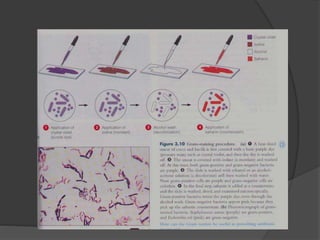
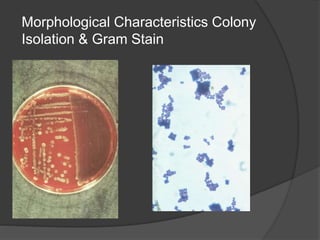
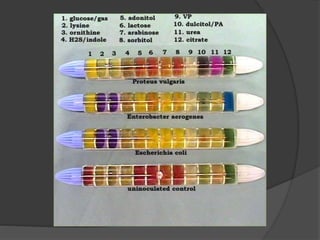
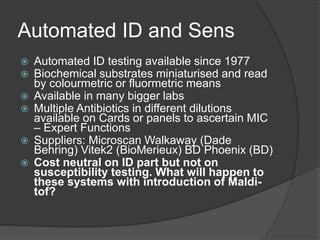
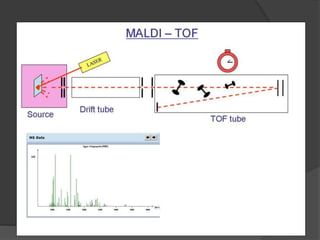
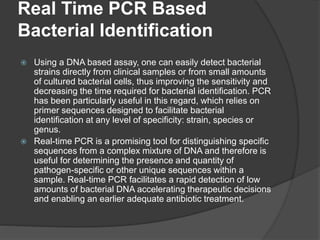
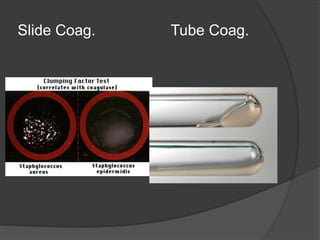
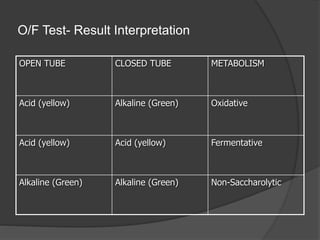
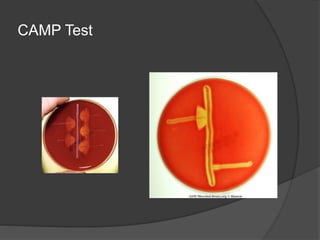
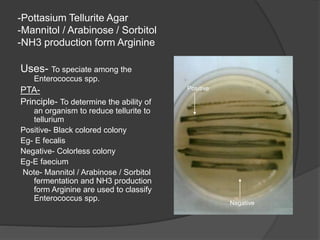
Traditional phenotypic methods and newer genotypic methods can both be used to identify bacteria. Phenotypic methods include gram staining, culturing, and analyzing biochemical characteristics and reactions. These methods have limitations as some bacteria cannot be cultured. Genotypic methods like MALDI-TOF, PCR, and microarrays identify bacteria based on their genetic material and can identify bacteria directly from clinical samples faster than phenotypic methods. A variety of biochemical tests are used as part of phenotypic identification to analyze carbohydrate metabolism, production of specific compounds, enzyme activity, and other characteristics.