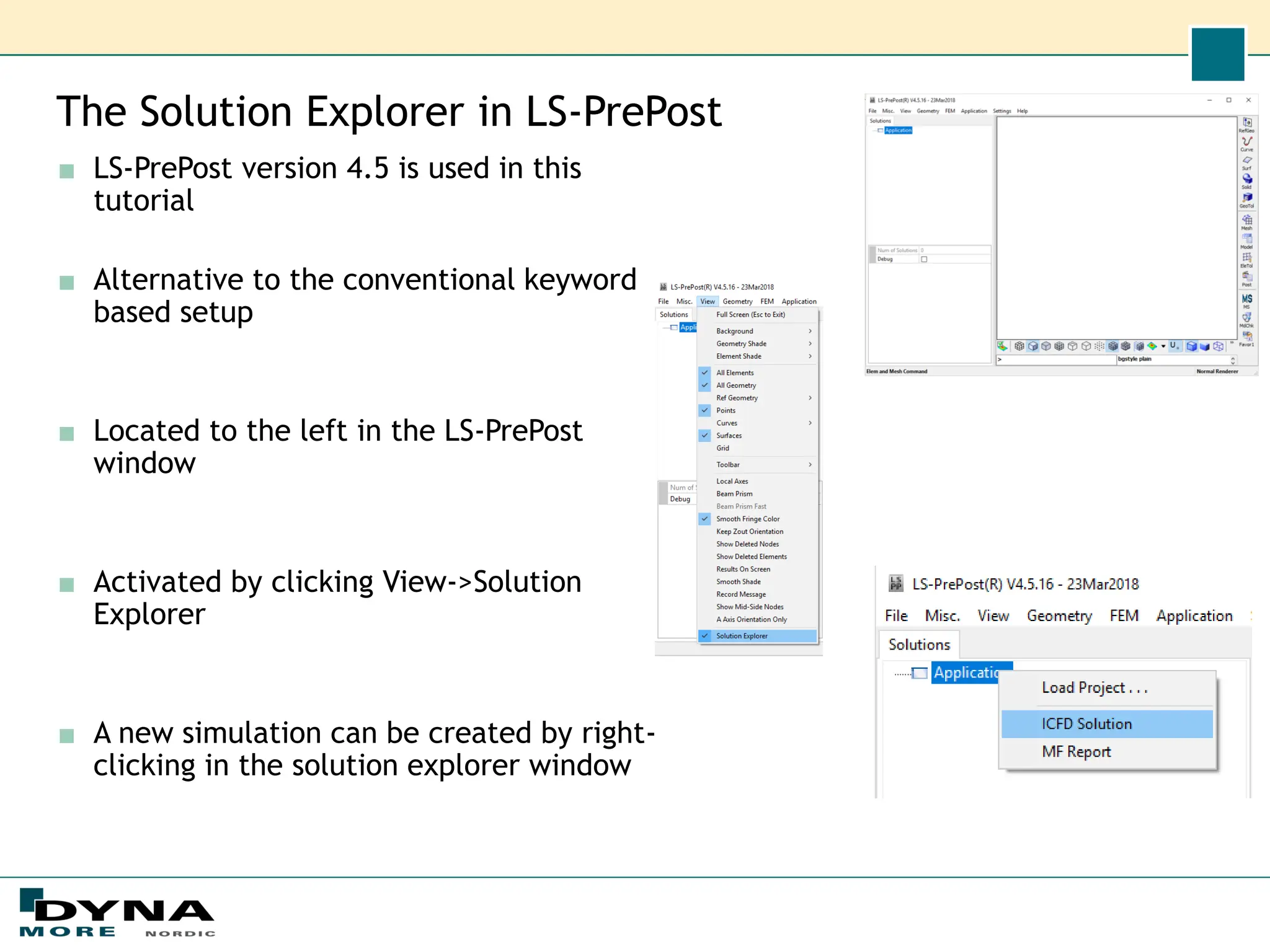
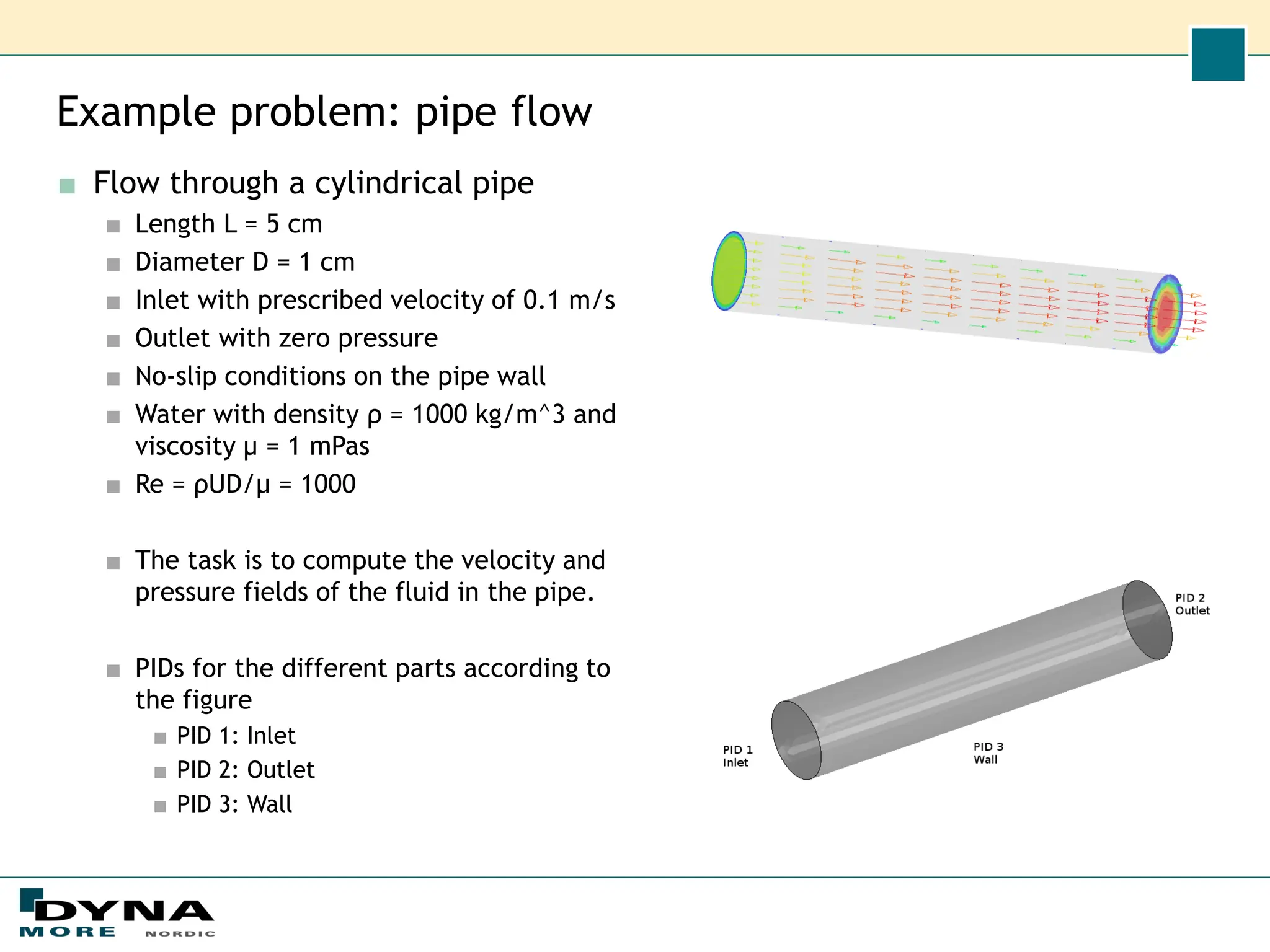
This document describes how to set up an incompressible fluid flow simulation using the ICFD solver in LS-DYNA and the new Solution Explorer GUI in LS-PrePost. It details creating a cylindrical pipe geometry and mesh, setting fluid material properties and boundary conditions like inlet velocity and outlet pressure, running the simulation, and visualizing the results to show pressure drop and velocity profile. The document emphasizes that the Solution Explorer provides an easier, more intuitive alternative to keyword-based setup for ICFD simulations compared to conventional methods.