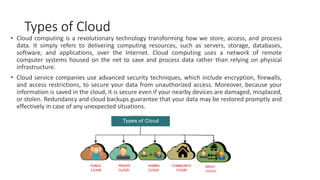
The document provides an overview of cloud computing types, emphasizing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each service model is defined, discussing advantages, disadvantages, and key features, such as scalability, security, and cost management. Additionally, it highlights various providers and the challenges that businesses might face when adopting these cloud services.