The document discusses the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and its revisions over time. Some key points include:
- ICD is the global standard for morbidity and mortality statistics used in clinical care, research, and resource allocation.
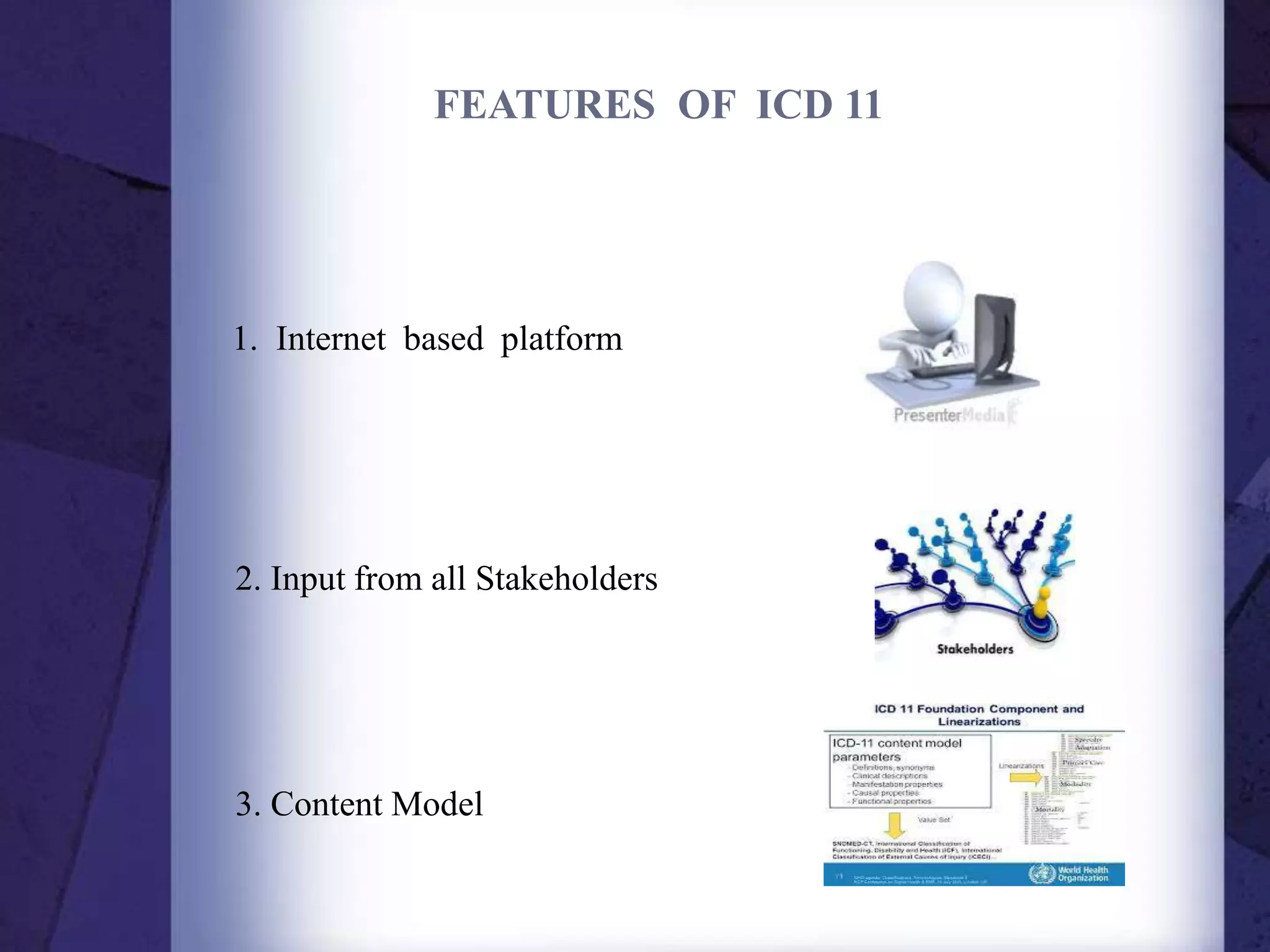
- ICD-11 features include an internet-based platform, input from stakeholders, content modeling, field trials, and multi-lingual representations.
- New elements in ICD-11 include new disease chapters and differences from ICD-10 such as expanded definitions.
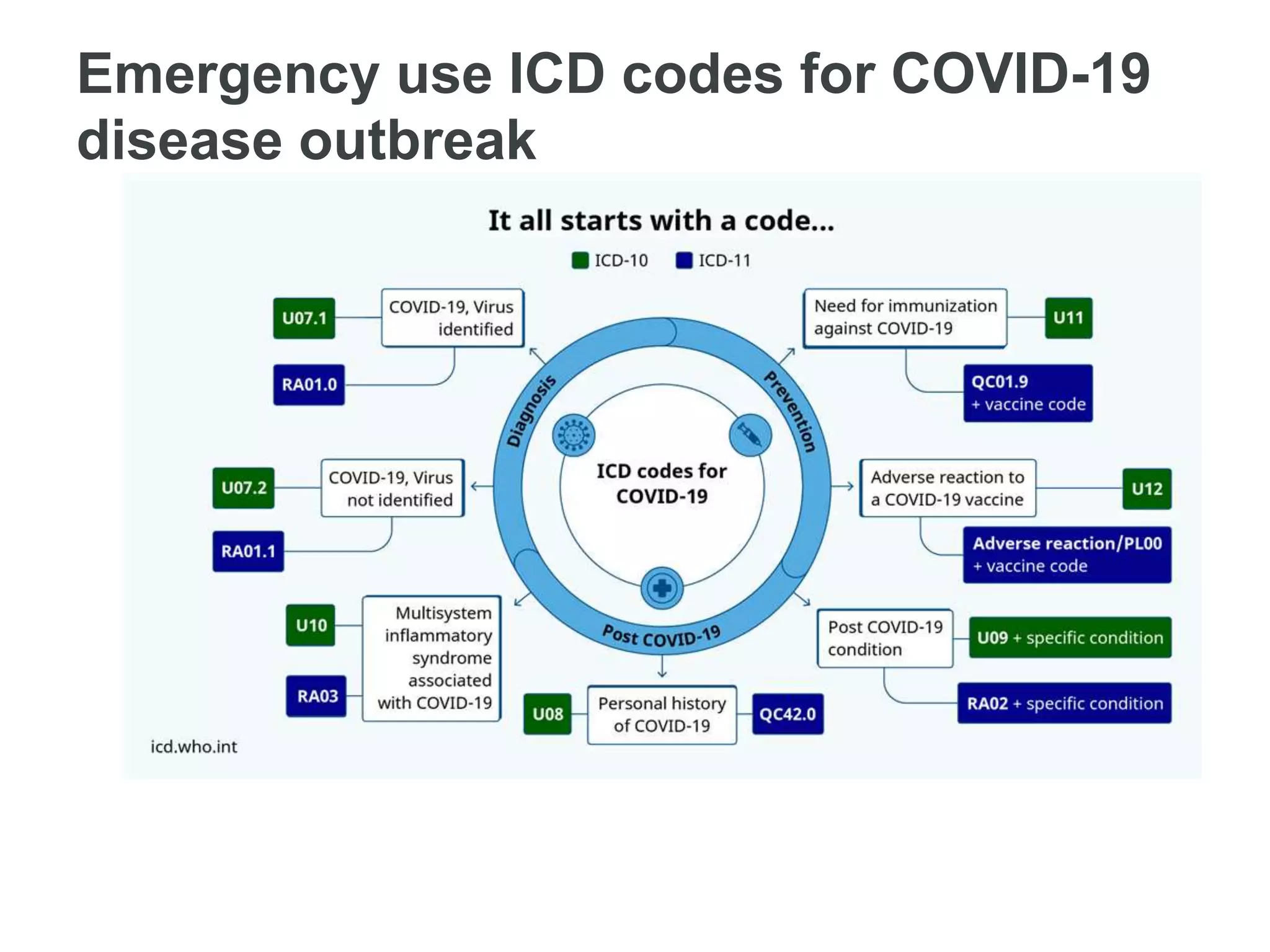
- Emergency codes were also created for the COVID-19 disease outbreak.