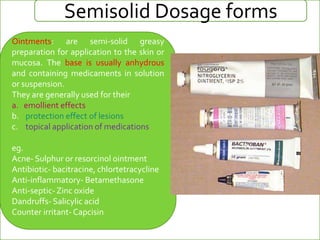
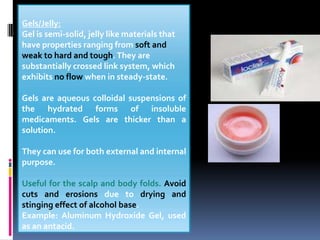
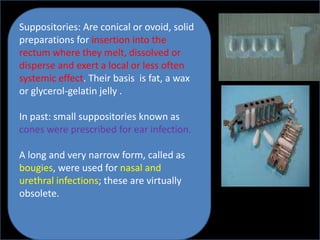
Semi-solid and liquid dosage forms can be used topically, orally, and parenterally. Semi-solid forms include ointments, creams, gels, pastes, liniments, suppositories, and poultices. Liquid forms include solutions, suspensions, emulsions, syrups, elixirs, lotions, and injections. Sterile dosage forms like injections must be free of microbes while non-sterile forms can be used orally or topically. Different routes like intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular and intravenous provide variable absorption and effects.