1) The document discusses concepts related to identity and intercultural communication including the self and other, social science approaches, identity management, and language and identity.
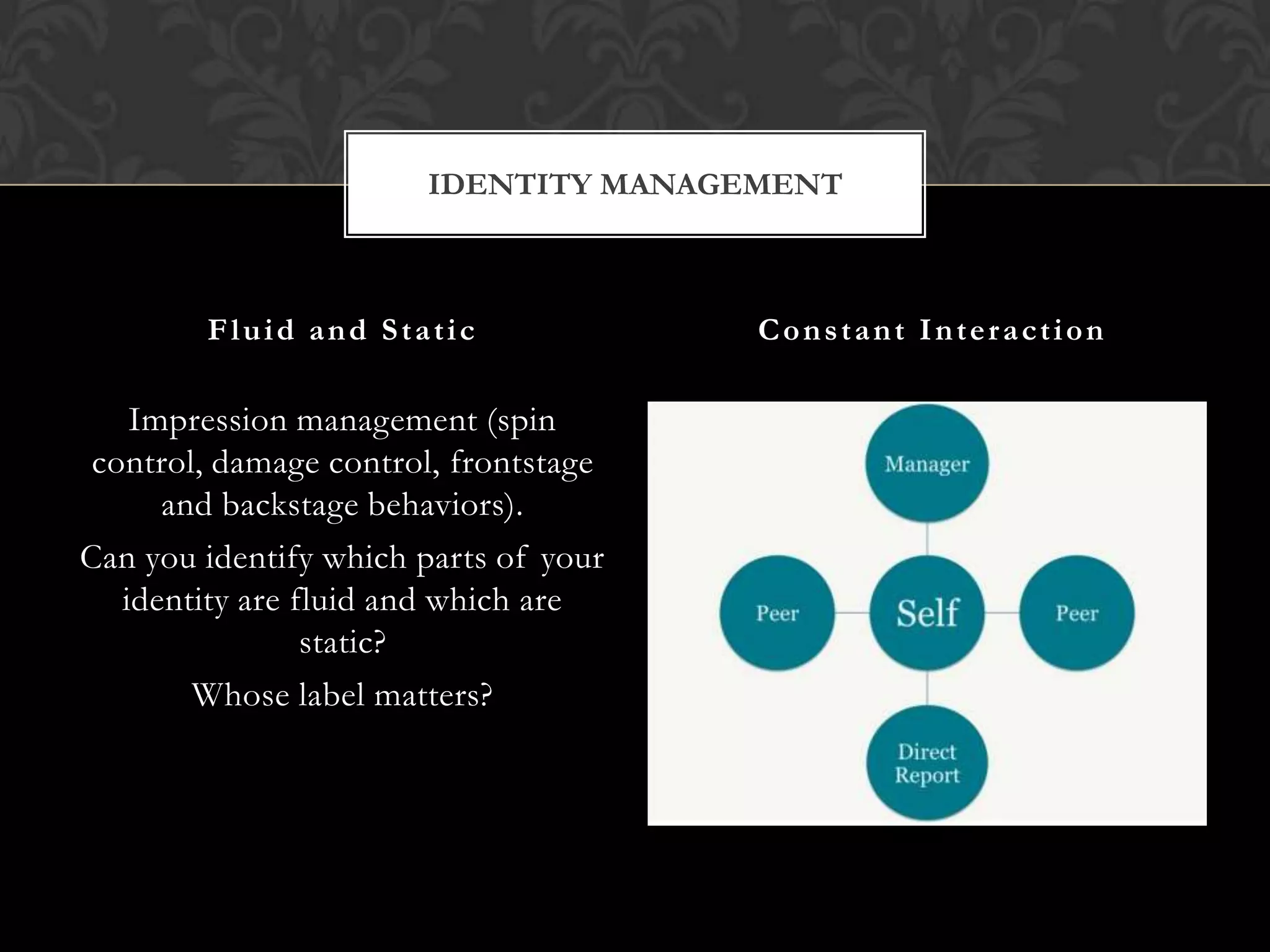
2) It presents perspectives on identity from social science, interpretive, critical, and dialectical approaches and discusses how identity is negotiated through constant interaction and labels.
3) Key aspects of identity development for both minority and majority groups are outlined in stages including unexamined identity, internalization, resistance/redefinition, and integration of identity.
4) Questions are posed about how people define themselves and are defined by others, and whether that influences communication with others.