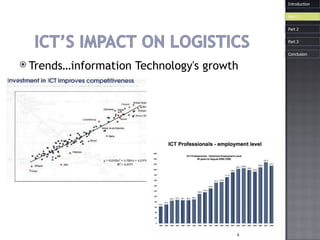
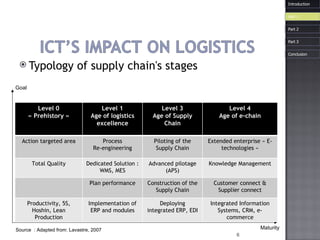
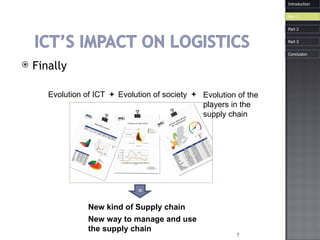
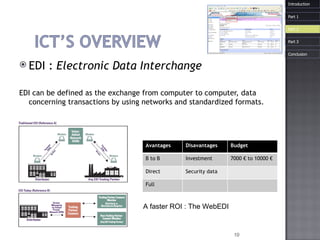
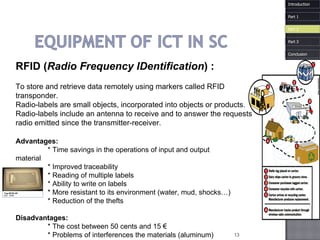
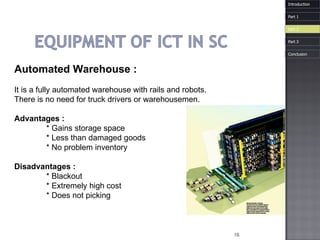
The document discusses how information and communication technologies (ICT) have impacted logistics and supply chains. It provides examples of common ICT tools like WMS, TMS, EDI, barcode scanning, GPS, and RFID and how they help with inventory management, transportation optimization, electronic data interchange, and real-time tracking of goods. The document also examines trends in e-commerce and the evolution of supply chain management approaches and players.