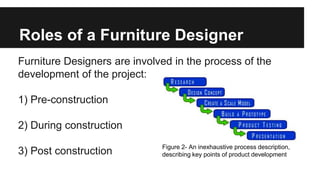
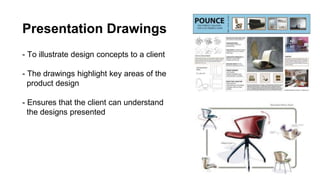
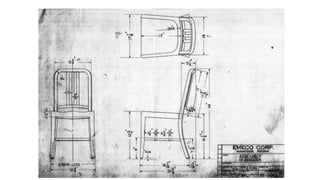
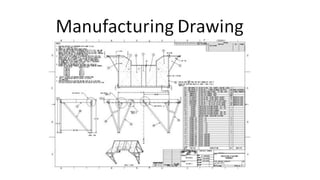
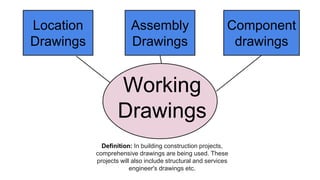
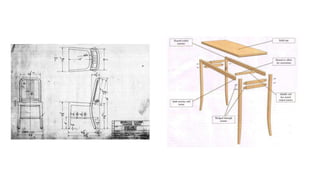
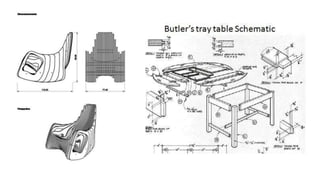
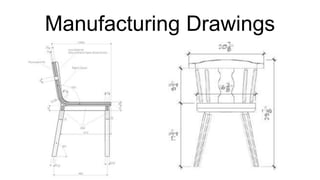
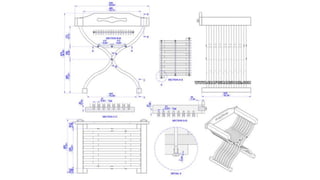
Furniture designers are involved in the construction process at various stages: pre-construction, construction, and post-construction. In pre-construction, designers work with clients and create process sketches, ideation sketches, and presentation drawings. During construction, they oversee manufacturing and installation. Post-construction activities include customer service and product optimization. Designers use different types of drawings throughout the process, including location drawings, assembly drawings, component drawings, schematic drawings, and manufacturing drawings.
















![References
1) Studiocraft (2011). Fascia Installation. [ONLINE] Available at: http://studiocraft-hm.com/?p=403. [Last Accessed 22 Aug
2014].
2) Jaime Derringer (2010). A DAY IN THE LIFE OF KINGSTON SHAW. [ONLINE] Available at: http://design-milk.
com/designer-dailies-kingston-shaw/. [Last Accessed 28 Aug 2014]
3) Sarah A. Rigg (2009). University of Michigan construction continues, but few large-scale projects on horizon. [ONLINE]
Available at: http://www.mlive.com/businessreview/annarbor/index.ssf/2009/01/university_of_michigan_constru.html.
[Last Accessed 20 Aug 2014].
4) Small Business Tool Kit (). What is Tendering. [ONLINE] Available at: http://toolkit.smallbiz.nsw.gov.au/part/26/134/623.
[Last Accessed 1 September 2014]
5) Karina Sokolava (2011). Basic Guidelines To Product Sketching. [ONLINE] Available at:
http://www.hongkiat.com/blog/basic-guidelines-to-product-sketching/. [Last Accessed 4 September 2014].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ici-20itd-141211152957-conversion-gate01/85/ICI-ITD-pptx-29-320.jpg)