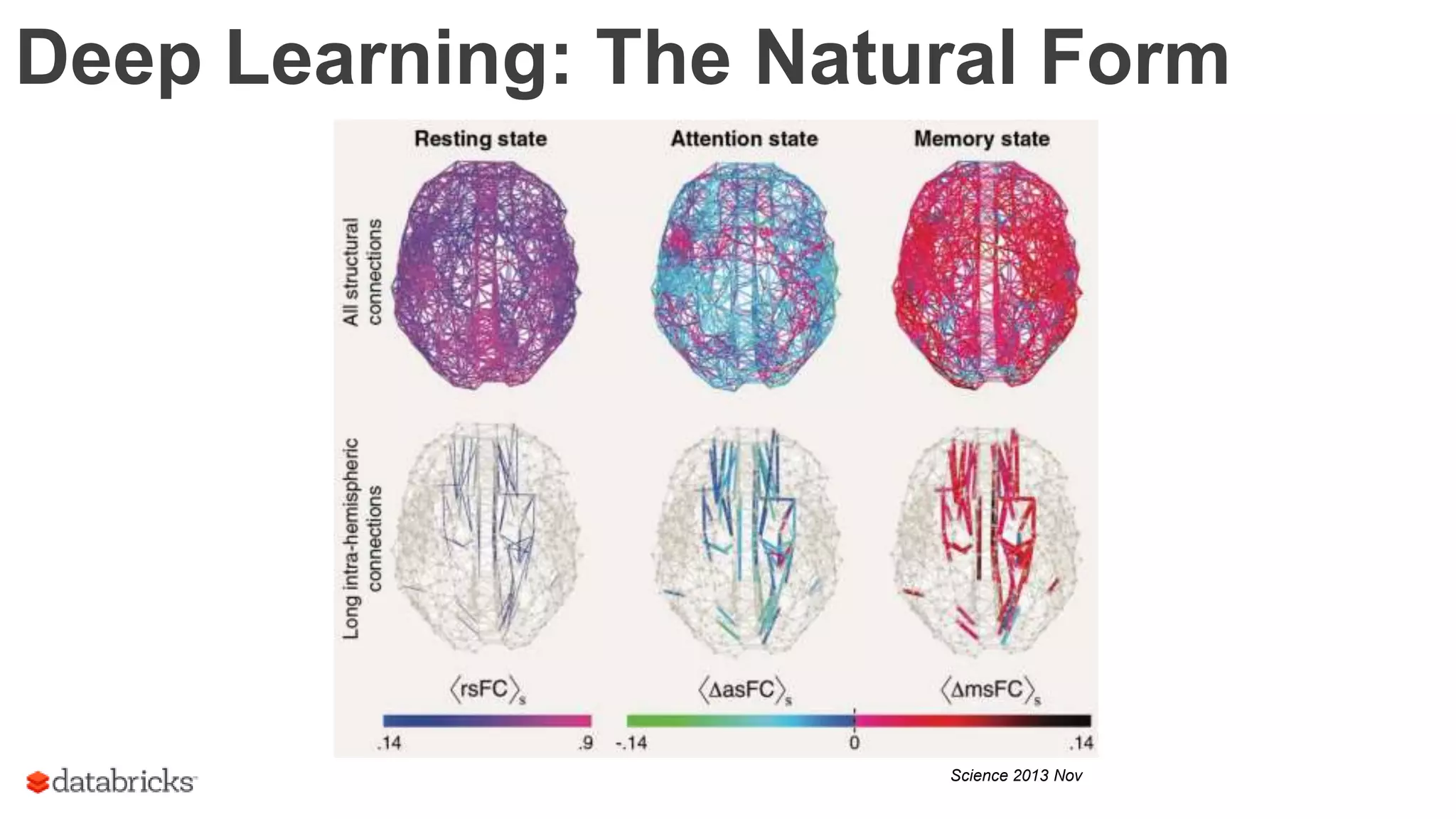
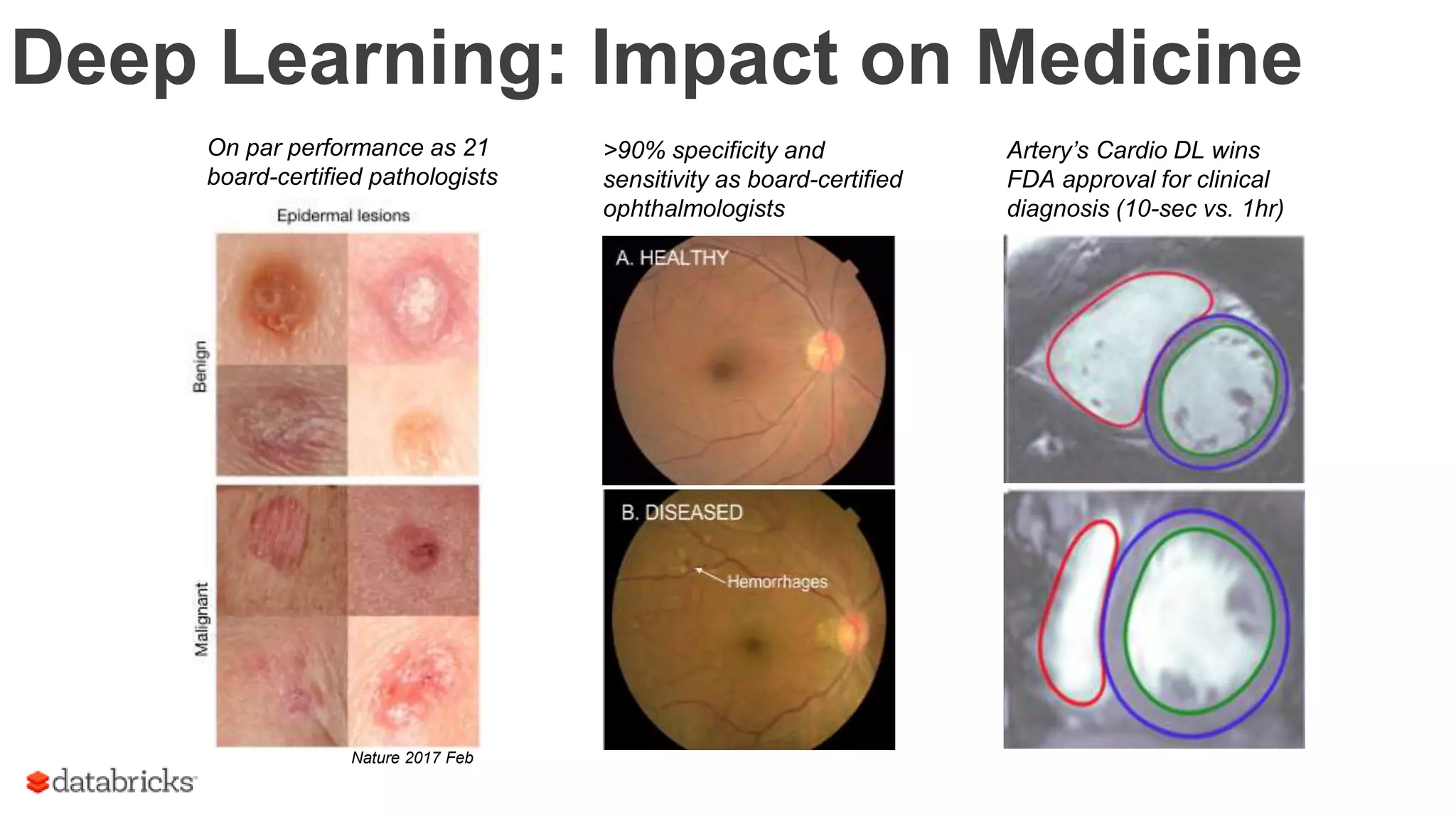
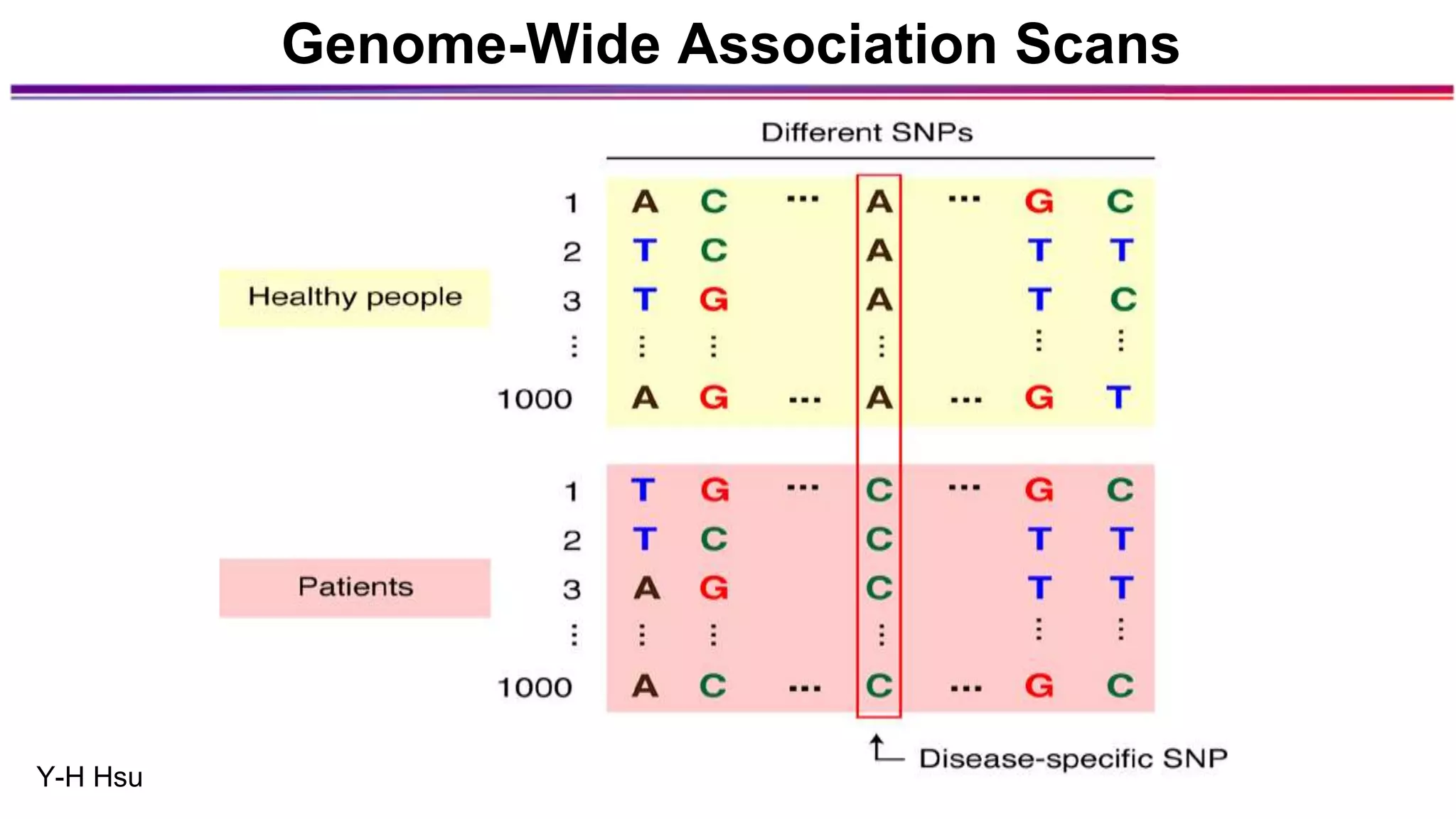
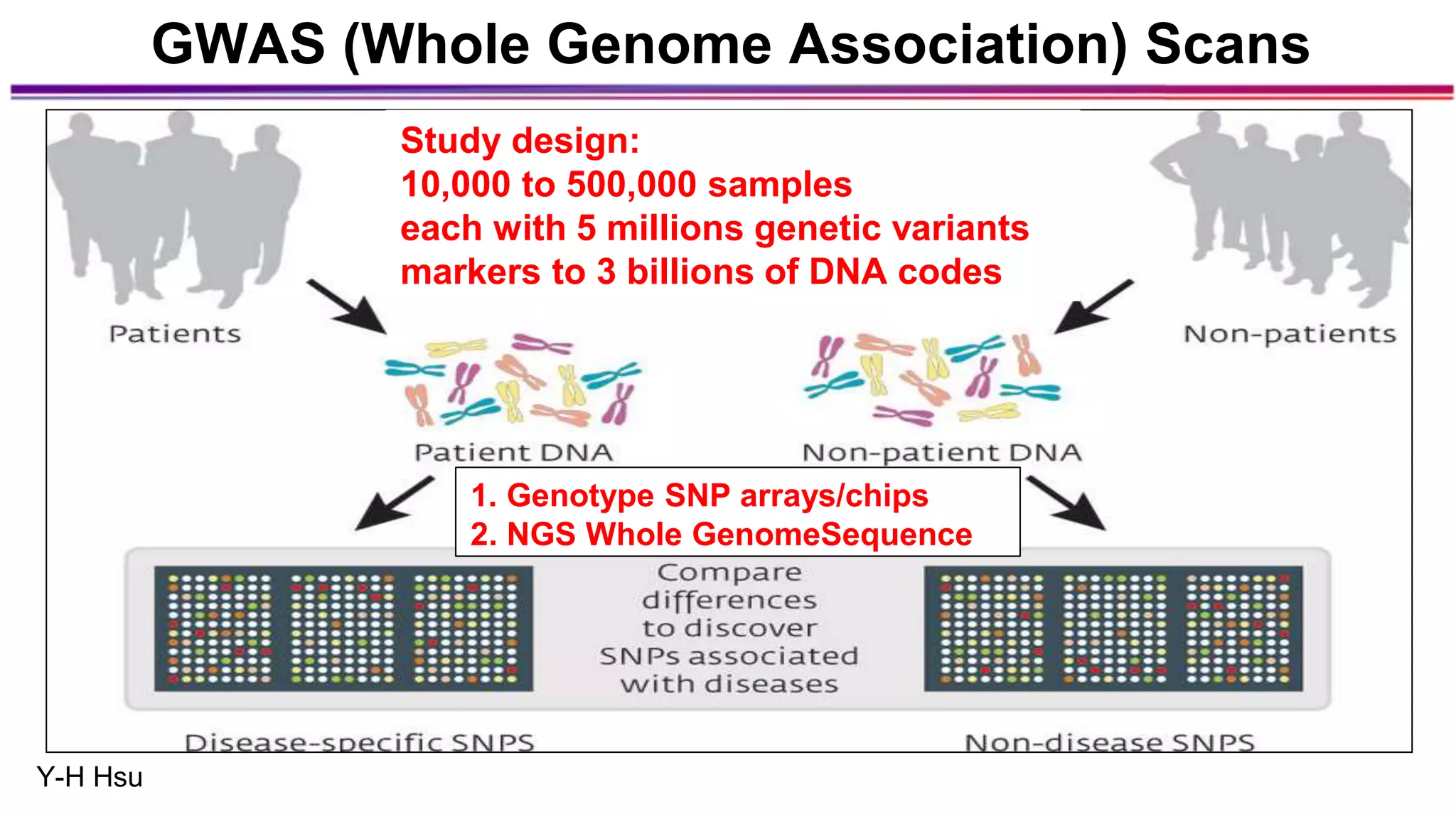
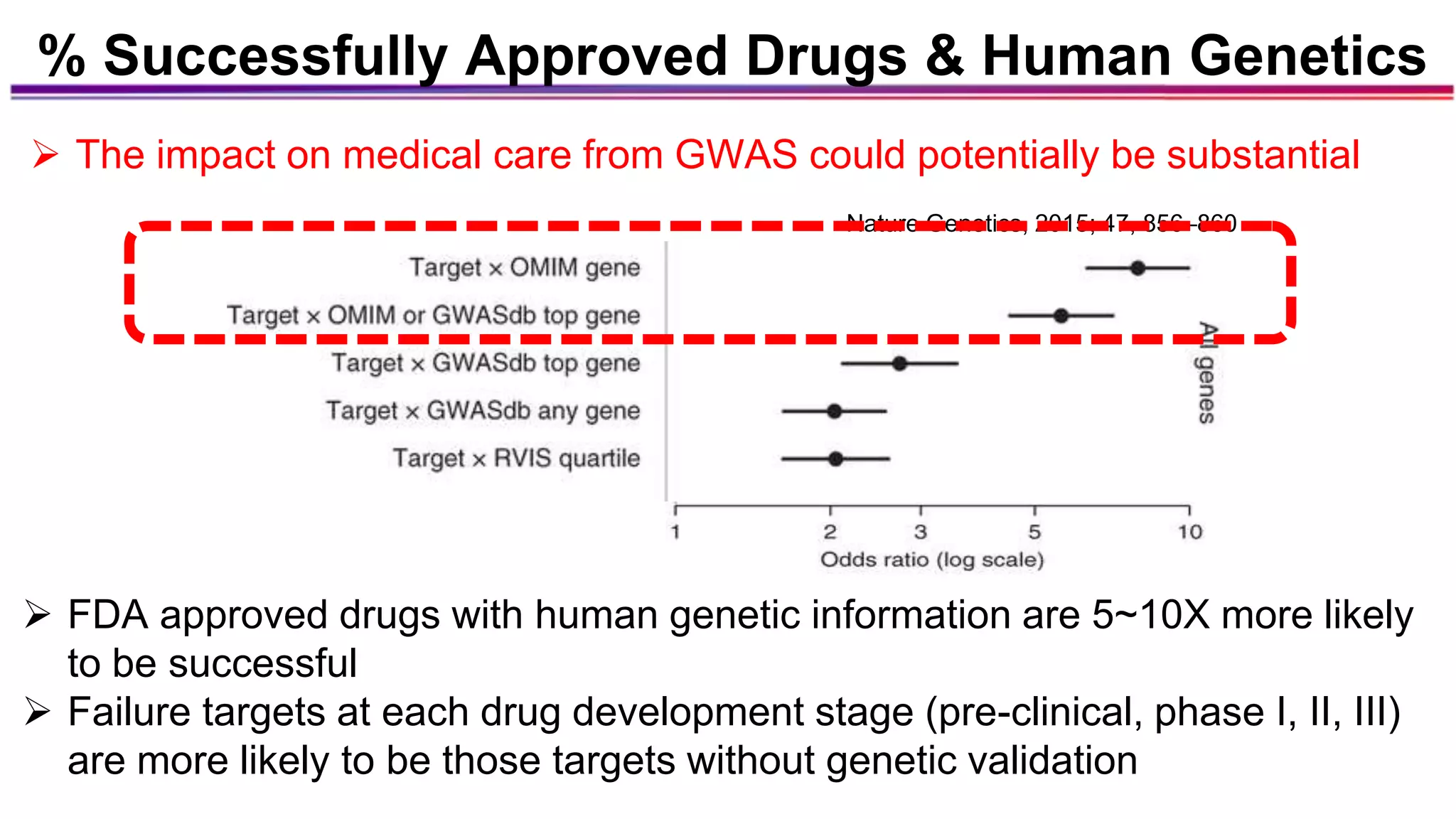
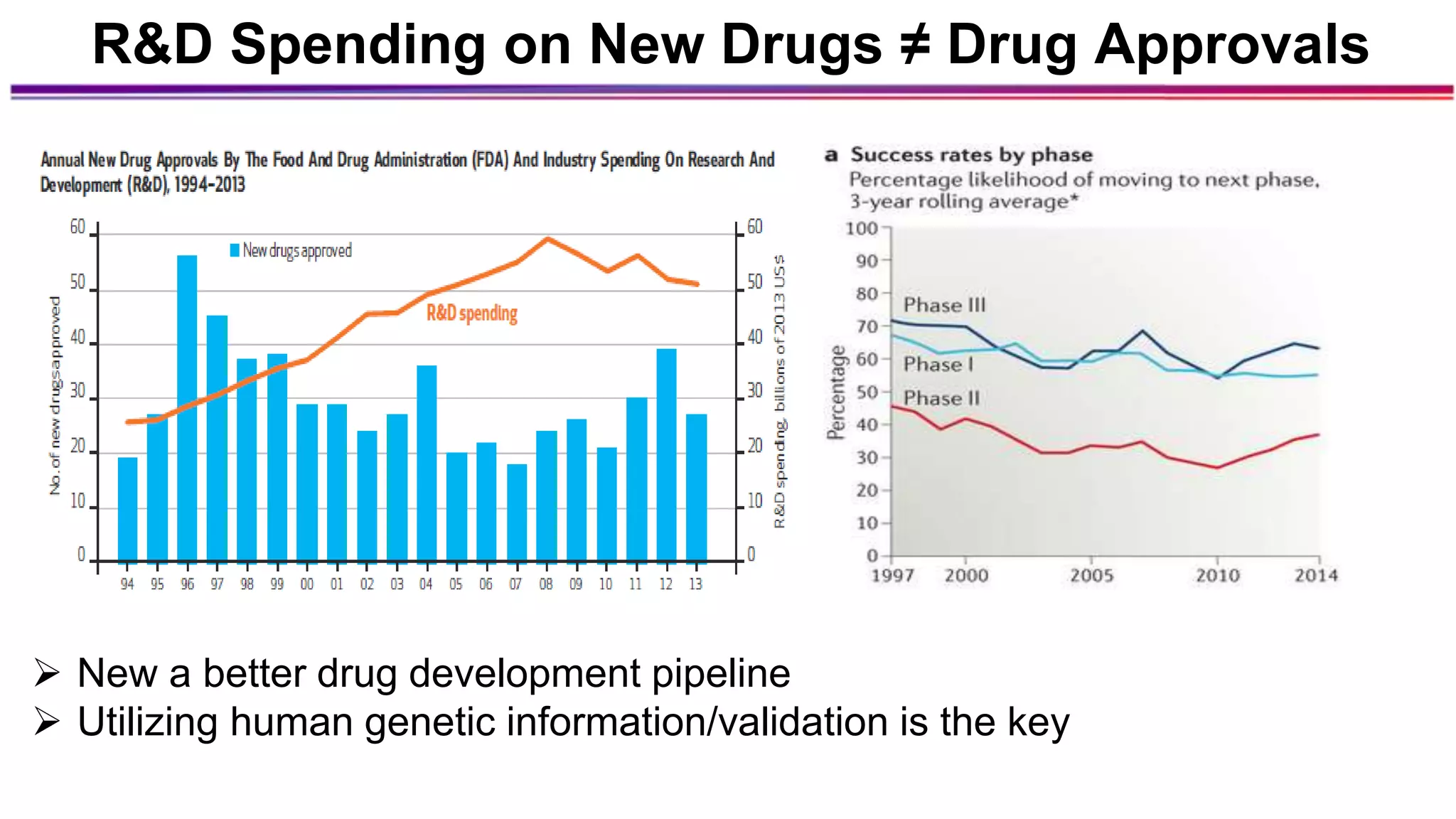
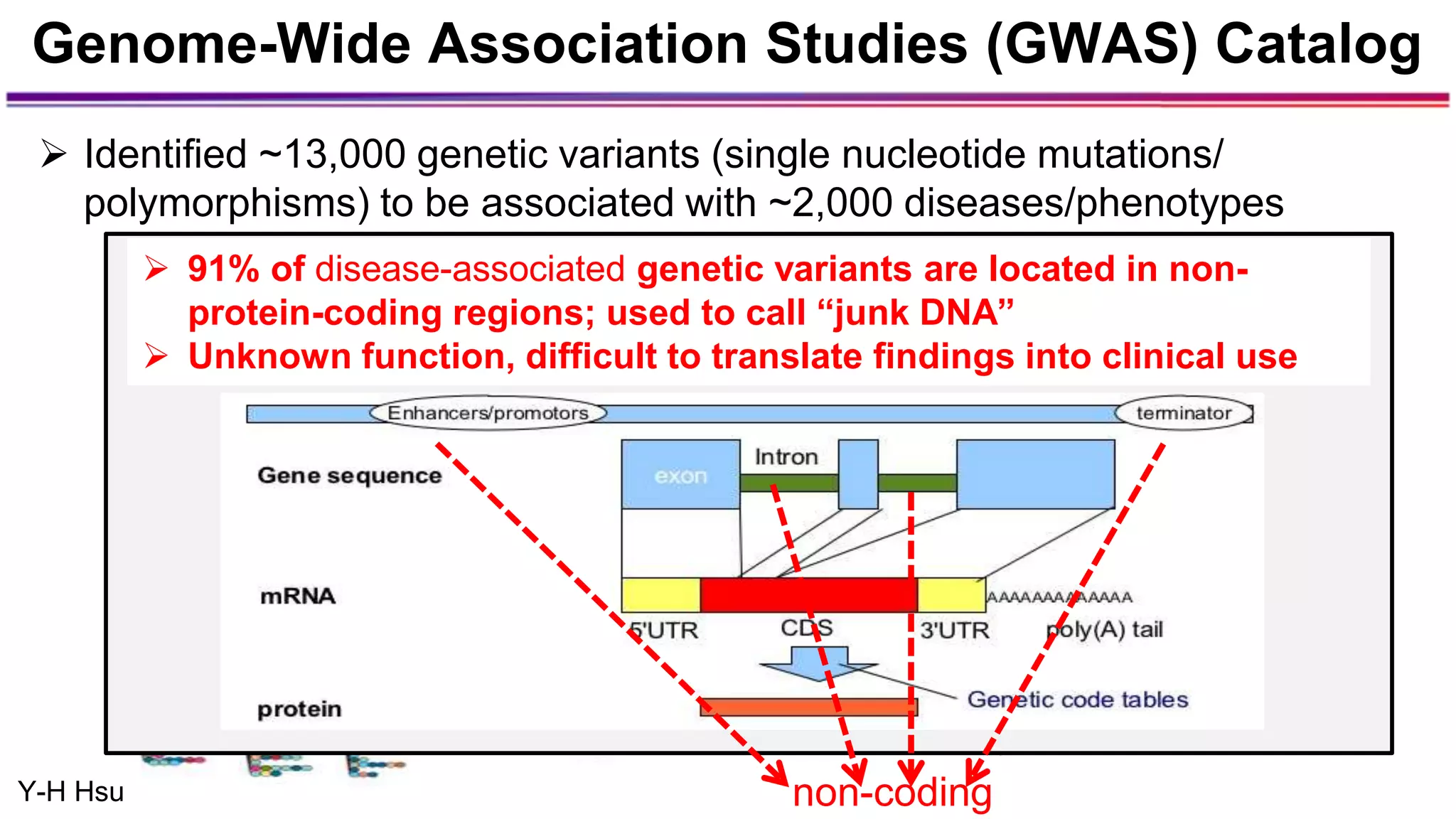
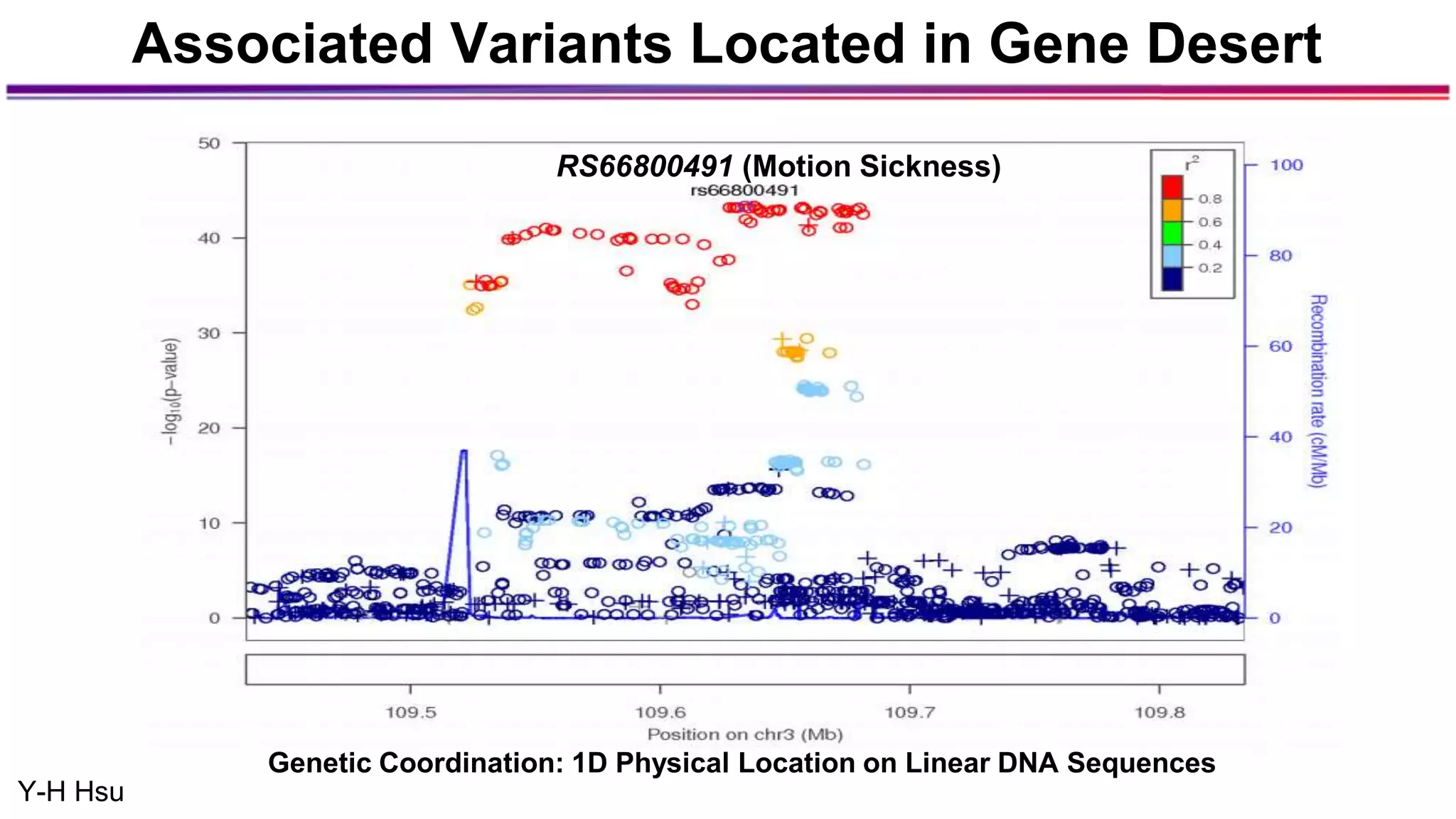
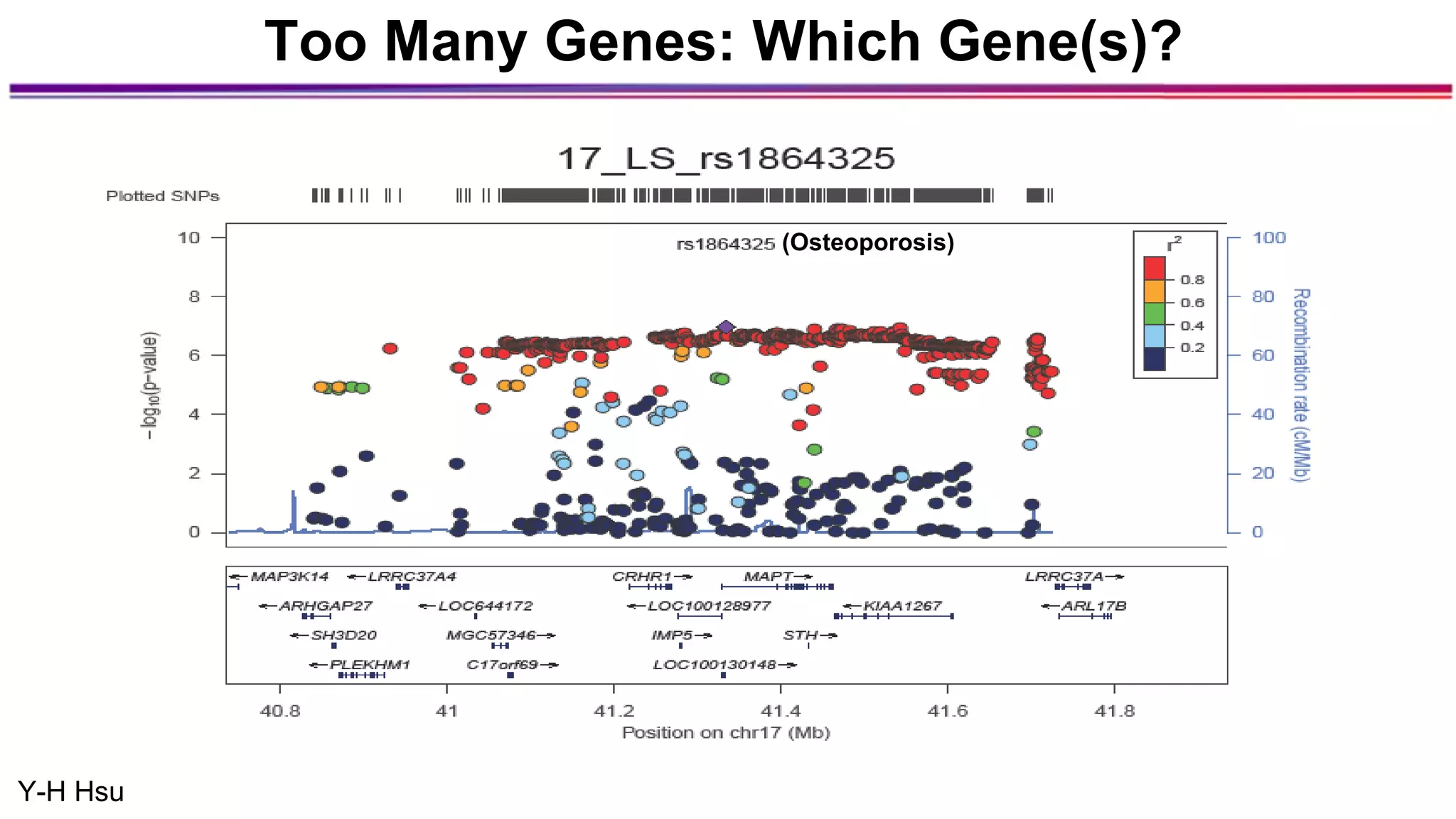
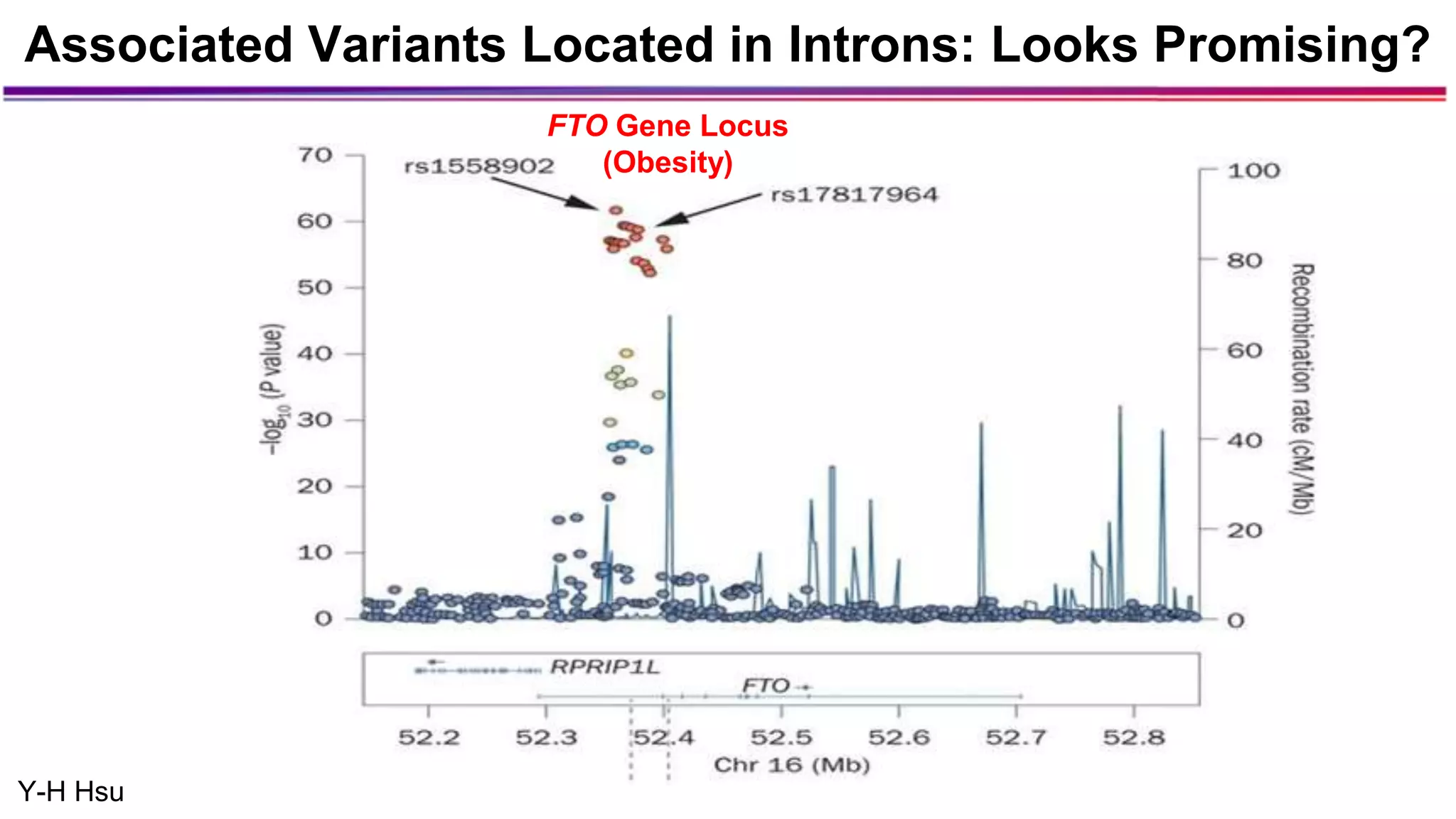
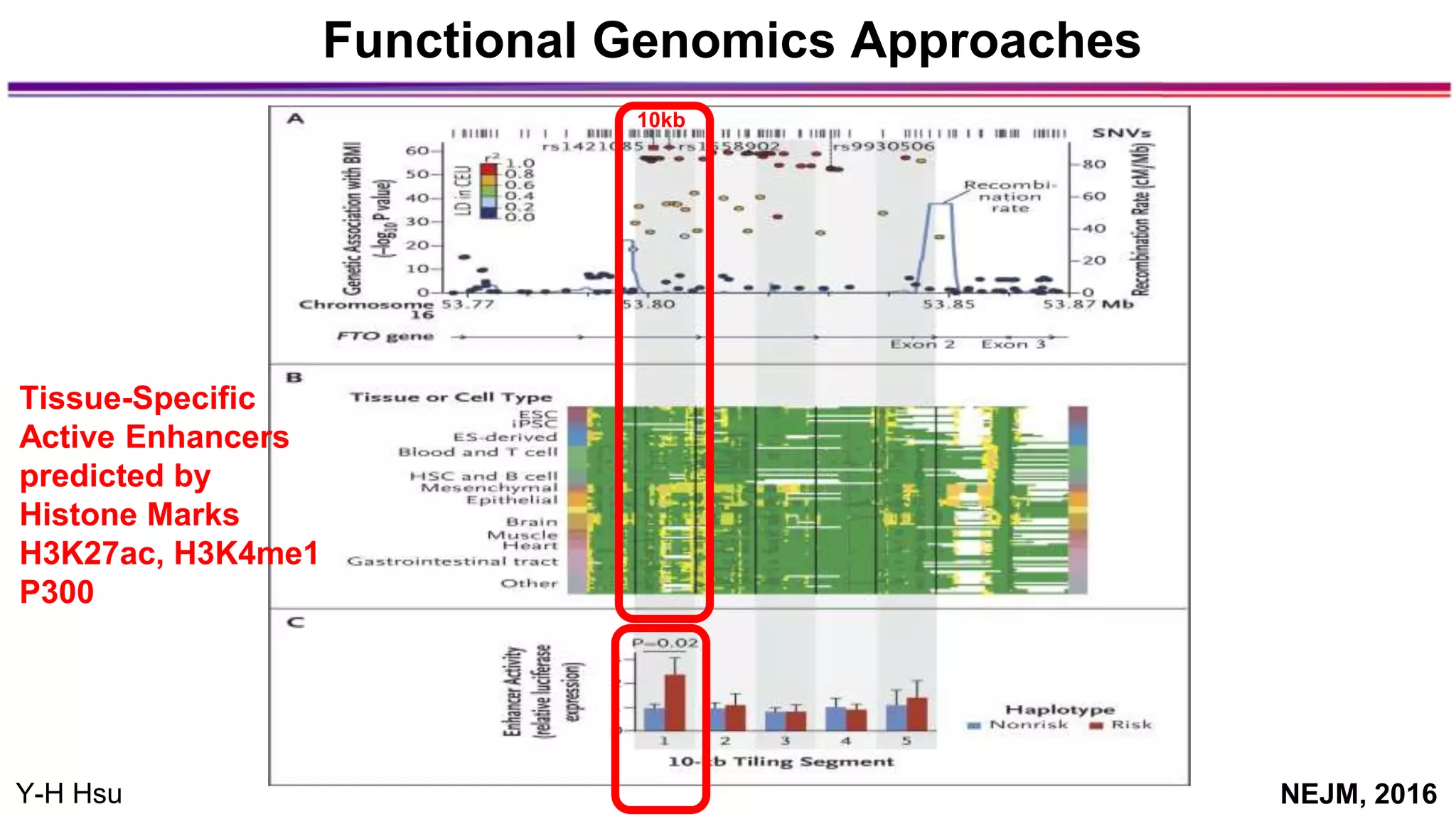
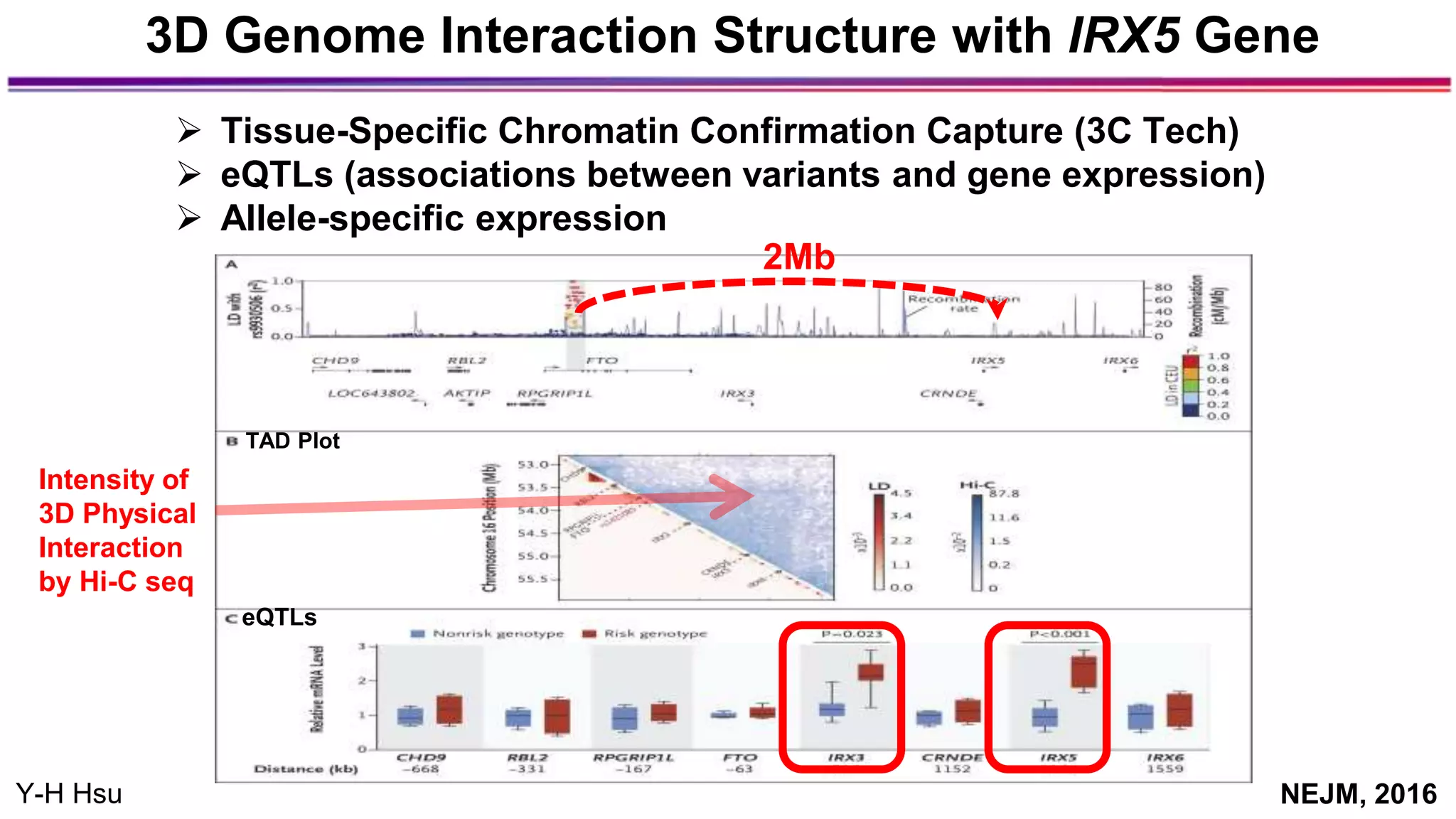
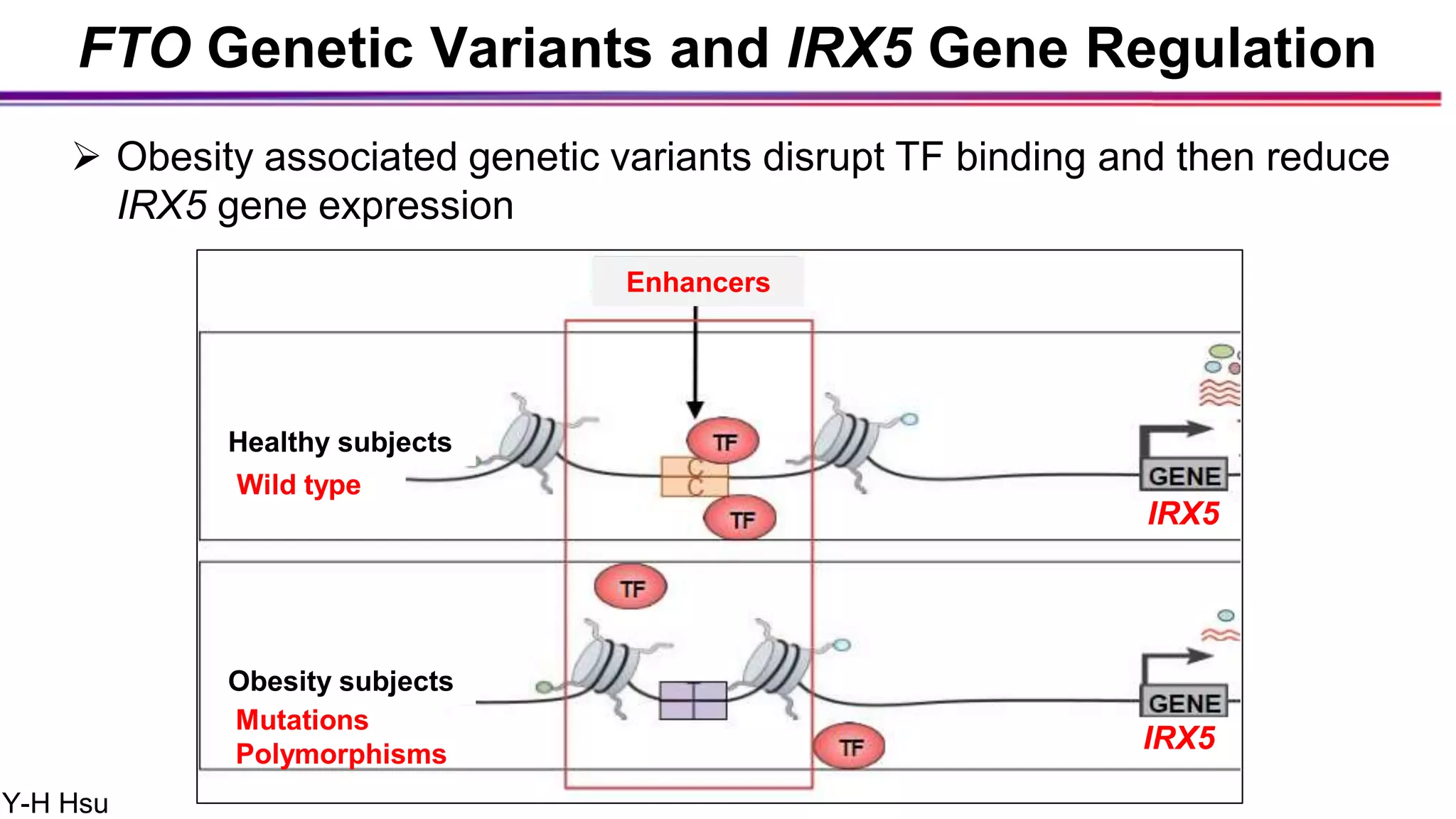
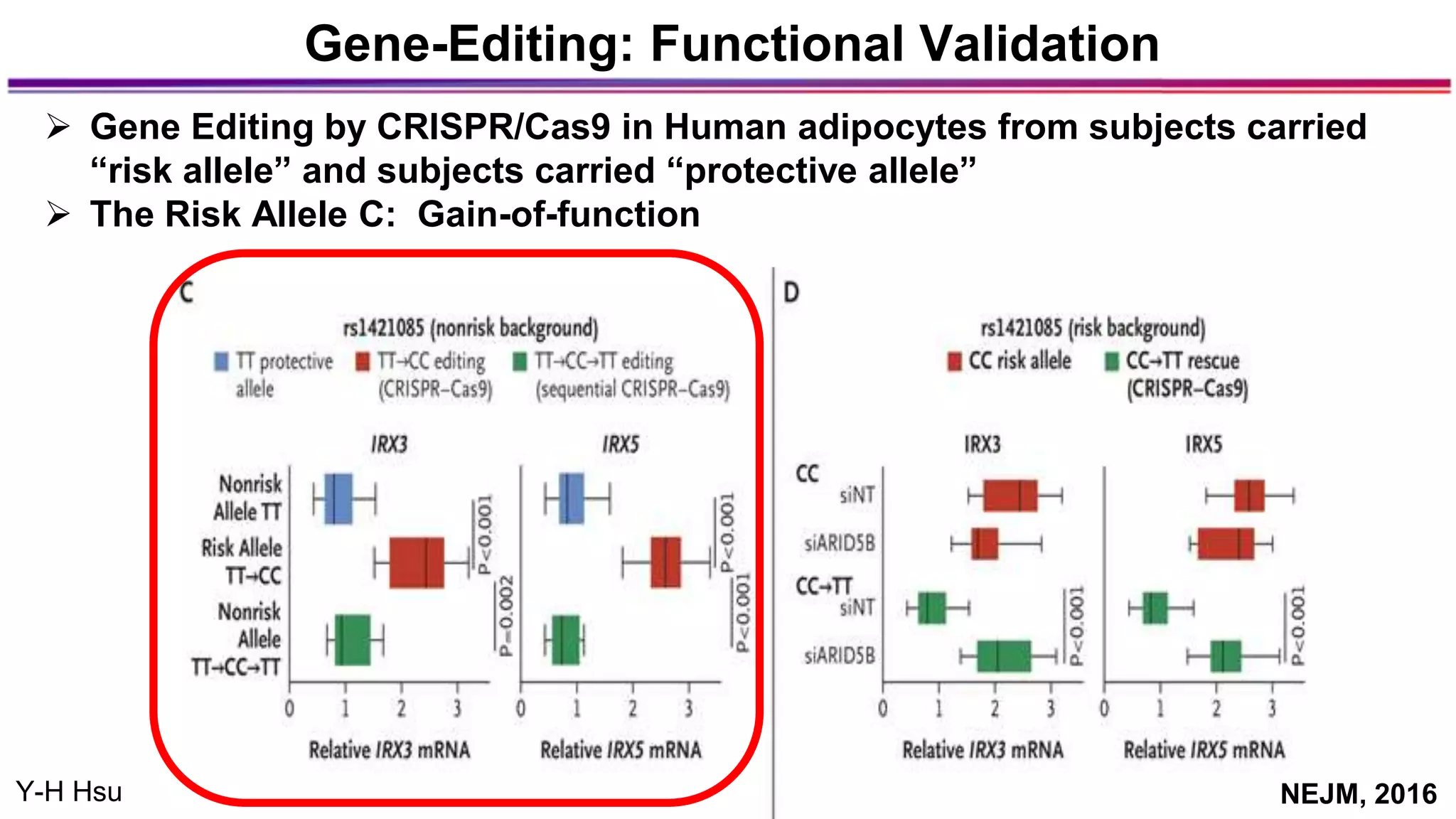
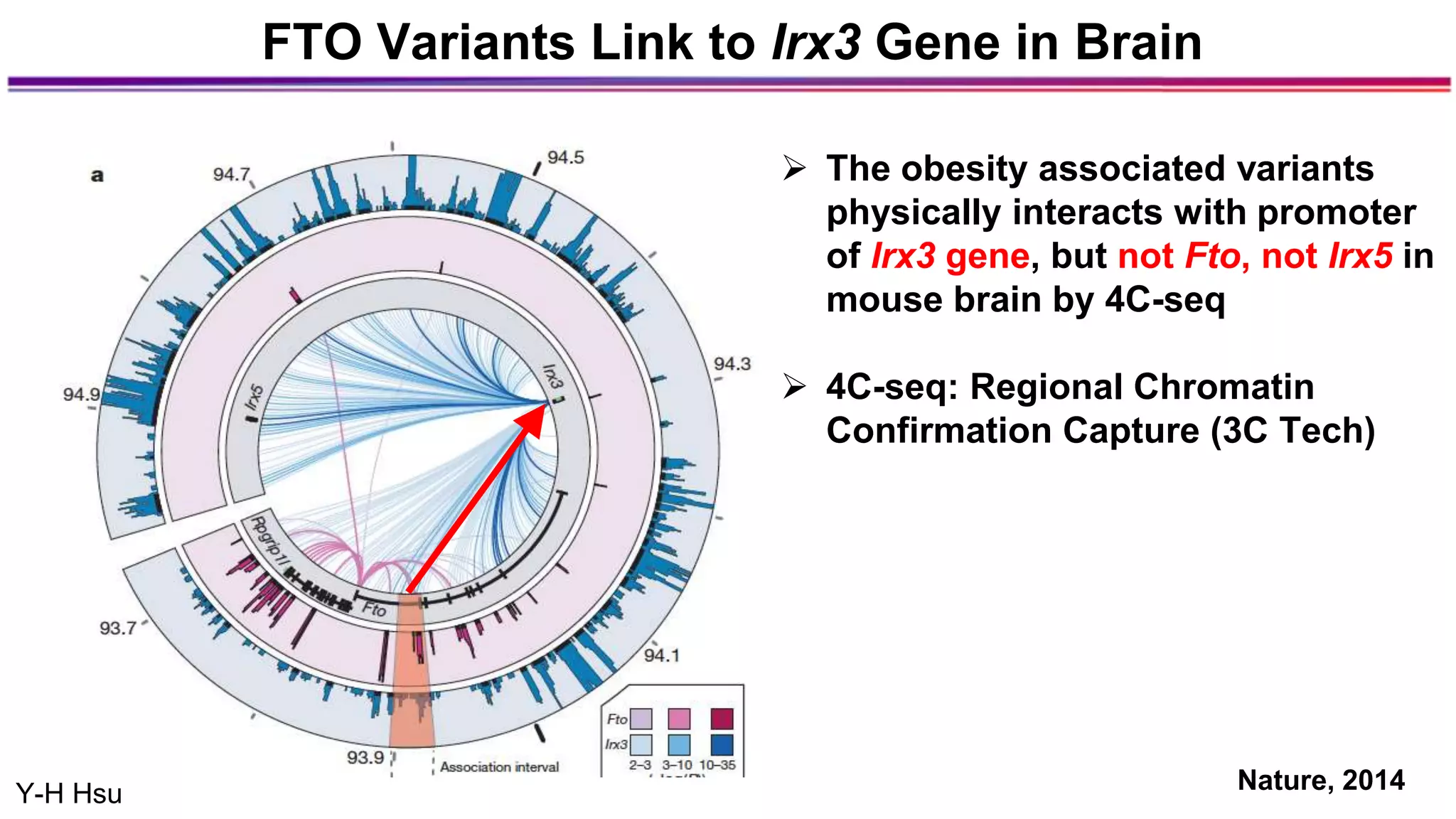
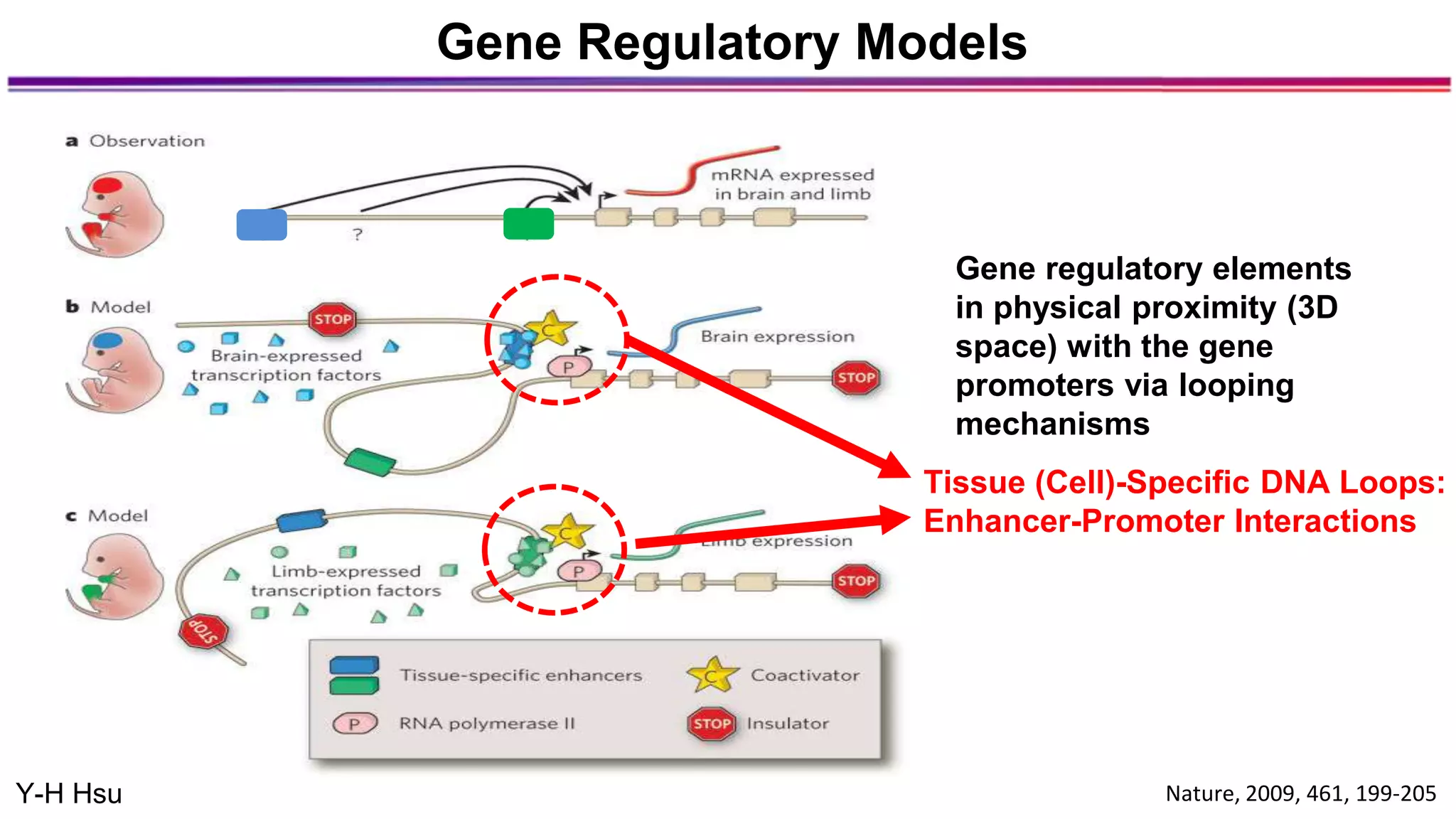
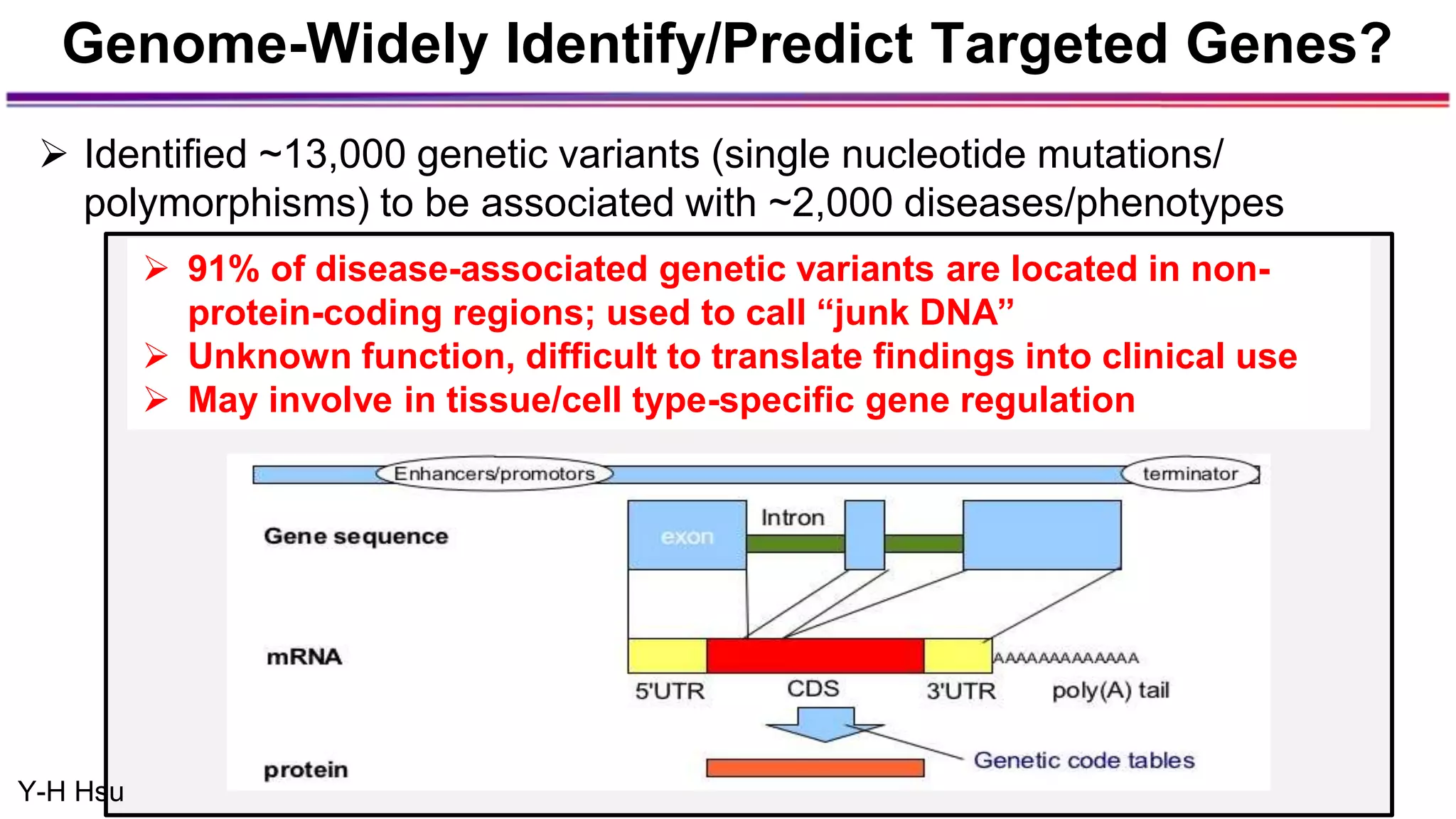
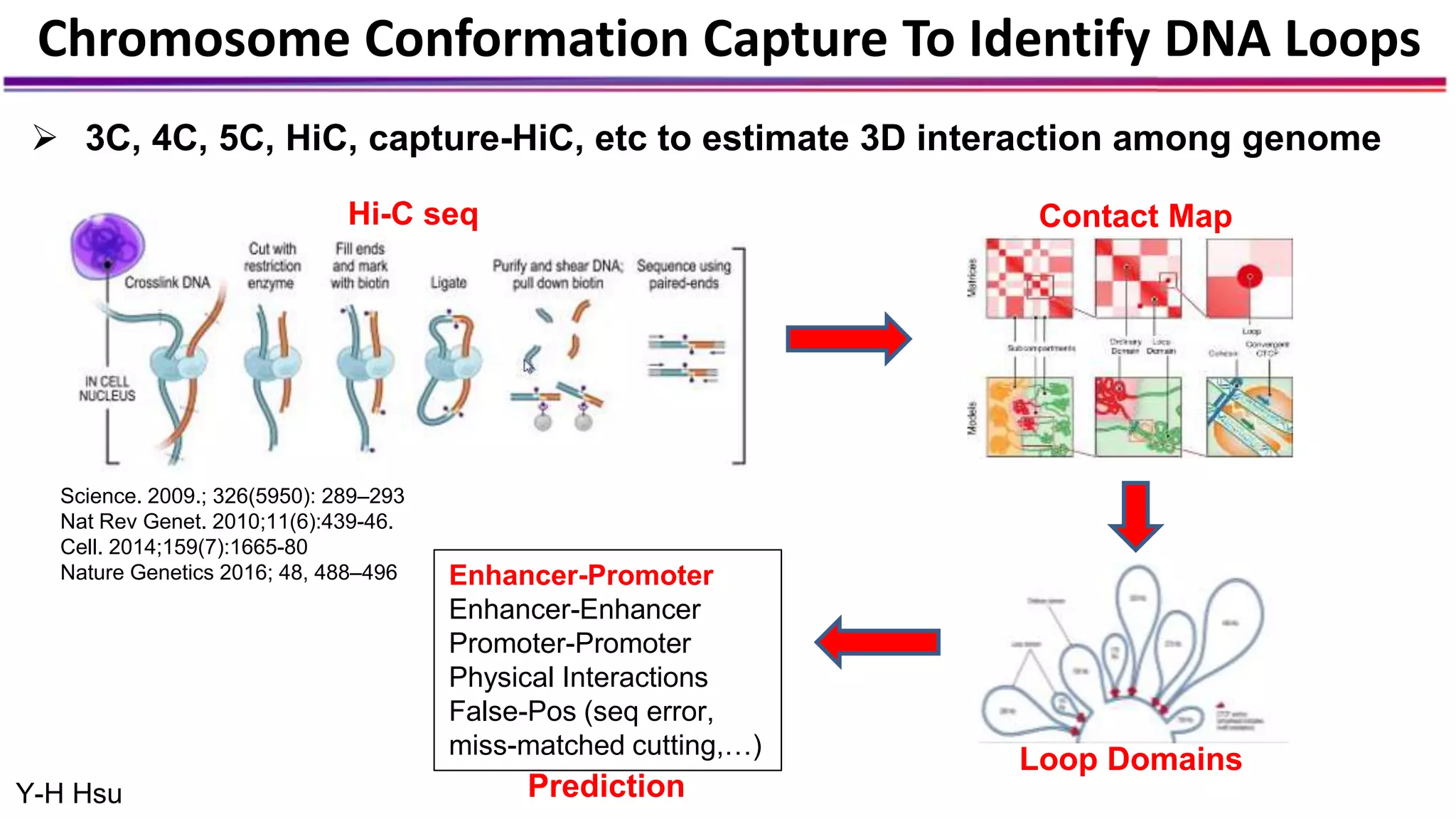
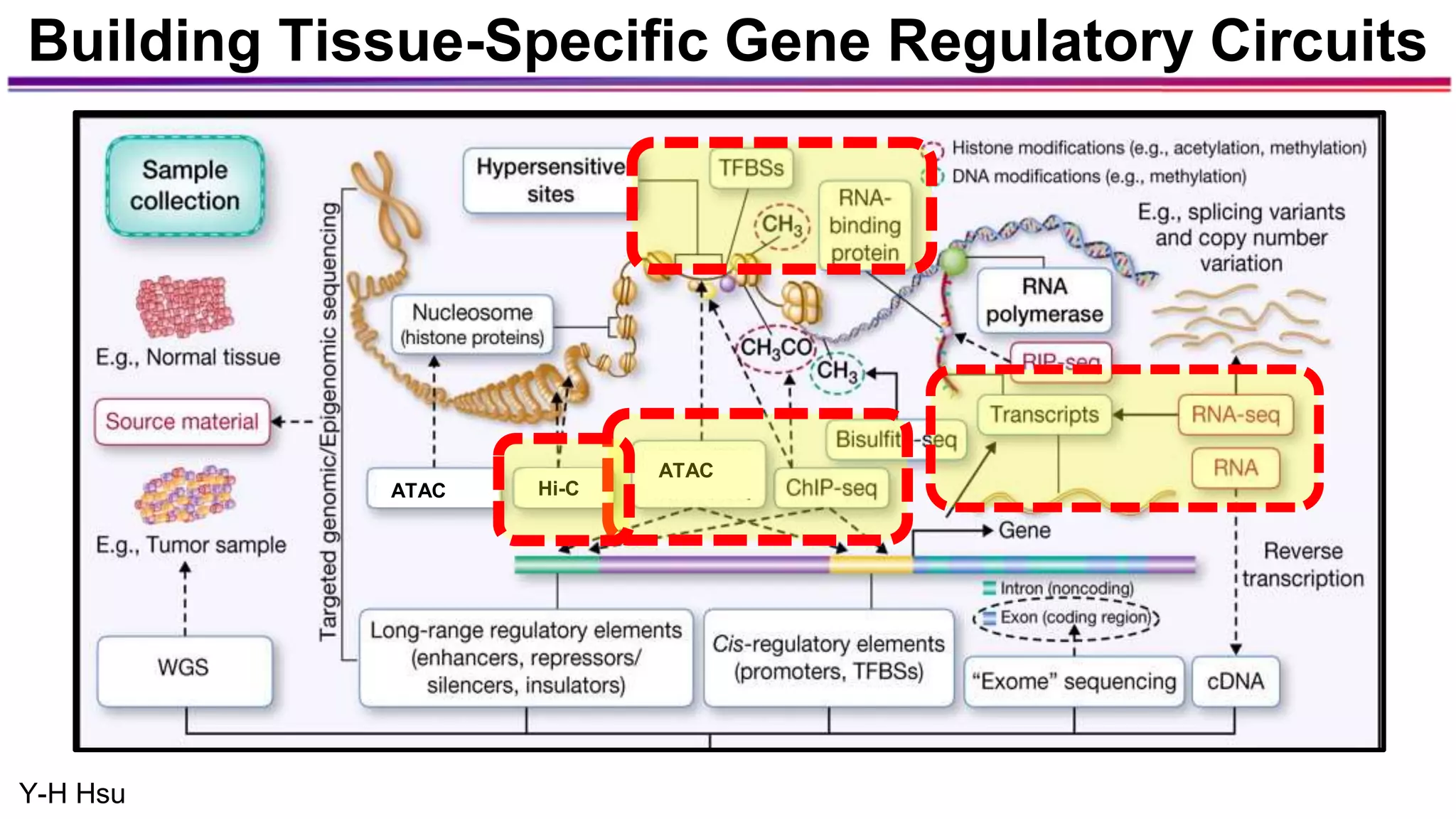
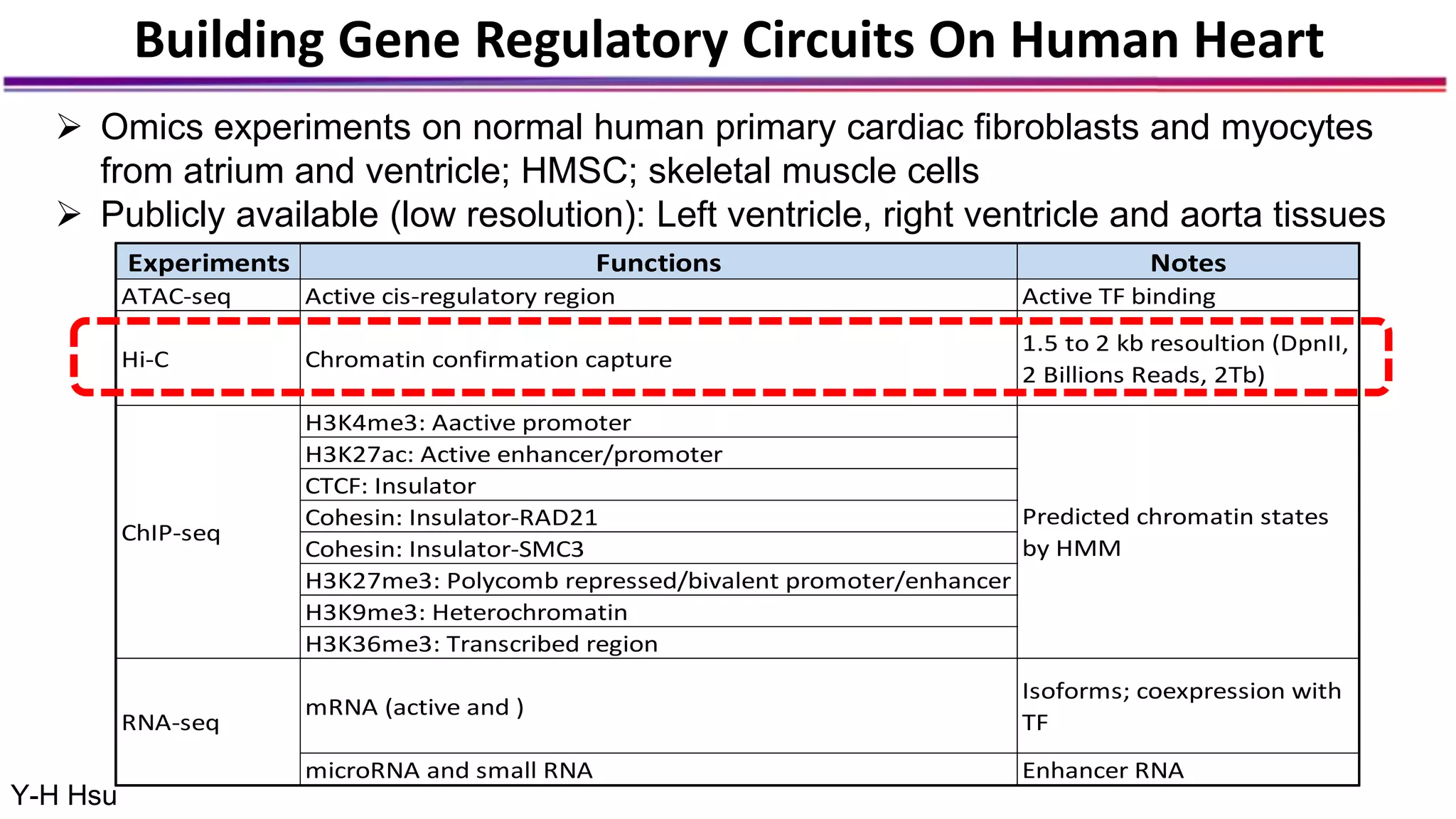
The document discusses the identification of disease-causal genes using 3D genome structure, regulatory landscapes, and deep learning. It highlights the potential of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in linking genetic variants to diseases and emphasizes the significance of utilizing human genetic information in drug development. Recent advancements in deep learning and genome structuring showcase promise for treating diseases at an individual level by targeting specific genetic variations.