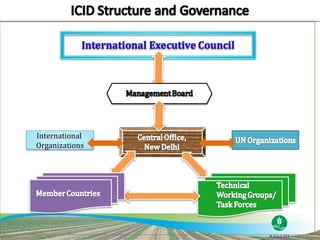
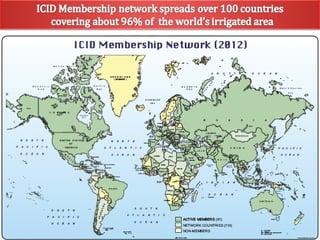
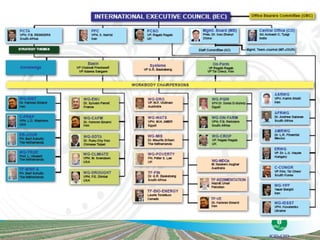
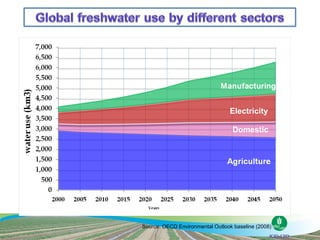
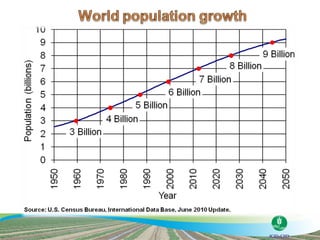
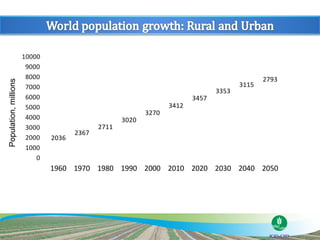
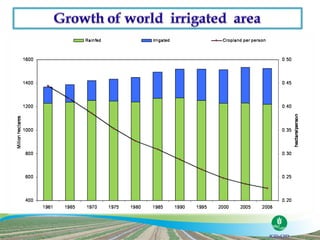
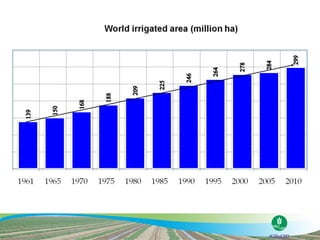
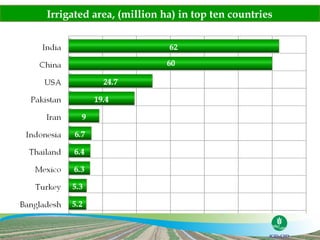
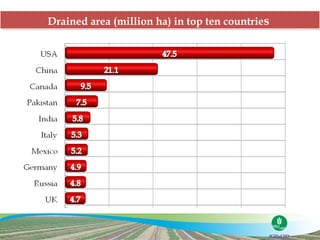
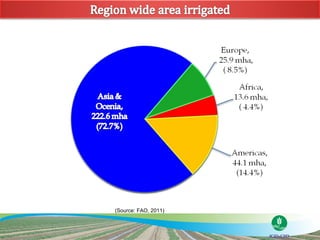
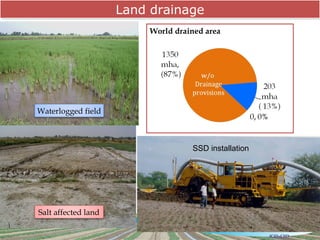
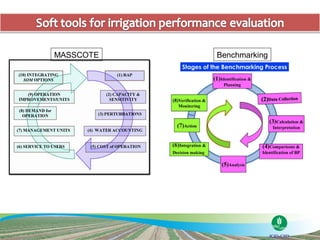
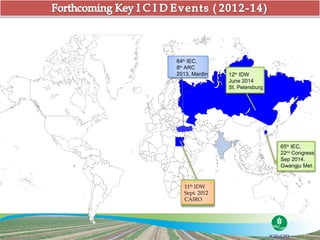
The document discusses the efforts and objectives of enhancing global food and fiber supply through improved water and land management, emphasizing irrigation, drainage, and flood management techniques. It highlights the need for collaboration among governments, organizations, and individuals to address challenges like climate change, water scarcity, and increasing water demand due to population growth and urbanization. Additionally, it mentions various international events and awards aimed at promoting best practices in irrigation and water conservation.