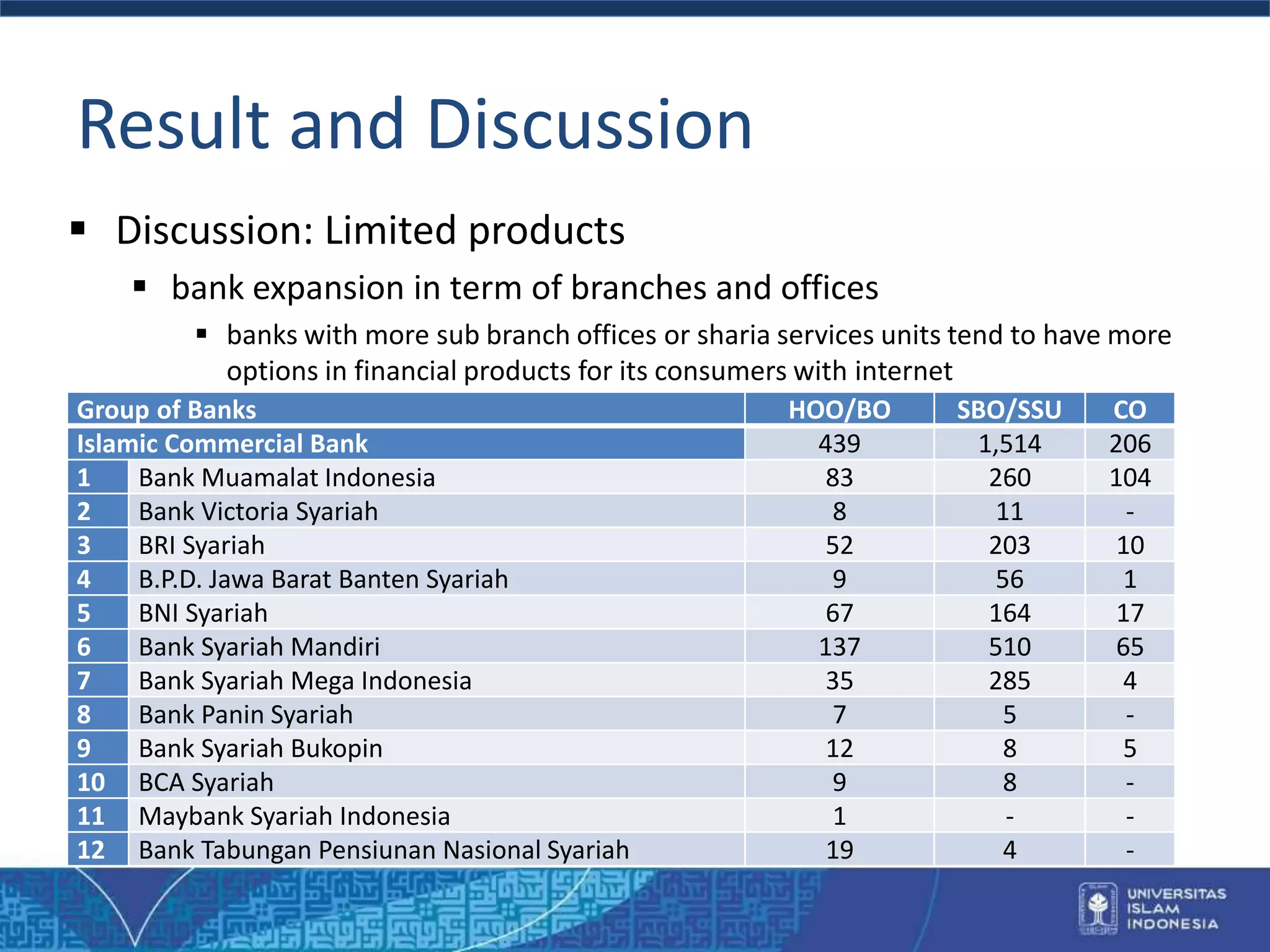
The document analyzes the internet-based products offered by Islamic banks in Indonesia, highlighting the growth and current offerings from various banks. It discusses the challenges related to consumer familiarity with such products, the limitations of offerings from newer banks, and the potential for internet banking to enhance financial inclusion in the country. The findings suggest that technological adoption in Islamic banks is limited, focusing largely on larger institutions, while emphasizing the need for increased digital product offerings to improve competitiveness with conventional banks.