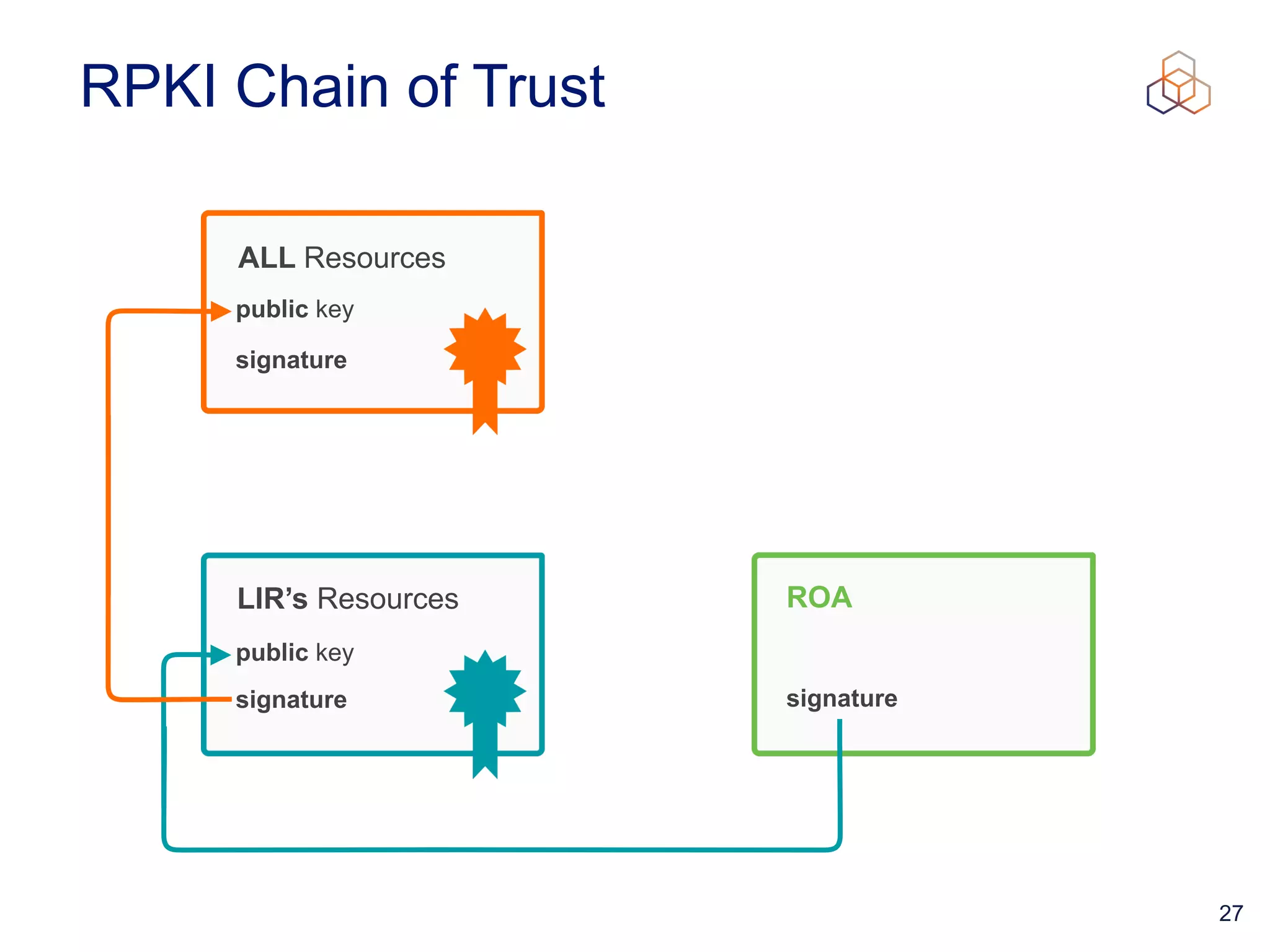
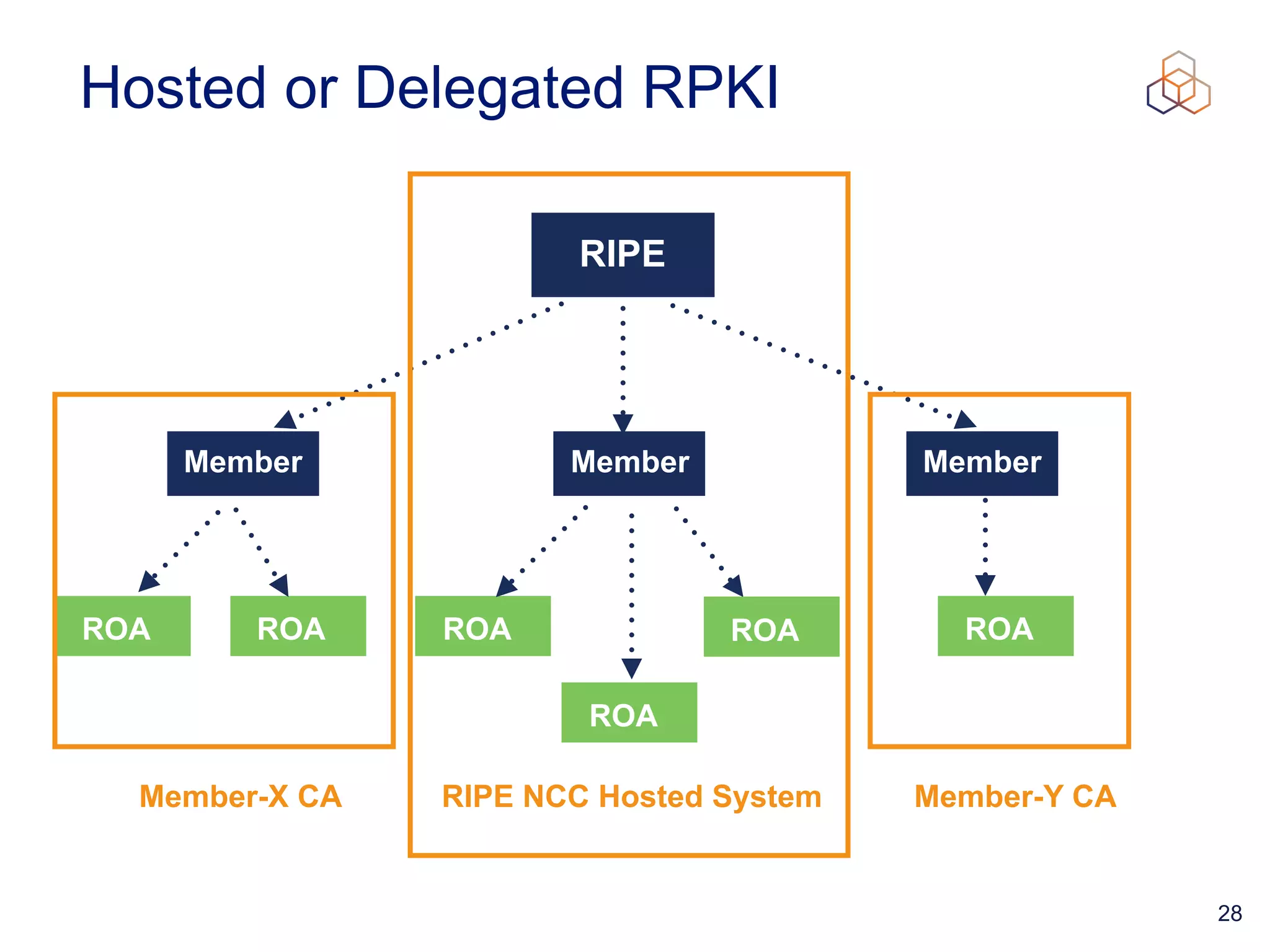
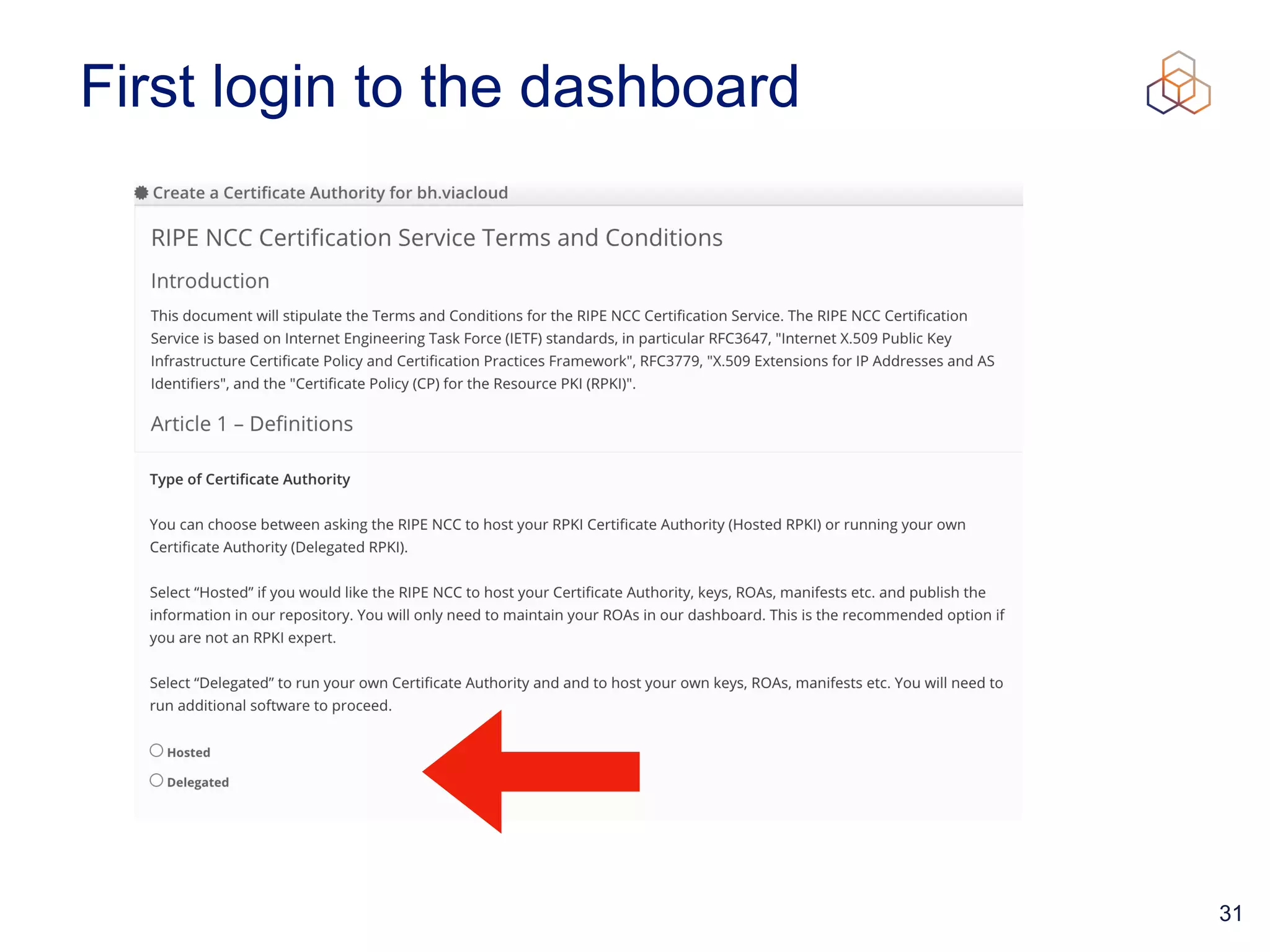
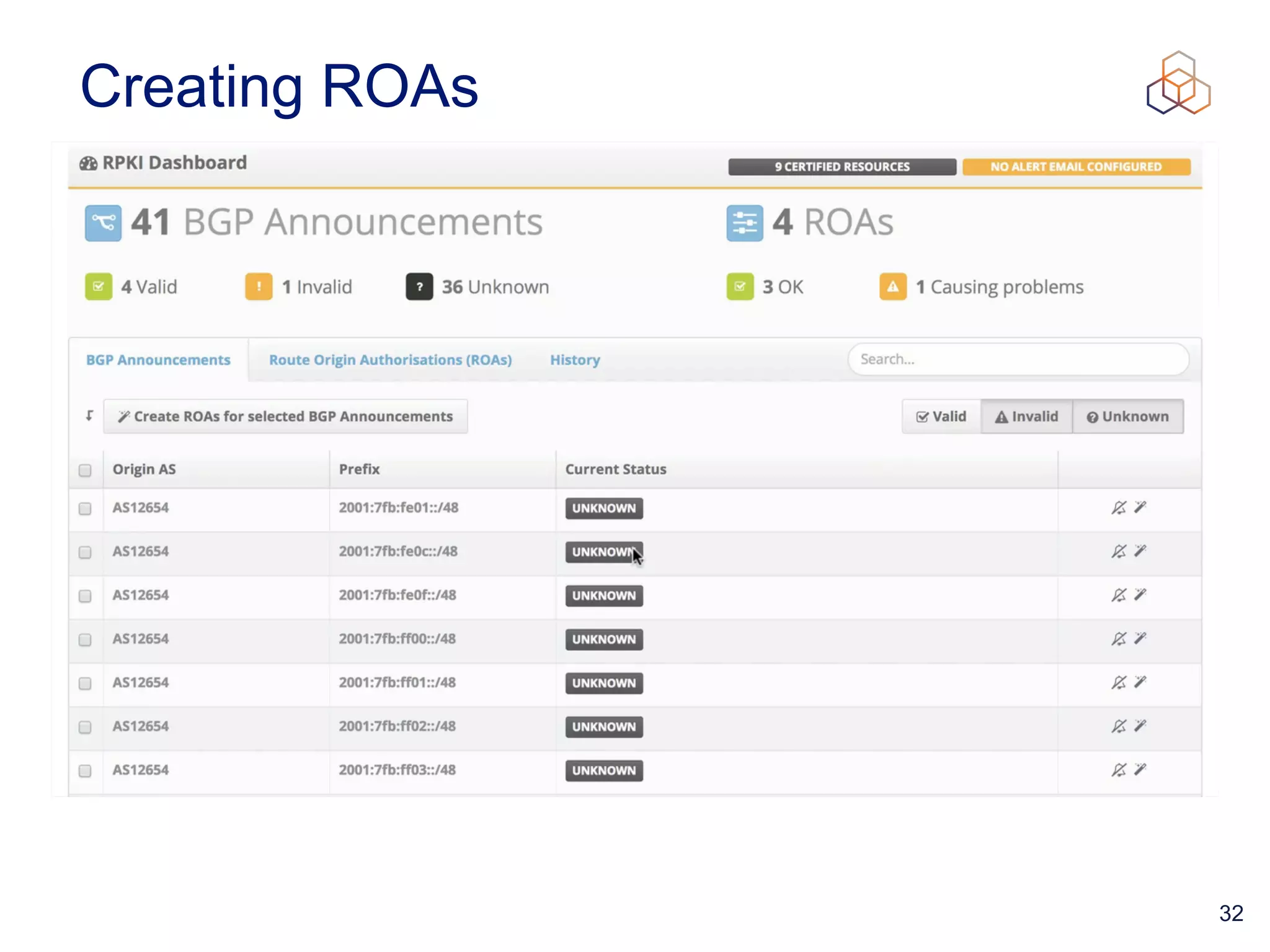
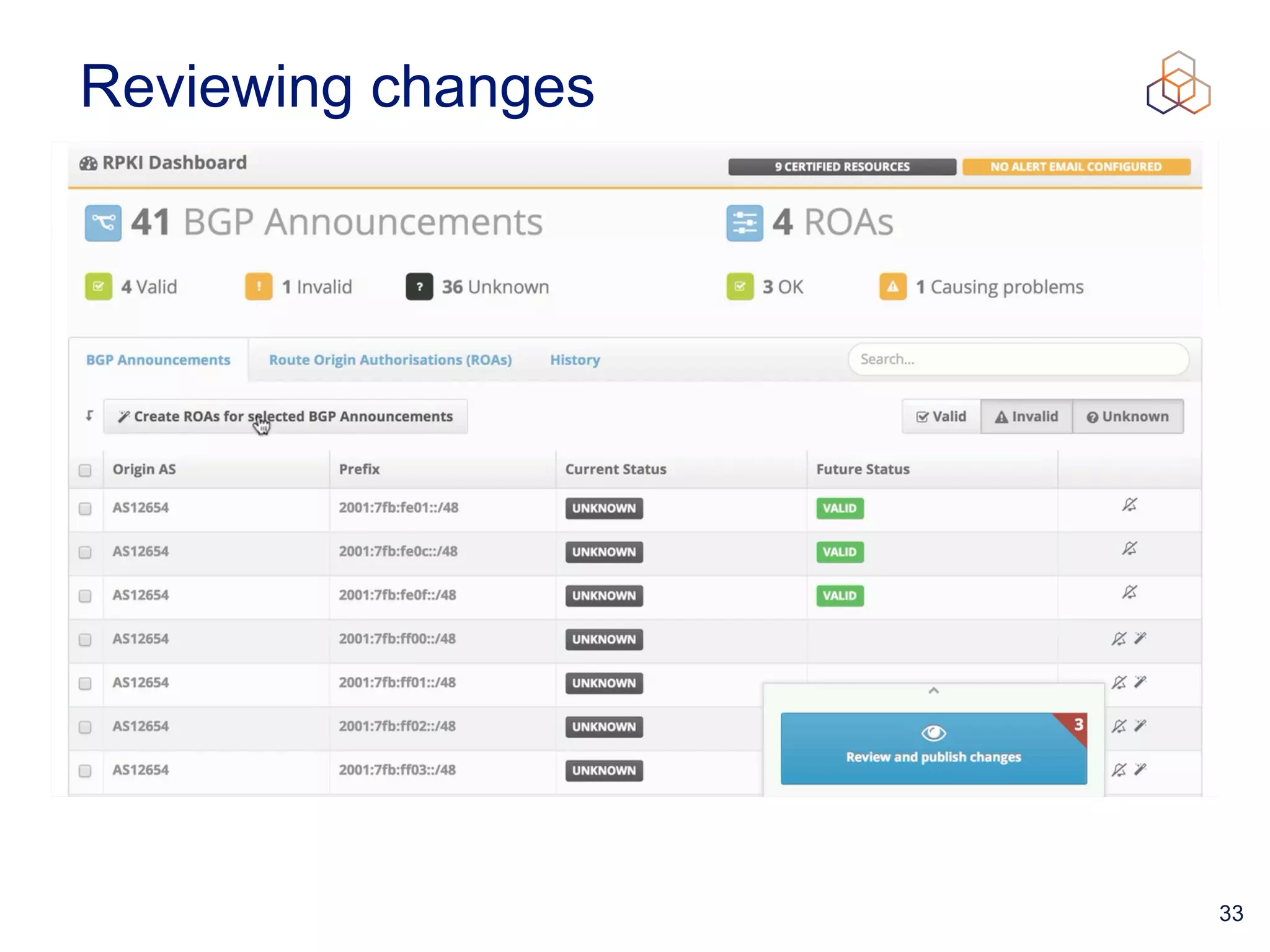
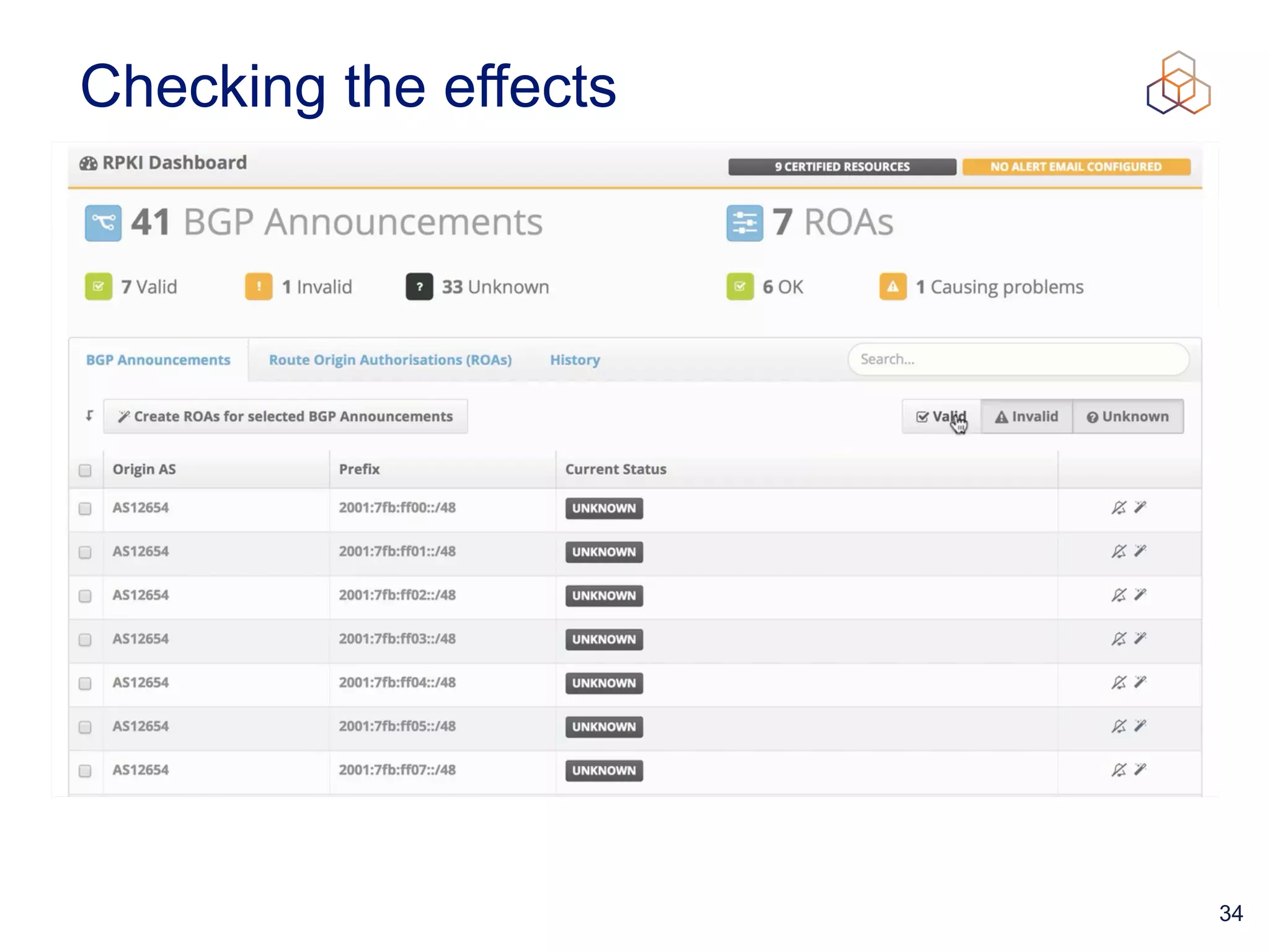
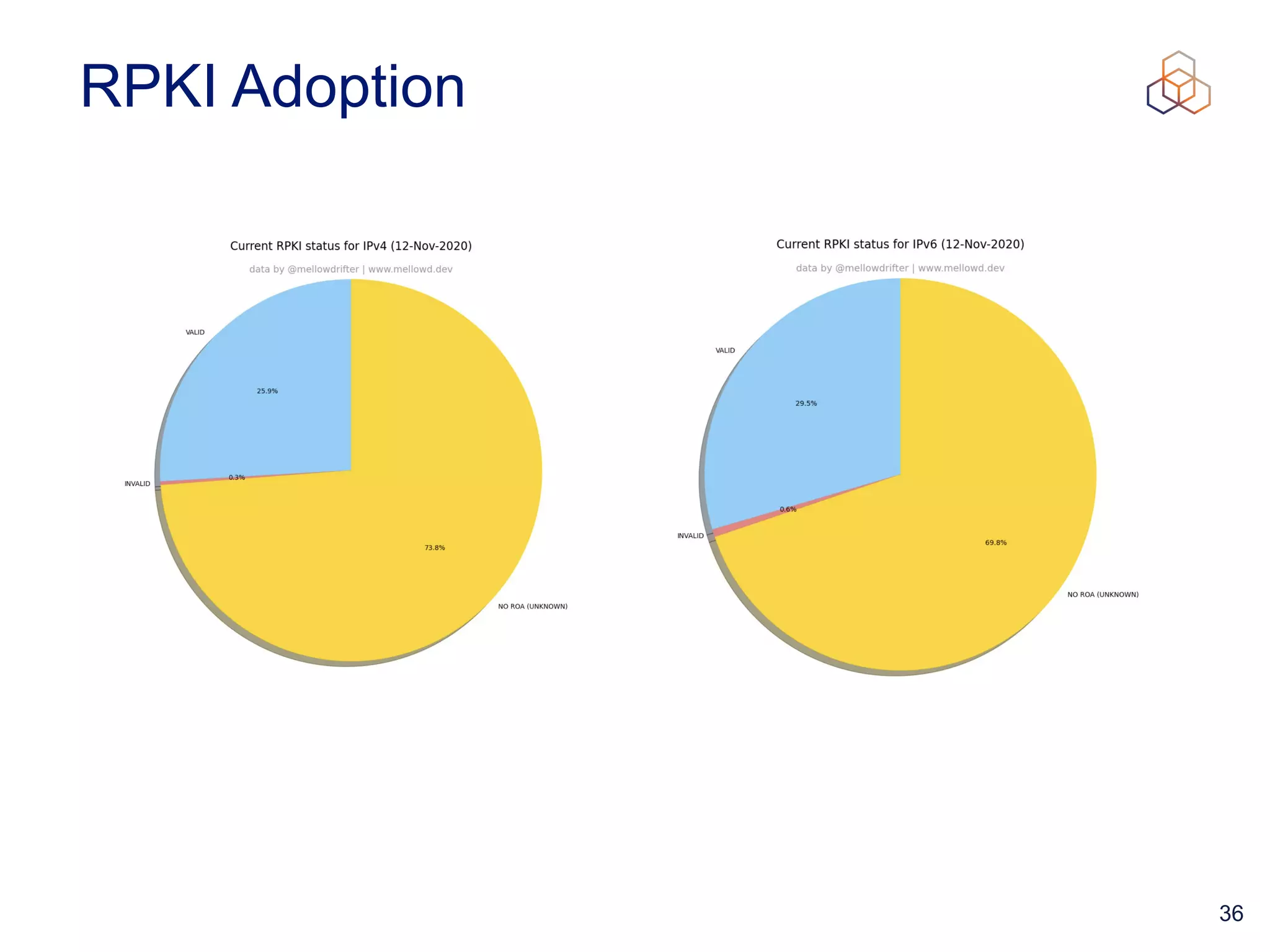
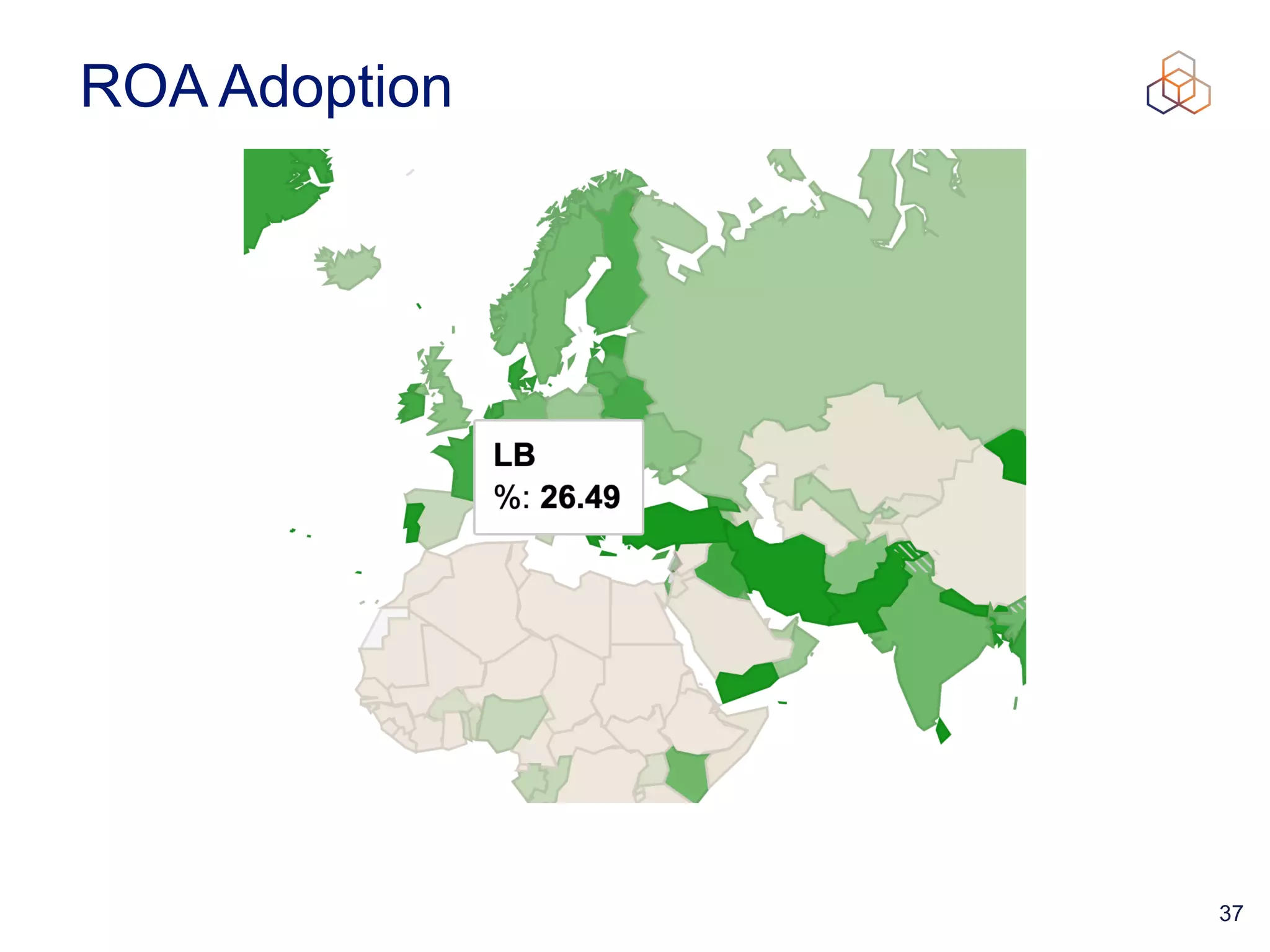
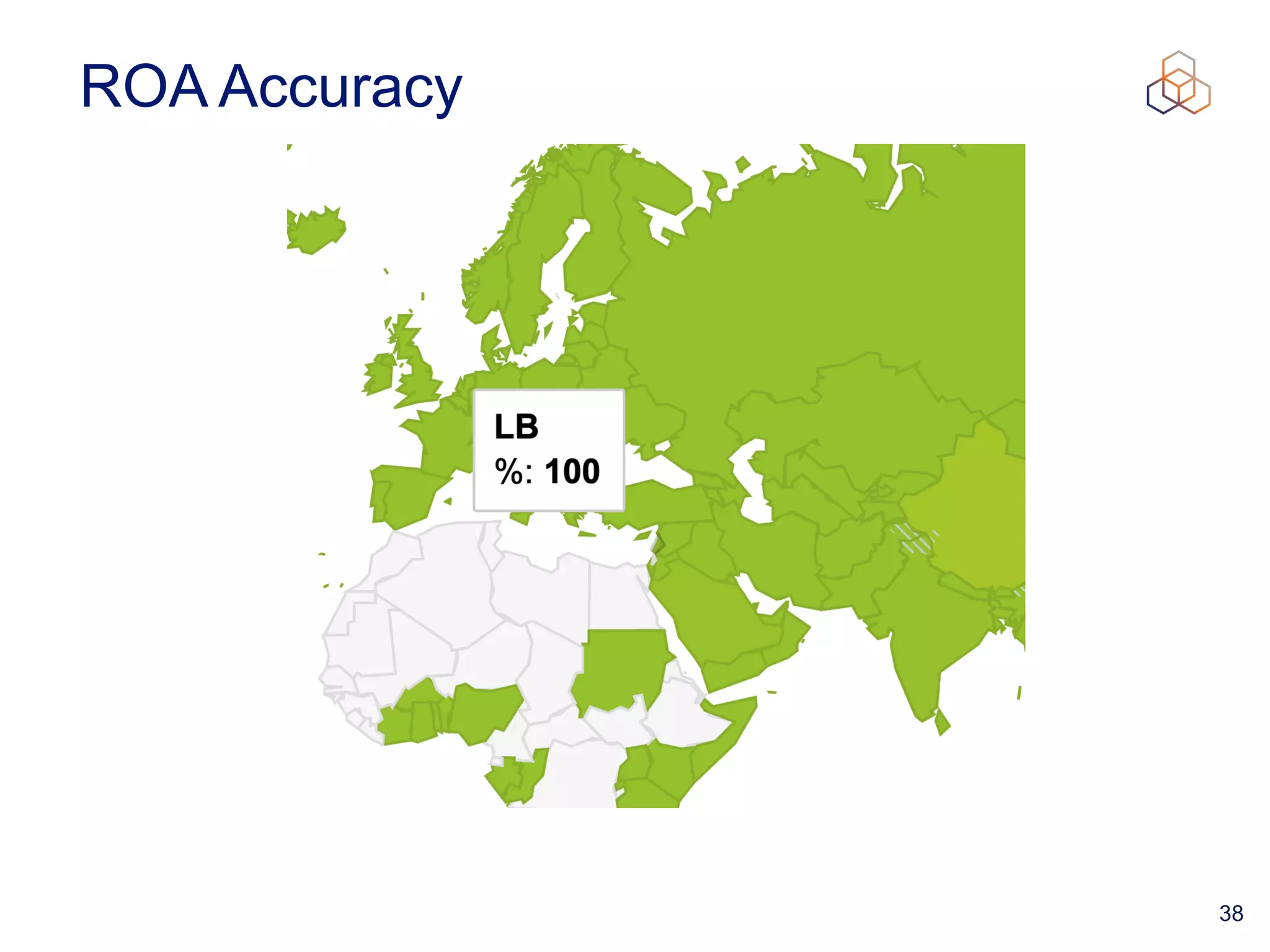
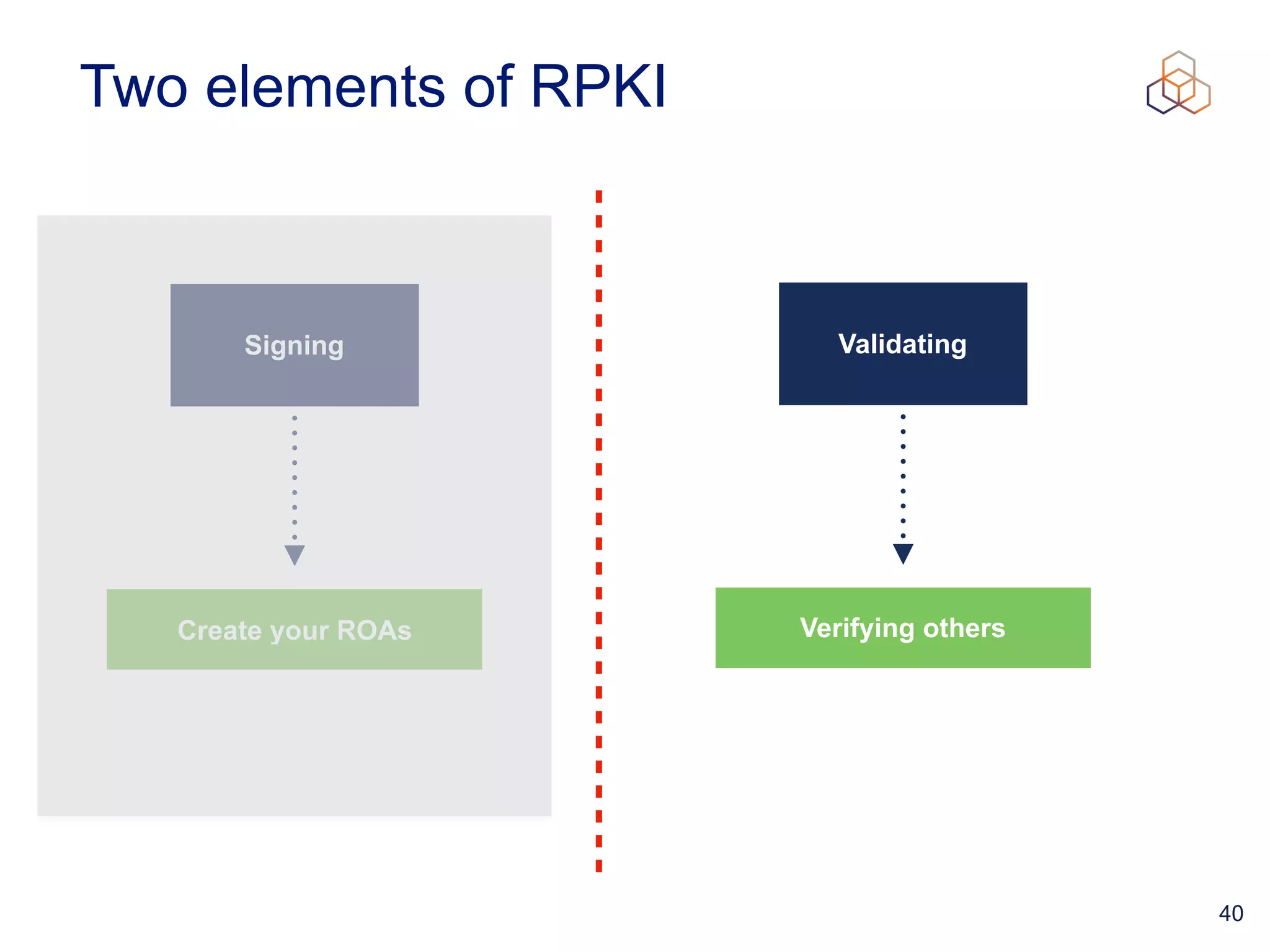
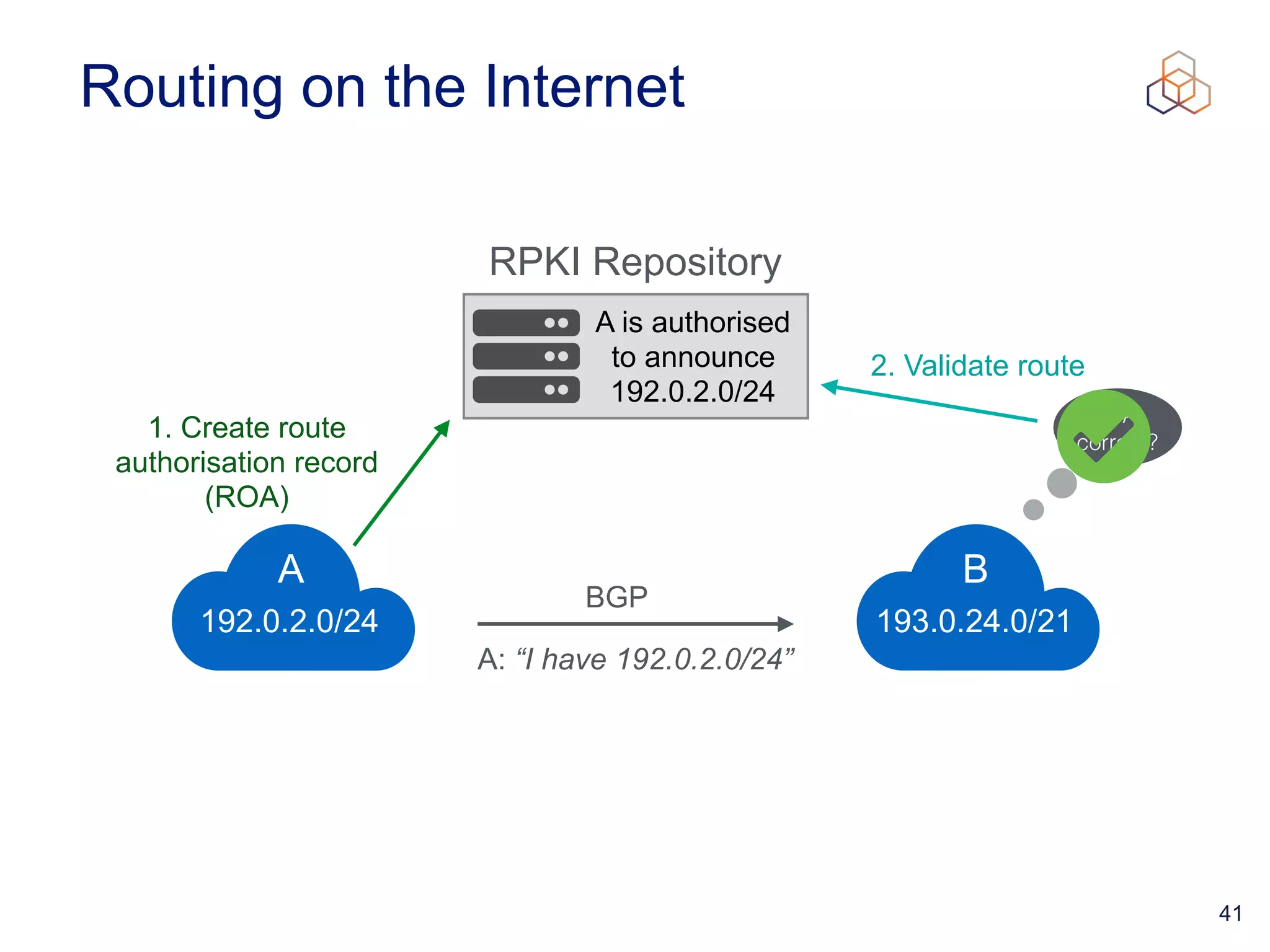
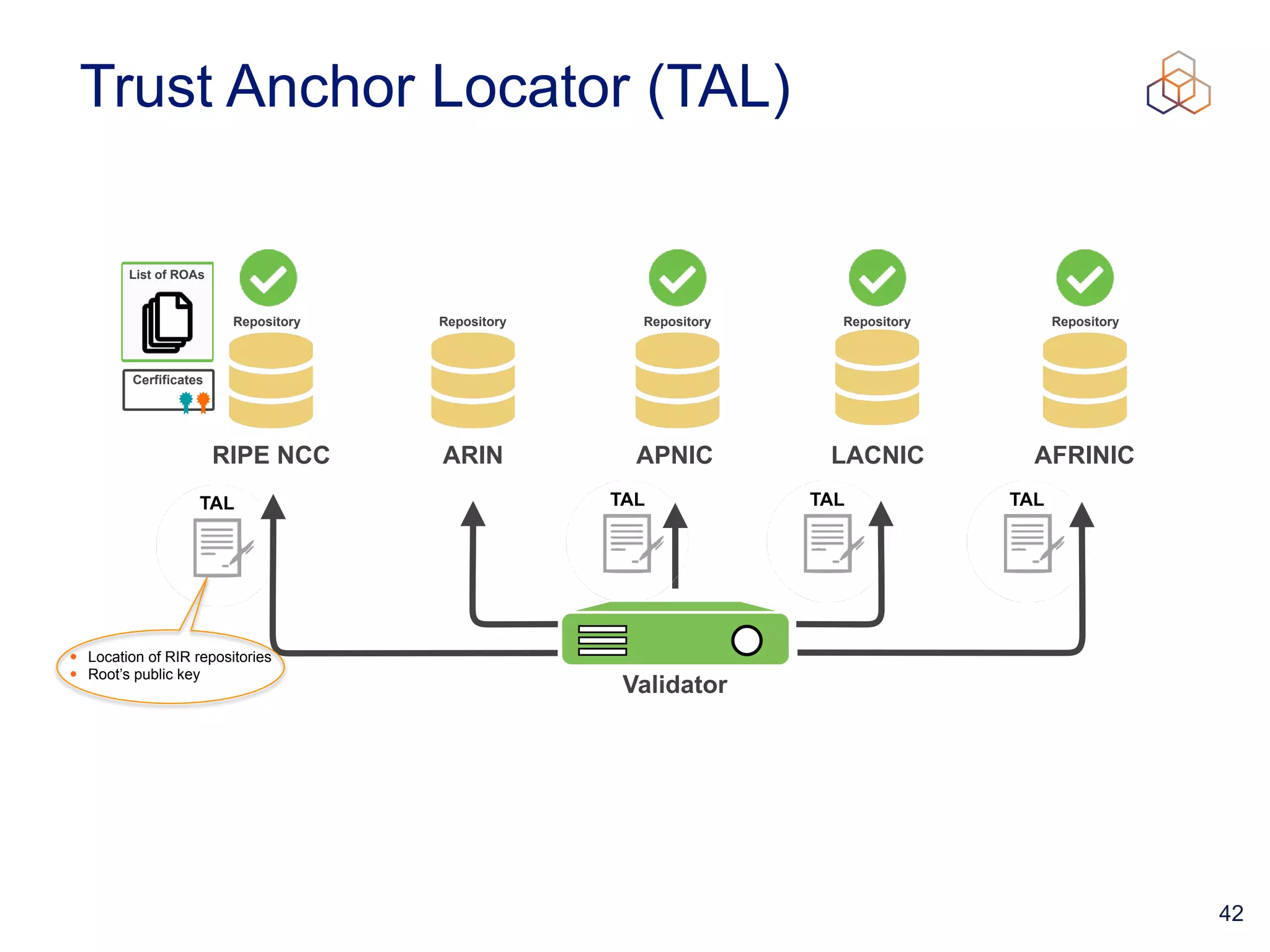
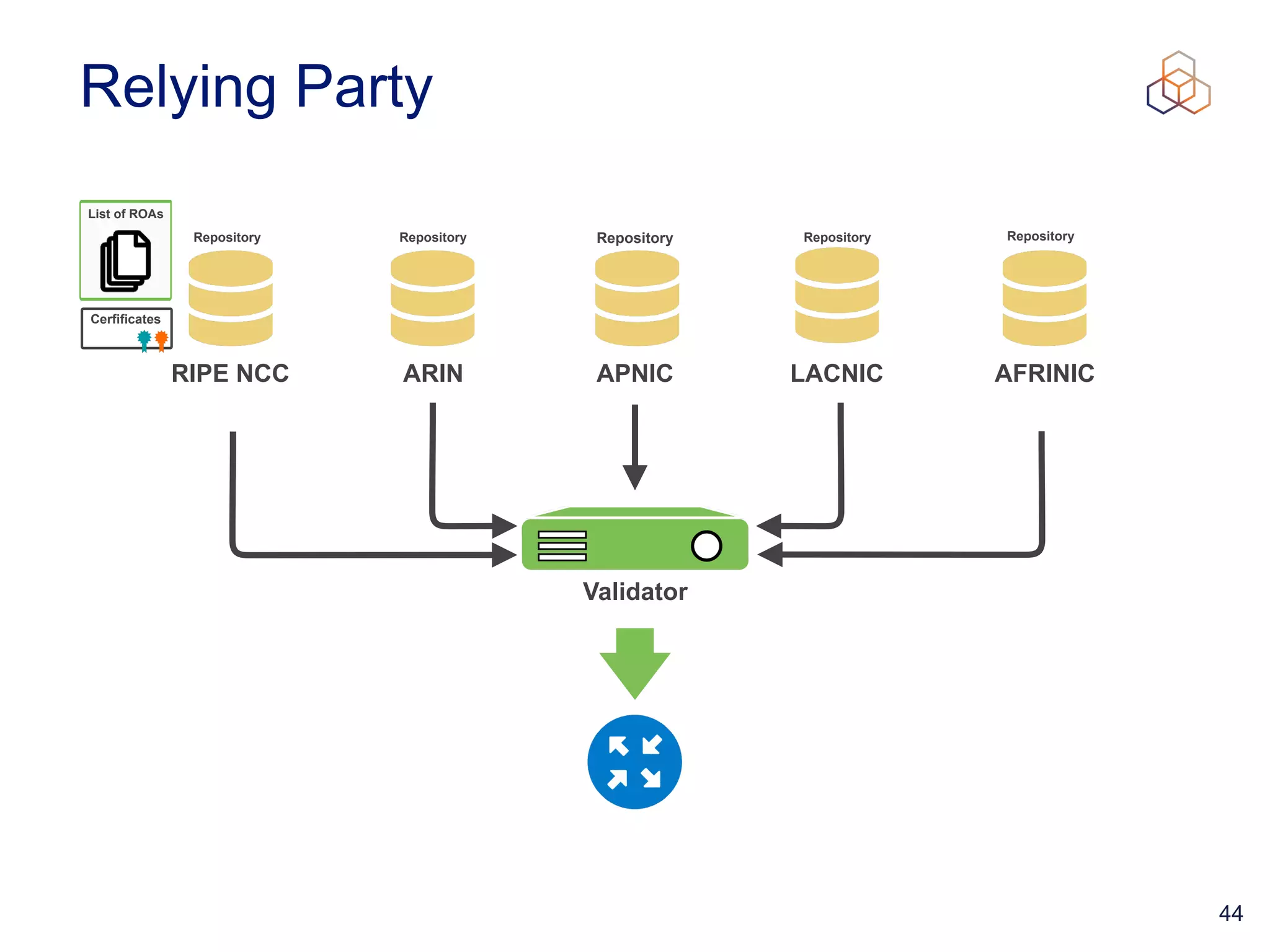
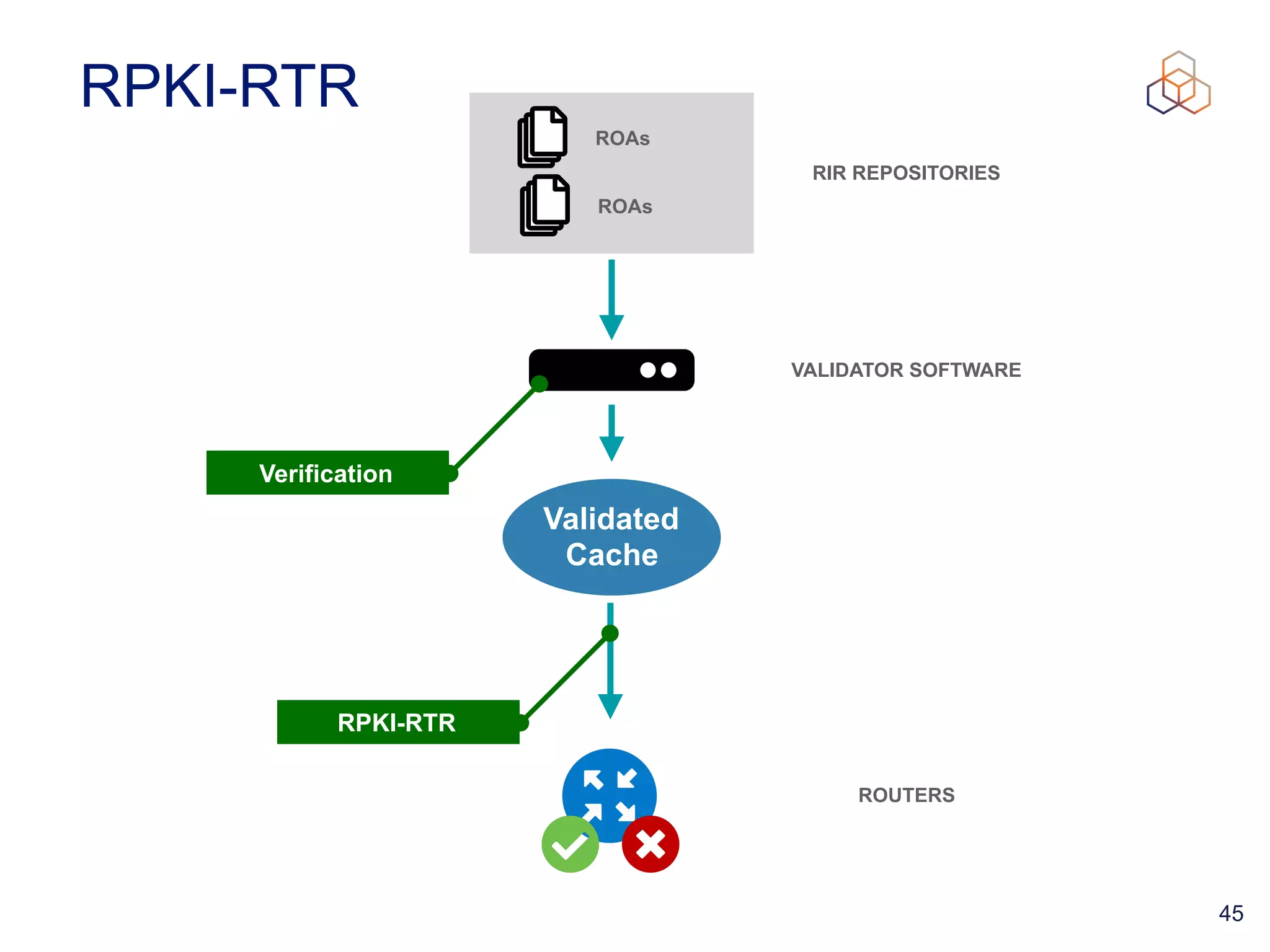
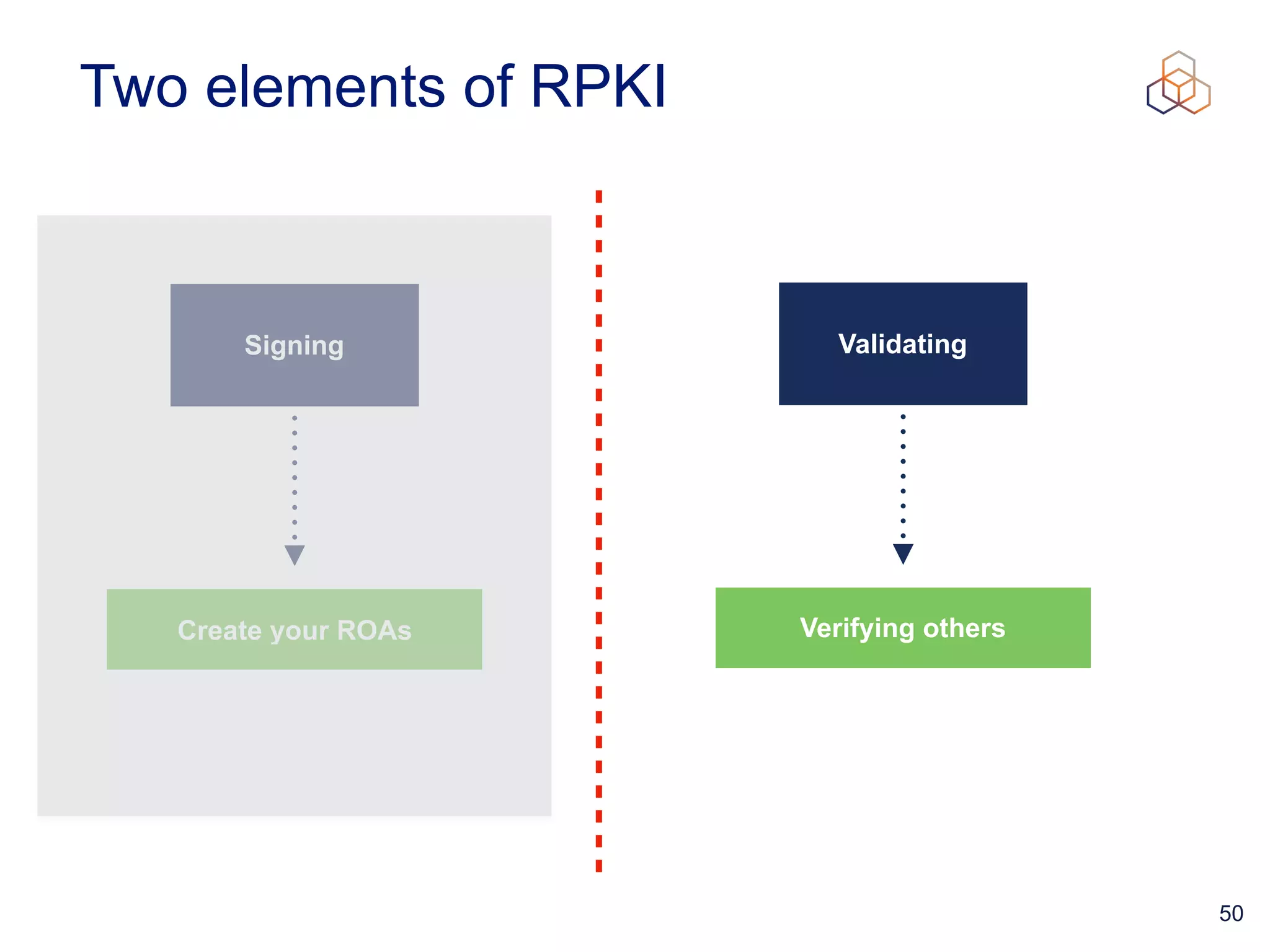
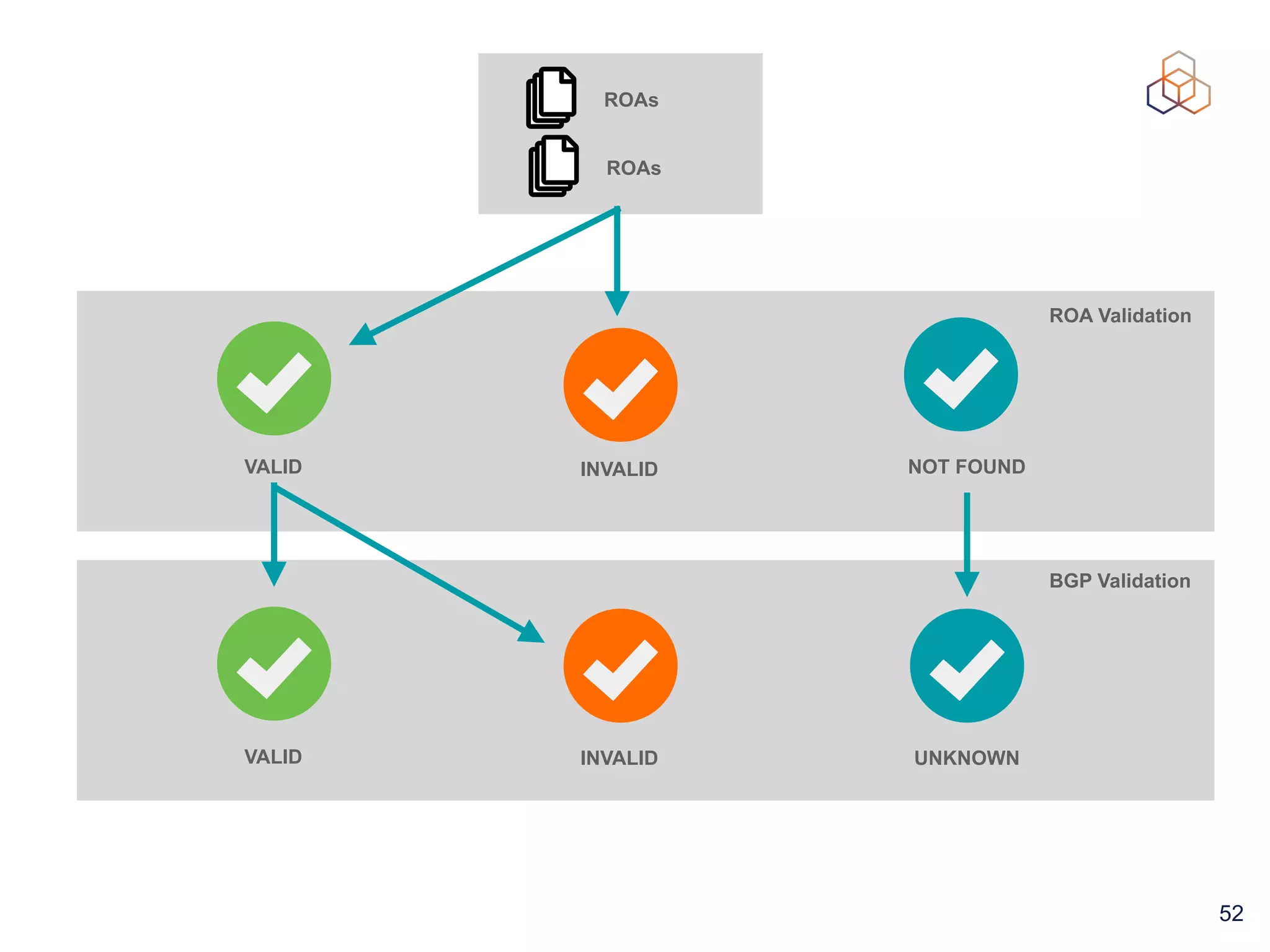
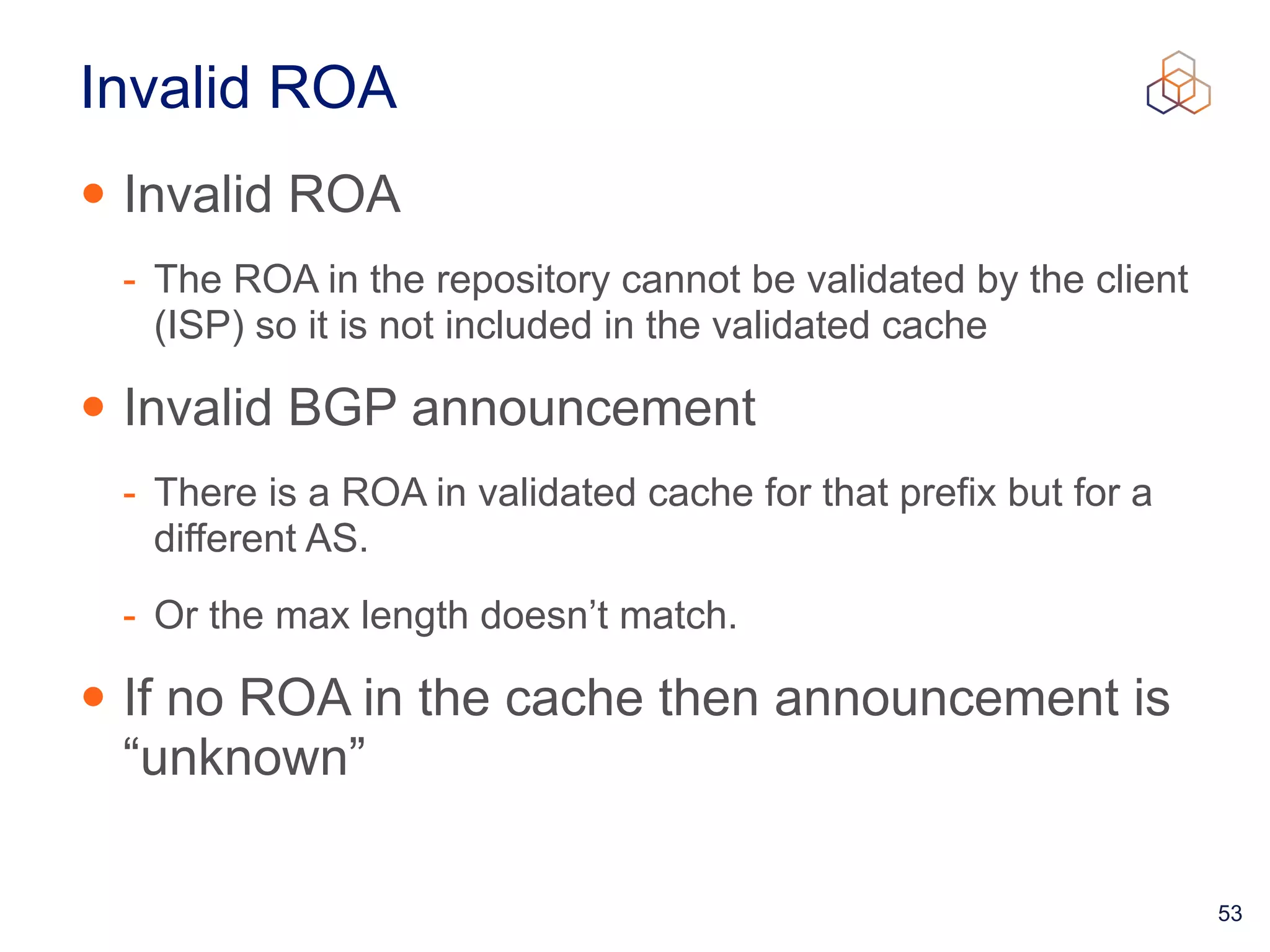
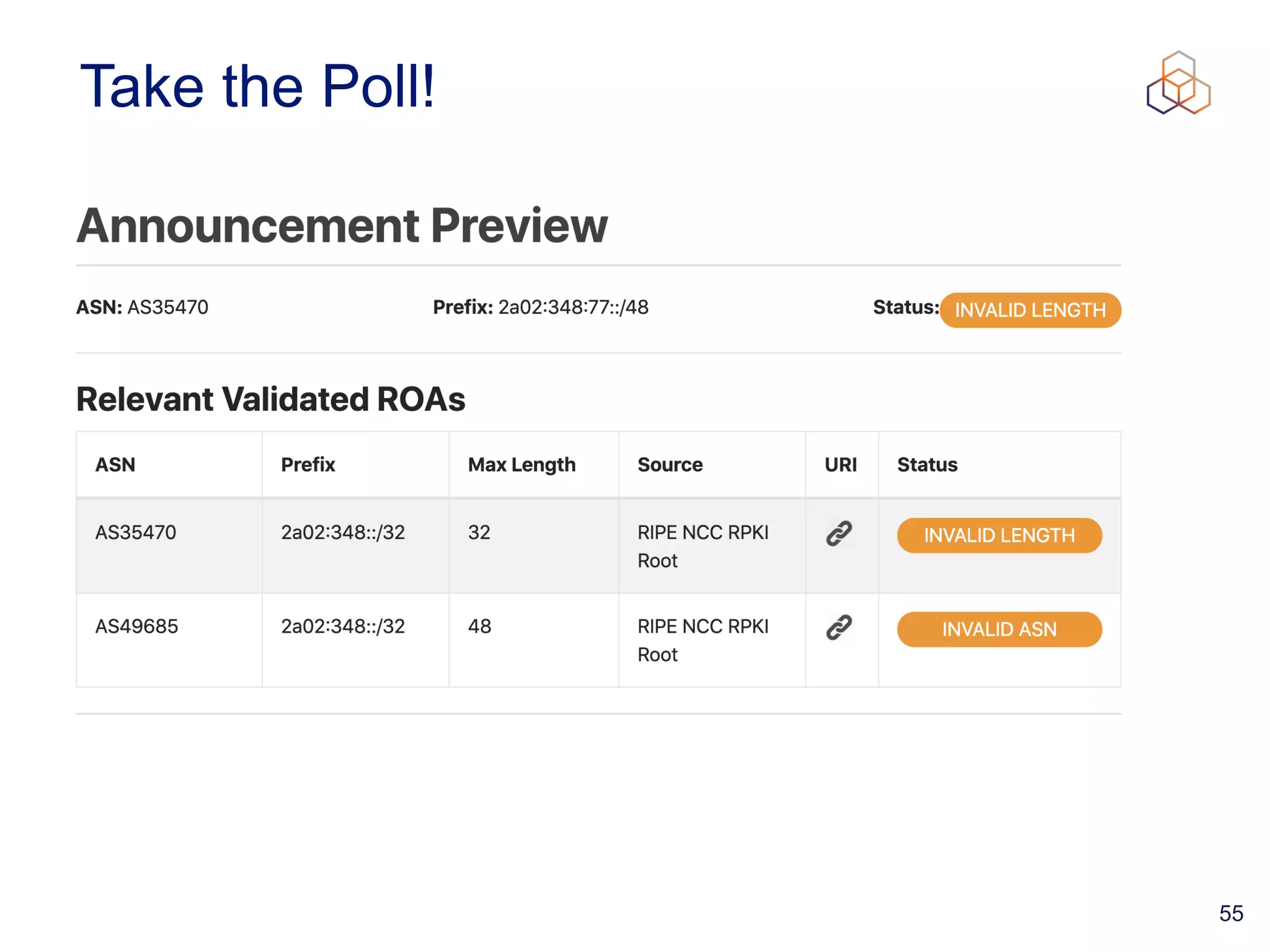
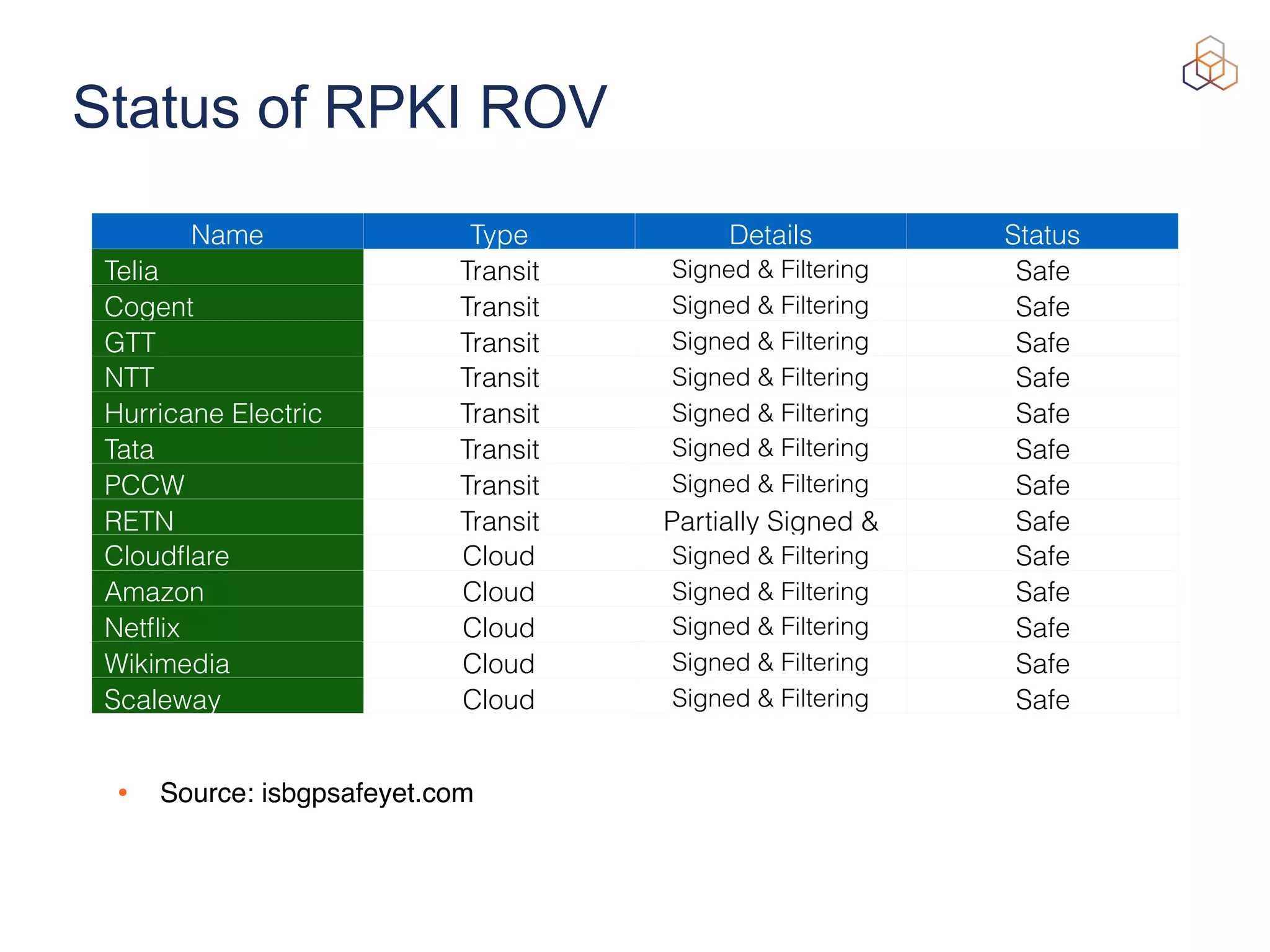
This document provides an introduction to BGP routing security and the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI). It explains that RPKI ties IP addresses and autonomous system numbers (ASNs) to public keys to validate route origination. It details how RPKI uses certificates signed by regional internet registries to establish a chain of trust from root certificates to route origin authorization (ROA) files created by network operators. It also discusses tools for validating ROAs and using the results to make routing decisions, as well as ongoing efforts to fully validate the security of inter-domain routing.